What is VLAN (Virtual LAN)?

In networking, as we know, switches are used to create networks, while routers are used to connect different networks. By default, switches forward both broadcast and multicast out of every port but not the originating one. However, if you require to divide a single broadcast domain into smaller ones with security in some networks, then it is possible with the VLAN concept. In this blog, we will understand what is VLAN and everything else you need to know about it. A broadcast sent from a host can easily reach all network devices in the absence of VLANs. Every device will process received broadcast frames. It can potentially increase CPU overhead on each device while decreasing overall network security. In case you place some interfaces on switches into separate VLANs, a broadcast from one host can reach only devices available inside the same VLAN. Hosts of VLANs will not even be aware that the communication took place, and all departments or groups work separately with their broadcast domain. VLAN stands for Virtual Local Area Networks; they are nothing but a logical grouping of switch ports to have separate broadcast domains. VLAN reduces the size of broadcast domains while increasing the number of broadcast domains. VLANs are typically configured on switches by assigning some interfaces to one broadcast domain and others to another. Each VLAN serves as a subset of the switch ports on an Ethernet LAN. VLANs can be configured on multiple switches, with each VLAN being treated as its own subnet or broadcast domain. The broadcasted frames onto the network will only be switched between the same VLAN ports. Before VLAN working of a switch After VLAN working of a switch Let’s take a deep dive into VLAN, starting with how it works. Here are step-by-step instructions on how VLAN works: The purpose of VLAN in networking is as follows – By limiting the amount of traffic a specific endpoint sees and processes, VLANs can enhance performance for devices on them. By dividing broadcast domains, VLANs limit the number of other hosts that a given device can see broadcasts from. For example, phones won’t receive any broadcast traffic created by workstations if they are all on one VLAN but all workstations are on another. Each can limit the traffic on their respective networks that is relevant. Different Traffic handling rules per VLAN can be defined by the Network Engineers. For example: To help ensure the functionality of telepresence devices, they can implement rules to prioritise video traffic on a VLAN that connects conference room equipment. 2. Enhanced security By allowing for greater control over which devices have access to one another, VLAN partitioning can also enhance security. for example, Network teams might limit management access to network hardware or IoT devices to particular VLANs. 3. Smooth administration Administrators can also organize devices for purely administrative, non-technical reasons by using VLANs to group endpoints. For example, they might group all computers used for accounting into one VLAN, all computers used for human resources into another, and so on. Moving on, let’s understand the advantages of VLAN. When the switch first boots up, all switch ports are added to the default VLAN. Generally, all switches have default VLAN as VLAN 1. VLAN1 allows any network device connected to any switch port to connect with other devices on other switch ports. The VLAN1, i.e., Default VLAN, can’t be renamed or deleted. Data VLAN is also known as a user VLAN. The data VLAN is only used for data generated by users. This VLAN carries data only. It does not carry management traffic or voice. Voice VLAN is configured to carry voice traffic. Voice VLANs typically have higher transmission priority than most other types of network traffic. We need a separate voice VLAN to save bandwidth for other applications. A management VLAN is used to configure the switch for management purposes. It manages system logging and monitoring. By default, VLAN 1 is the management VLAN. This VLAN is used to carry untagged (not belonging to any VLAN) traffic. These are the five types of VLAN. These are some advantages of VLAN. Here are some disadvantages of VLAN – A VLAN port, also known as a tagged port or trunk port, is a network port that is configured to transmit traffic for multiple VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks). It is typically used to connect switches or network devices together while carrying traffic for multiple VLANs simultaneously. VLAN ports add a special VLAN tag to each packet, indicating the VLAN to which the packet belongs. This allows the switches or devices to differentiate and direct the traffic to the appropriate VLANs across the network. There are two types of ports used in VLANs – The access port is a member of only a single VLAN. By default, all switch ports on the Cisco switch are access ports. So, any device connected to any switch port becomes a member of that VLAN. When VLANs are configured on multiple switches, a mechanism is required to identify which VLAN a frame belongs to. This is accomplished through frame tagging, which adds a VLAN ID in each frame. These tagged frames are sent over Trunk ports. A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a method of creating virtual networks within a physical network infrastructure. It is used to improve network flexibility, security, and performance by logically separating devices into distinct groups, regardless of their physical location. VLANs enable efficient network management and enhance overall network efficiency. A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a virtual network that allows devices to communicate as if they were on the same physical network, providing segmentation and security. For example, in an educational institution, VLANs can be set up for students, faculty, and administration, enabling separate networks while utilizing the same network infrastructure. The three types of VLANs are: VLAN trunking is used to transport traffic for multiple VLANs over a single network link, enabling efficient utilization of network resources. It simplifies network design, reduces the number of physical connections needed, and facilitates the exchange of VLAN traffic between switches or network devices. In this article, we have discussed what is VLAN, how it works, what are the different types of VLAN, its advantages, disadvantages, and range. You can Join our CCNA Training for a better understanding of VLAN. Our CCNA training is rated among the top CCNA training in India and we have also launched a free CCNA program to help all aspiring network engineers. To conclude, VLAN is showing a promising future in the networking field and this knowledge will be beneficial for any network engineer. If you are still with us, we are sure you have learned most things about VLAN. If you have any suggestions or feedback for us, you can comment down in the comment box. We would love to hear from you. For more useful insights, you can also check out this video,Introduction
What is VLAN (Virtual LAN)?
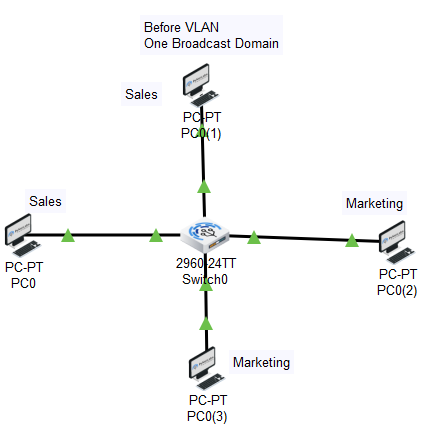
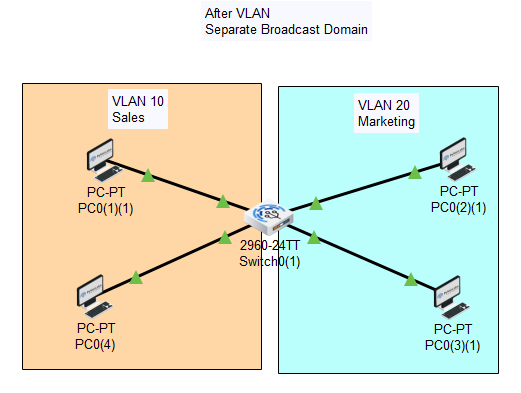
How VLAN works?
Purpose of VLAN
VLAN Range
Range Description VLAN 0-4095 This range of VLAN IDs is to be used on switches. VLAN 1 This is the default VLAN of switches.
It can be used, but you can’t delete or edit it.VLAN 2-1001 It is a normal VLAN range. It can be created, edited, and deleted by you. VLAN 1002-1005 These ranges are CISCO defaults for token rings and FDDI.
You cannot delete this VLAN.VLAN 1006-4094 It is an extended range of VLANs. Types of VLAN
1. Default VLAN
2. Data VLAN
3. Voice VLAN
4. Management VLAN
5. Native VLAN
Advantages of VLAN
Disadvantages of Virtual LAN (VLAN)
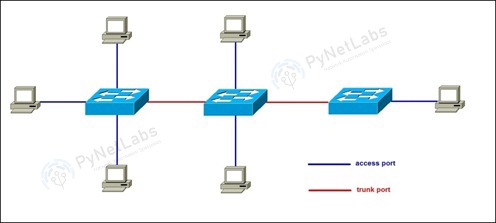
VLAN Ports
1. Access Port
2. Trunk Port
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is VLAN and why it is used?
Q2 – What is a VLAN with example?
Q3 – What are the 3 types of VLANs?
Q4 – Why is VLAN trunking used?
Conclusion







