What is ARP Poisoning?

The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a widely used protocol that enables devices within a LAN to communicate by linking their IP addresses with their MAC addresses. However, this protocol has a flaw as it cannot verify the authenticity of received ARP messages. This vulnerability exposes it to a type of cyberattack called ARP poisoning or ARP spoofing. In an ARP poisoning attack, a malicious individual sends falsified ARP messages into a network to disrupt, redirect, or monitor network traffic. By doing this, the attacker can associate their MAC address with the IP address of another device on the network, such as a router, server, or computer. The attacker’s primary purpose is to deceive devices by sending data packets to them instead of reaching their intended destination. In this blog, we will discuss ARP poisoning in detail, different ARP poisoning attacks, its detection, and its different prevention methods. To understand how ARP poisoning works, we first have to understand how ARP operates. Below, we have discussed the overview of ARP for better understanding. ARP, or Address Routing Protocol, is a protocol that works on the data link layer of the OSI model. When we talk about its purpose, it allows devices within a Local Area Network to find and keep track of the connection between their IP addresses and MAC addresses. When a device needs to communicate with another device, it must obtain the MAC address of that device. This is achieved through a two-step process: Once received, the sender updates its ARP cache, which acts as a table storing mappings between IP addresses and MAC addresses of devices on the LAN. With this information, the sender can then directly send data packets to the target using its MAC address. However, this process has a flaw; it lacks authentication for received ARP messages. Any device on the LAN can respond to an ARP request. Further, it can send an ARP reply without verifying if it is the intended recipient or not. This situation allows an intruder to manipulate the LAN potentially by sending ARP messages to devices, causing their ARP caches to be filled with incorrect mappings. Now that we have a basic understanding of ARP and how it operates. Let’s now discuss the ARP poisoning. ARP poisoning is a technique that allows an attacker to manipulate the ARP cache of a device. The ARP cache is a table that stores the mappings between IP addresses and MAC addresses of devices on the same network. The ARP cache is updated whenever a device sends or receives an ARP request or reply. An attacker can poison the ARP cache by sending spoofed ARP messages claiming to have another device’s MAC address on the network. ARP poisoning can have a serious impact in terms of network security and performance. With ARP poisoning, one can: Therefore, studying ARP poisoning and learning how to detect and prevent it is important. Let’s now discuss how an ARP poisoning attack works. Firstly, the attacker monitors the network traffic in order to identify the IP and MAC addresses of the two devices that are communicating with each other. These devices can be a user’s computer and a router. This is how ARP Poisoning works. After manipulating the ARP cache of devices on the local area network (LAN), attackers can easily carry out various types of attacks. Below, we have discussed the most common attacks. Attackers can intercept and examine data packets passing through their devices. This allows them to steal information like passwords, credit card numbers, or confidential documents. Additionally, they can redirect the traffic to websites or servers designed for phishing or distributing malware. By blocking or discarding data packets that traverse their device, attackers can disrupt user’s access to network resources and services such as email, web pages, or file servers. This can lead to network downtime, performance issues, or even data loss. Attackers gain the capability to modify or tamper with data packets flowing through their devices. Consequently, they can manipulate the content or behavior of network communication by altering website text or images, injecting code or commands, and even impersonating users or entities. Now, the question that arises is how one can detect ARP poisoning. ARP poisoning is hard to detect using antivirus software or firewalls. However, there are some methods that can help to identify and monitor ARP poisoning on a network. Some of these are: With the help of passive detection, one can monitor the ARP traffic on the network and look for any inconsistencies in the ARP messages or cache entries. Let’s take an example for better understanding. Let’s take a device that receives multiple ARP replies from different MAC addresses for the same IP address. It is also possible that the device receives an ARP reply without sending an ARP request. Both situations indicate an ARP poisoning attempt. Passive detection can be either done manually or using tools such as Wireshark or tcpdumb, or it can be done automatically using tools such as XArp or Arpwatch. One can also compare their ARP caches with other devices on the network via CMD by typing arp -a. Below we have shown the image for better understanding. If the table contains two separate IP addresses with the same MAC address, an ARP attack happens. With the help of Active Detection, one can easily detect ARP poisoning by sending falsified ARP packets to the network and observing responses. For example, let’s take a device that sends an ARP request for an IP address that does not exist on the network, and it receives an ARP reply from another device, it simply indicates that the device is an attacker. Active detection can be done via using tools such as arp-scan or arping. After detecting ARP poisoning, one has to act to prevent it. Below, we have explained how one can prevent ARP poisoning. ARP poisoning results in network security threats as well as leads to an effect the performance. Hence, taking preventive measures to protect the network from such attacks is crucial. Some of the preventive measures one can take are: With the help of this method, one can manually configure the devices on the network with static ARP entries that further map their IP addresses to their MAC addresses. With the help of this, the devices no longer need to use ARP to discover each other’s MAC addresses and also do not rely on dynamic ARP cache updates. This helps in preventing the attacker from poisoning the ARP cache with false mappings. Apart from all the merits this technique has, there are also some demerits. Some of the demerits include scalability issues, maintenance overhead, and lack of flexibility. One can also prevent ARP poisoning through DHCP snooping. In this method, one uses a switch feature that assists in filtering DHCP messages on the network and also builds a database of IP-to-MAC mappings for each port on the switch. This way, the switch can validate any ARP messages that match these mappings and further discard any ARP messages that do not match these mappings. With the help of this technique, one can prevent an attacker from sending fake ARP messages to other devices on the network. However, this method requires a DHCP server and also a switch that supports DHCP snooping. Using network segmentation or VLANs, one can isolate different parts of your network and limit the scope of ARP poisoning attacks. This is the ways how one can prevent ARP Poisoning. ARP is a type of cyberattack for intercepting network traffic by sending falsified messages that associate the attacker’s MAC address with the IP address of a target device. ARP poisoning can be prevented by various means. Some of these are: Yes, ARP poisoning is a threat to network security. ARP poisoning and DNS poisoning are network attacks that spoof IP or domain names to redirect traffic or steal data. ARP poisoning is a type of cyberattack that can compromise network security and performance. By understanding how it works, the different types of attacks it can lead to, how one can detect it, and how to prevent it, one can protect their network from ARP poisoning and, in return, ensure network reliability and integrity. Address Resolution Protocol is an integral part of CCNA Course. However, if you want to learn more about ARP Poisoning, you should opt for CCNP ENARSI Training.Introduction
What is ARP?
What is ARP Poisoning?
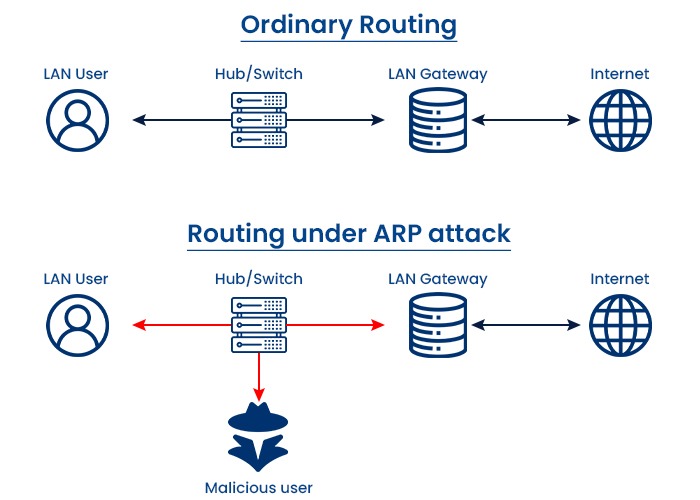
How does an ARP poisoning attack work?
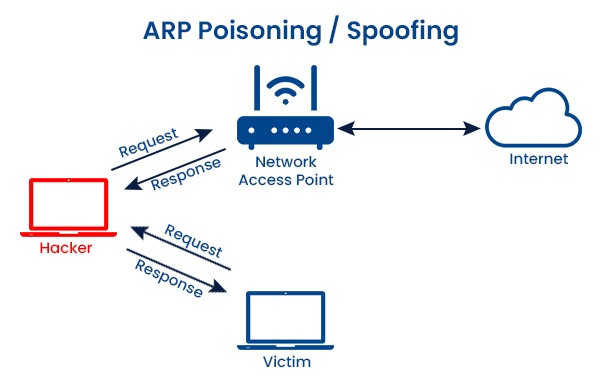
Types of ARP Poisoning Attacks
Traffic Interception
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks
Man in the middle attacks
How to Detect ARP Poisoning?
Passive Detection
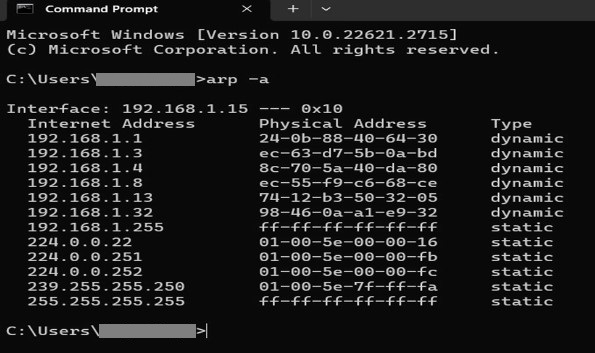
Active Detection
How to Prevent ARP Poisoning?
Static ARP Entries
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Snooping
Network Segmentation
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is ARP poisoning a method for?
Q2. How is ARP poisoning prevented?
Q3. Is ARP poisoning a threat?
Q4. How do ARP poisoning and DNS poisoning attacks work?
Conclusion







