What is a Router in Computer Network?
Data can be found anywhere nowadays. We use it for work, study, fun, and communication. But how is information delivered between devices? How can we guarantee the security and dependability of our data? Routers are the solution. A router in computer network is a component that connects various networks and routes data packets to their desired locations. They are necessary for the operation of networked systems such as the Internet. In this blog, we will explain what is a router, the different types of routers, their working, their uses, advantages, and disadvantages. Before getting into more details, let’s first understand what a router really is. Devices may connect to routers to exchange Internet or intranet data. A router is a gateway that sends data across LANs or local area networks. Routers use the Internet Protocol (IP) to transmit IP packets, which include data and the IP addresses of sending and receiving devices that are connected to different local area networks. Between these LANs, which are connected to the transmitting and receiving devices, are routers. Devices may be connected together over many router “hops,” or they may be located on several LANs that are all directly connected to the same router. Now that you have a basic understanding of Router in network devices, you should also know that all the routers are not same. There are different types of routers available in market. There are different types of routers; some of these are: Using a wireless router, Wi-Fi gadgets like computers and smartphones can connect to the internet. Additionally, they may provide standard Ethernet routing. The range of an inside connection is 150 feet, whilst the range of an outdoor connection is 300 feet. VoIP (voice over Internet Protocol) technology links a broadband router to the Internet and provides high-speed Internet access. Data packets may be routed by a core router inside a single network, but not across networks. They serve as the network’s backbone, helping connect all of the gadgets. Low-capacity edge routers, which reside at the network’s peripherals, are the most common kind. An edge router may transport data packets across networks and connect the internal network to the external networks. For connection, they use the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). Label edge routers and subscriber edge routers are the two different kinds of edge routers. These are customized routers with bridge functionality. Like bridges, b-routers facilitate the transfer of data across networks. Additionally, they distribute data across network devices like a router. These are the different types of routers. Now let’s understand the architecture of the router before we understand the working of a router. Below we have explained the architecture of the router with an image. The input port is responsible for executing the physical layer function of terminating an incoming physical link to a router. In order to communicate with the data link layer functionality on the other side of the incoming connection, it performs the data link layer functionality that is necessary. The input port also performs a lookup and forwarding operation to ensure that a datagram transmitted into the router’s switching fabric reaches the intended output port. The output port performs link-layer and physical-layer operations to deliver packets from the switching fabric to the incoming connection after storing them there. The output port performs identical functions to the input port in terms of reverse data link and physical layer operations. Data is sent from one network node to the next node in the network through the correct port using a combination of hardware and software. Routing processors execute routing protocols. Both forwarding tables and routing information are stored there. Within the router, it also manages network management. Below, we have explained the working of the router. Various routing protocols are used in the process of routing packets from source to destination. After understanding what is a router and how it works, you must be wondering where it is used. Let’s understand the different applications of routers in detail. Some of the applications of a router are: It connects several networks and sends packets to directly connected or distantly connected networks. It controls network traffic by sending data packets to the intended address. Additionally, it allows numerous addresses to share a single internet connection. Numerous Internet Service Providers (ISPs) are connected via large routers. Network access for households and offices is provided via small routers. Routers are used to link several subnets—logical groupings of connected computers—with various network prefixes. Private ISPs also use them for port forwarding. A router decides which data packet should be processed first using QoS. We now have a basic understanding of how a router works and its applications in computer networks. Let’s now understand the advantages and disadvantages of using a router. There are various advantages of using a router. These are: Sharing a single network connection across several devices is the router’s primary job. This enables numerous people to connect to the internet, boosting total productivity. Besides that, routers have connections between various media and network designs. Without a doubt, installing a router is the first step in securing a network connection. Because using a modem to connect directly to the internet exposes your PC to several security risks, the environment is secure, so routers are utilized as an intermediary between two networks. The router utilizes dynamic routing strategies that help in network communication. The internetwork’s optimum route is chosen through dynamic routing. Additionally, it generates collision domain and broadcast domain. Overall, this may reduce network traffic. Switching between packets and filtering packets are two more router functions. Routers use a collection of filtering rules to filter the network. The packets are either permitted or passed through in accordance with these guidelines. Routers utilize backup sections if one of the external network components fails to prevent issues with traffic routing. This is used by organizations, particularly big ones, to manage traffic effectively. Some of the disadvantages of using a router are: Routers read more than only the top two levels of information, in contrast to repeaters and bridges. It examines data in every detail, from the physical to the network layer. The connection could get slow as a result. Additionally, routers allow numerous computers to share a network, which causes a condition known as “Connection Wait” on the router. This can make the connection even slower. More than any other networking component, routers are expensive. Security, hub, and bridge are included in this. Therefore, from a financial standpoint, routers are not always the best choice. Additionally, the router has compatibility problems, particularly with the 5GHz band. You can only profit from 5GHz settings if your PC and its adapters support them. As a result, you need to consider choosing a less expensive router. Routers are not always reliable. Even now, a few modern gadgets utilize the 2.4GHz band, which is regularly interrupted. People who live in flats and apartments often suffer these sorts of disconnections. The routers use dynamic routing strategies to facilitate communication. This can result in increased networking overheads. Large amounts of bandwidth are used by networking overheads, which causes a bandwidth shortage. In addition to updating routing tables, routers do routine network maintenance. The utilization of bandwidth could suffer from this as well. These are the advantages and disadvantages of using a router in computer network. A router is a type of networking device that takes data packets from computer networks and other devices, analyzes them, and then routes them. The third tier of the OSI model, the network layer, is where it operates. Mainly, there are five types of routers. These are: Switch: Connects devices in a network and forwards data to the right destination. Hub: Connects devices in a network and broadcasts data to all devices. Router: Connects different networks and routes data packets based on their addresses. Routers connect your gadgets to the Internet. The router controls the flow of data to and from each device as well as the modem, ensuring that it all arrives securely at its intended destination. The three types of routing are: Router in network devices is of great importance. They provide network segmentation, allow communication across various networks, and give extra features like filtering, prioritizing, and security. Computer networks could only operate as effectively, safely, and consistently with routers. In this blog, we have explained what is router, its architecture, working, advantages, and disadvantages.Introduction
What is a Router in Computer Network?
Different Types of Routers
Wireless Routers
Broadband Routers
Core Routers
Edge Routers
B-routers
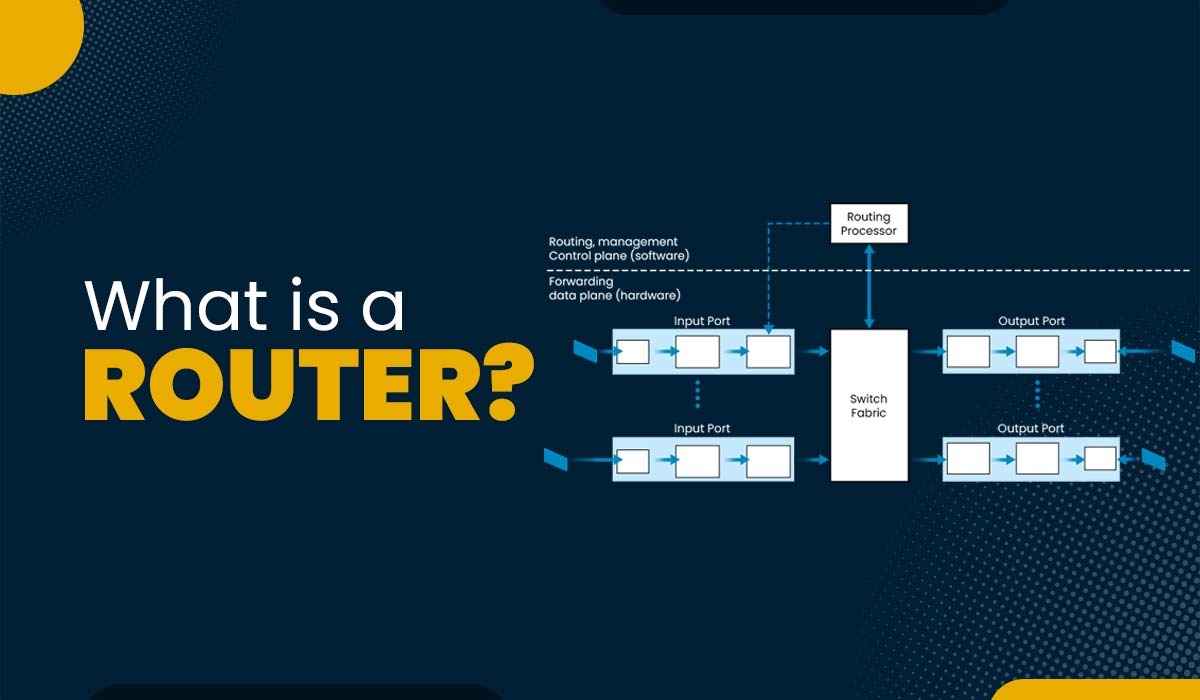
Architecture of the router
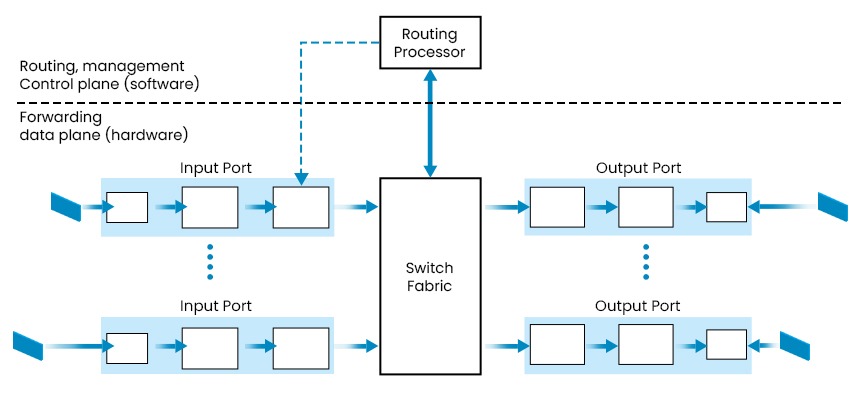
Input Port
Output Port
Switching Fabric
Routing Processor
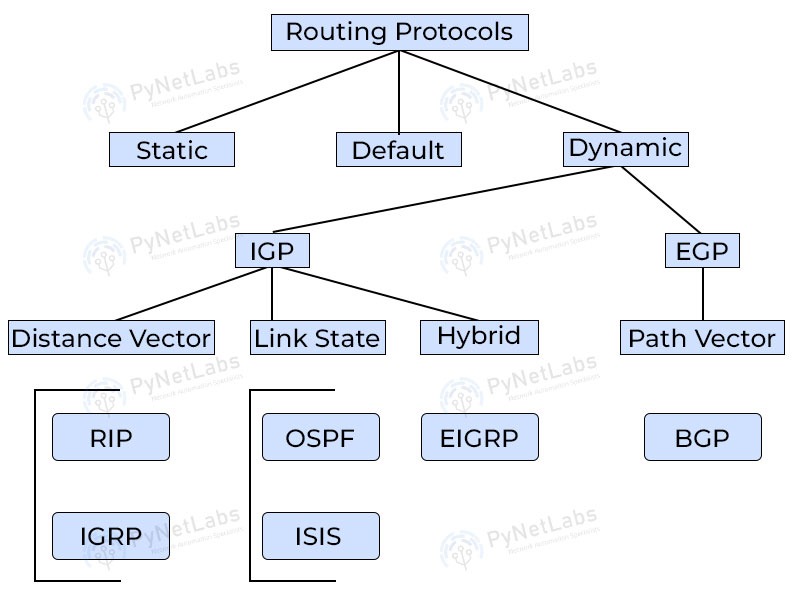
How do Router in Computer Networks Work?
Application of Router in Computer Network
Different network connections
Managing congestion
Providing connectivity
Connecting subnets
Port forwarding
Traffic classification
Advantages of using a Router
Connection
Security
Dynamic Routing
Packet Filtering
Backup Plan
Disadvantages of using a Router
Speed
Cost
Compatibility
Reliability
Bandwidth Shortage
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is router and type?
Q2 – What is switch hub and router?
Q3 – Why router is used?
Q4 – What are the three types of routing?
Conclusion







