What is MAC (Media Access Control) Address?

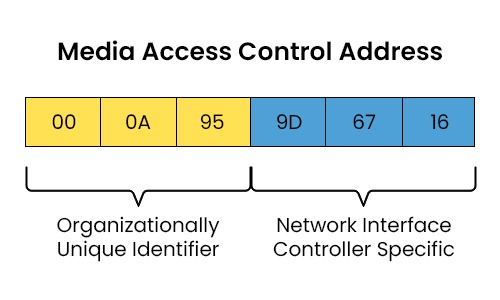
A MAC address, also known as a Media Access Control address, is an identifier given to a network interface controller (NIC) in a device that communicates through a network. They have uses, including filtering, routing, security, and identifying devices. In this blog, we will explain the MAC address and its purpose. We will also discuss its different types available and how to find MAC address on different devices or OS. Before getting into more details, let’s first understand what a MAC address really is. A MAC address, also known as a Media Access Control Address, serves as an identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC). It is mainly for communication purposes within a network segment. An NIC is a hardware component that enables device connectivity to networks like Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth. A MAC address is typically represented by 12 hexadecimal digits (0-9 and A-F) separated by colons or dashes. For instance, 00:0A:95:9D:67:16 or 00-0A-95-9D-67-16. Each hexadecimal digit represents four bits, and every pair of digits signifies one byte or octet. The initial six digits in a MAC address indicate the NIC manufacturers, known as Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI), while the remaining six digits are assigned by the manufacturer to identify the NIC. In the given example, 00:0A:95:9D:67:16, the OUI 00:0A:95 belongs to Hewlett Packard Company, and the NIC-specific part is 9D:67:16. Now that we have a basic understanding of the Media Access Control address, let’s discuss its purpose. The primary purpose of a MAC address is to ensure that each device that is part of the network has its distinct and unchanging identification method. Unlike IP addresses, these addresses are typically permanent and pre-programmed into the network interface card (NIC) by the manufacturer. This implies that even if a device alters its IP address or switches networks, its MAC address remains unchanged. These addresses are utilized by protocols within the data link layer of the OSI model. This layer is responsible for facilitating data transfer between neighboring nodes on a network. One such protocol is the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), which maps IP addresses to MAC addresses. When a device intends to communicate with another device on the network segment, it needs to know the Media Access Control address of that device. To obtain this information, the device sends an ARP request broadcasting the IP address of the desired destination and requesting its corresponding MAC address. The device with a matching IP address responds with an ARP reply providing its Media Access Control address. The sender then stores this information in its ARP cache for reference. Another protocol that relies on it is Ethernet, which serves as the used standard for networks. Ethernet frames act as units of data transmitted over an Ethernet network. Each Ethernet frame includes a header containing both source and destination MAC addresses and details such as frame type and length. The source address identifies the sending device, while the destination address specifies which device should receive it. The Ethernet switch or hub is in charge of connecting the devices within a network segment and utilizes these addresses to direct the frames to their ports. Learn the difference between Hub and Switch. There are three types of MAC addresses: unicast, multicast, and broadcast. A unicast MAC address is used to identify a single device within a network. It is also referred to as a globally unique address. It can be distinguished by having the least significant bit (LSB) of the first octet set to 0. For instance, 00:0A:95:9D:67:16 is an example of a unicast address because its first octet is 00, and the LSB is 0. The OUI portion of this address can be further classified into two categories: universally administered addresses (UAA) and locally administered addresses (LAA). The manufacturer of the NIC assigns a UAA and adheres to IEEE standards for OUI allocation. On the other hand, an LAA is assigned by the network administrator that does not follow any specific standards for OUI allocation. An LAA can be identified by having its second least significant bit (SLSB) of the first octet set to 1. For example, 02:0A:95:9D:67:16 represents an LAA because its first octet is 02 (00000010), and the SLSB is 1. A multicast MAC address is used to identify a group of devices on a network that share a common interest or function. It is also known as a group address. In a multicast address, the LSB of the first octet is set to 1. For instance, if we take the example 01:0A:95:9D:67:16, it qualifies as a multicast Media Access Control address because its first octet is 01 and its LSB is 1. A broadcast MAC address is mainly used to identify all devices within a network segment. It is also referred to as a universal address. In a broadcast address, all bits are set to 1. For instance, if we consider FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF as an example, it represents a broadcast address since all its bits are set to 1. The purpose of using a broadcast Media Access Control address is to send frames to all devices within the network segment without considering their individual MAC addresses. For example, an ARP request utilizes a broadcast address as its destination address in order to reach all devices within the network segment. Here are the difference between Broadcast and Multicast. Here are some differences between MAC and IP Address – Especially in the structure of the OSI model, the reason for having both MAC and IP addresses depends on the way the Internet works. How the data is sent and received over a network is described by the OSI model also known as a conceptual framework. It is divided into seven layers and each of these layers performs specific functions. A MAC (Media Access Control) address is used in Layer 2 (Data Link Layer). These are unique numbers that are linked to network interfaces to facilitate data link layer communication. Media Access Control addresses’ primary function is to manage how data is transported from one network node to another on a direct, physical basis – this is also known as “hop to hop” delivery. Nonetheless, an IP (Internet Protocol) address is used by Layer 3 (Network Layer). Devices on a network are identified by their IP addresses, which are also used to route data between networks. IP addresses guarantee that data travels from its original source to its destination; this process is known as “end-to-end” data transmission. An IP header, which contains the source and destination IP addresses, is first sent with data by a computer. The source and destination MAC addresses for the current “hop” in the path are included in the MAC header, which encapsulates the data and the IP header. The MAC address header is removed, and a new one is created for the next hop as data moves from one router to the next. But until it gets to its destination, the IP header—which was created by the original computer—remains intact. This procedure demonstrates the way the MAC headers handle the “hop to hop” delivery and the IP header controls the “end to end” delivery. Therefore, IP addresses and MAC addresses are both necessary for the Internet to work. IP addresses guarantee that the data reaches its intended destination, whereas Media Access Control addresses enable the direct, physical transfer of data between network nodes. Here are the major characteristics of a Media Access Control address: Some of the advantages are: Some of the disadvantages are: Now, many of the students or enthusiasts have a keen interest in finding the MAC address of a device. But how to find it? Below, we have explained the whole process on various devices in easy steps. Here are different ways of finding Media Access Control address of various devices – Here is how you can locate the MAC address on Windows: To locate the MAC address on Mac OS, one can follow the below steps: Here’s a step-by-step guide to locating the MAC address on Linux: A MAC address serves as an identification for a network device like a router or computer. On the other hand, an IP address is a label that helps identify devices on networks such as the Internet or local area networks. Finding a MAC address is different in different machines or OS. For example, in the case of Windows, one can find the MAC address by typing ipconfig/all in the CMD. For Linux, one can find it by typing ifconfig -a in the terminal. The three types of MAC addresses are: The full form of MAC is Media Access Control. In this blog post, we’ve covered all the crucial concepts of MAC addresses in networking. We discussed what it is, its purpose, structure, and types. Apart from that, we also explained how to find it on a device and shared some facts about MAC addresses. We hope this information has helped you gain an understanding of these addresses and their significance in networking. MAC Address is an essential part of CCNA Training. If you want to learn more about it, you should check out PyNet Labs’ CCNA Course. If you have already completed with the CCNA Training, you should check out CCNP ENCOR Training to advance your knowledge.Introduction
What is MAC Address?
Format of MAC Address
Purpose of MAC Address
Types of MAC Addresses
Unicast
Multicast
Broadcast
Difference between MAC Address and IP Address
MAC Address IP Address MAC – Media Access Control IP – Internet Protocol The manufacturer provides the unique address ISP or Internet Service Provider provides the logical address This is a physical address of the device’s NIC that is used to identify a device within a network. This is a logical address that identifies a network or device on the internet. Operates on the data link layer. Operates on the network Layer. 6 -bytes hexadecimal address. 4 bytes for IPv4 and 8 bytes for IPv6 addresses. Reasons to have both IP and MAC Address
Characteristics of MAC Address
Advantages of MAC Address
Disadvantages of MAC Address
How to find MAC Address of a Device?
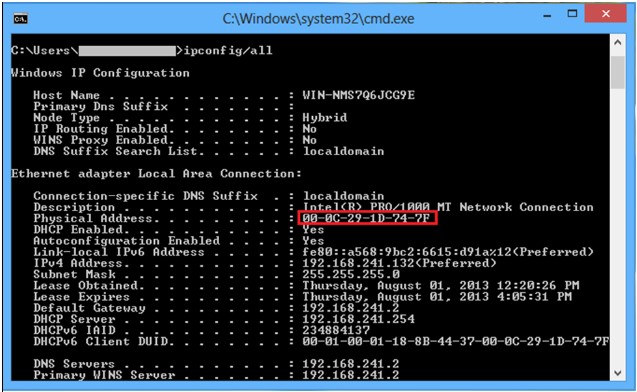
Windows
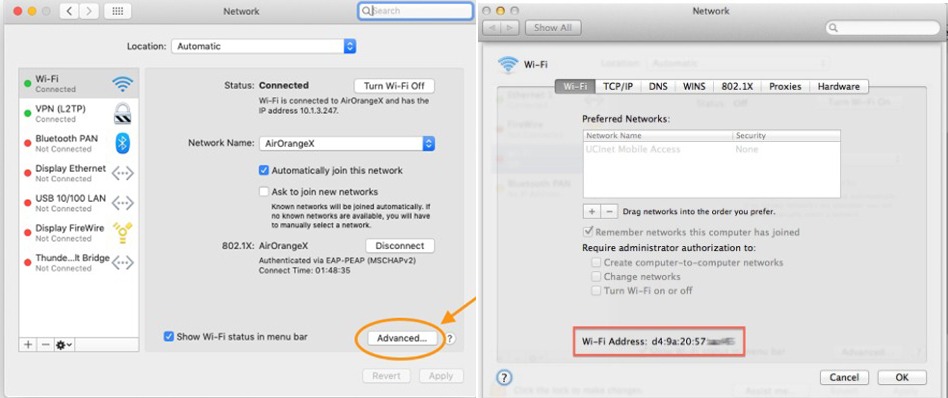
Mac OS
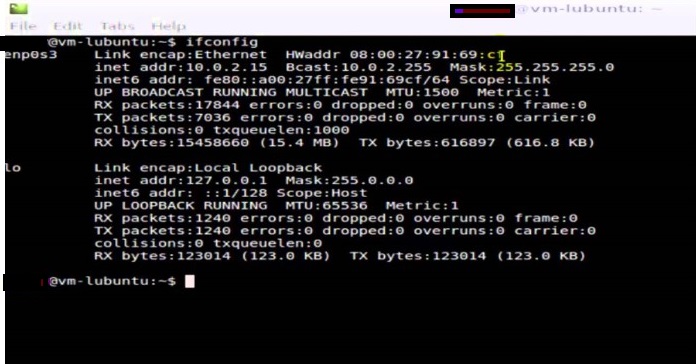
Linux
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is MAC address and IP address?
Q2. How to find a MAC address?
Q3. What are the 3 types of MAC address?
Q4. What is the full form of MAC?
Conclusion







