Firewall and Its Types

Finding the right tools may be difficult for businesses thinking about protecting sensitive information. When it comes to keeping sensitive data safe, every system may benefit from using any number of easily accessible tools. Installing a firewall can prevent unauthorized access to your network and its components. In this Blog, we will focus on firewall and its types, and they assist in securing your network. Before getting into the details of types of firewalls, let’s first understand what a firewall really is. A firewall is a cybersecurity solution that is used to selectively regulate network traffic by filtering it. Firewalls provide the capability to separate network nodes from both external and internal traffic sources, as well as from particular applications. Firewalls include several forms, including software, hardware, and cloud-based configurations, each showing different advantages and disadvantages. A firewall in computer is used to block the passage of harmful traffic requests and data packets while permitting the flow of legitimate traffic. A Firewall is an integral part of any effective cybersecurity plan for a business. Most PCs already have a firewall installed, but it may not provide enough protection. The question that arises now is how a firewall can ensure our safety. Some of the functions of a firewall have discussed below. We already understand what is a firewall in computer; below, we have explained the different types of firewalls. Different firewalls may be separated into several groups based on their overall design and function. Firewalls and its types are generally categorized into: One of the earliest and most “basic” types of firewall architecture, It acts as a checkpoint in a network’s routing or switching infrastructure. The firewall does a surface-level inspection of data packets passing through the router, looking at things like the source and destination IP addresses, the packet type, the port number, and so on, but without really opening the packet to see what’s within. If the data packet doesn’t make it through the checkpoint, it is immediately discarded. These firewalls have the advantage of being quite light on system resources. They are straightforward and have little effect on system performance since they use fewer resources. However, they can be easily bypassed in contrast to firewalls that do a more thorough examination. Advantages of packet-filtering firewalls – Disadvantages of packet filtering firewalls – Proxy firewalls function at the application layer to efficiently monitor incoming traffic between your computer’s network and the source of the traffic. This is why they are commonly referred to as “application-level gateways.” The firewalls are deployed using either a cloud-based solution or another proxy device. The proxy firewall initiates a connection to the traffic source and continues to examine the incoming data packet, instead of allowing direct connectivity. The packet and the TCP handshake protocol are both examined by proxy firewalls. It is the same as in a stateful inspection firewall. Deep-layer packet inspections, in which the proxy firewall deeply examines each individual data packet to ensure it is malware-free. After making sure it’s safe to proceed with the connection, the proxy then passes the packet along. This provides further anonymity and security for your network by hiding the identities of specific devices between the “client” (the system from which the packet originated) and the rest of your network. Note: Proxy Service firewalls have one major problem: they may significantly slow down the transit of data packets. Advantages – Disadvantages – This particular type of firewall integrates packet inspection technology and TCP handshake verification to enhance the level of protection beyond what each architecture could individually offer. Nevertheless, utilizing these firewalls imposes an additional burden on computational resources. The transfer of legitimate packets may experience a decrease in speed when compared to alternative solutions. Advantages – Disadvantages – Circuit-level gateways are a type of firewall that is designed to efficiently process and control network traffic by making quick decisions to allow or block it, all while minimizing the utilization of computational resources. Circuit-level gateways operate by verifying the TCP handshake. The purpose of this TCP handshake check is to verify the authenticity of the originating session of the packet. Although highly efficient regarding resource usage, these firewalls do not perform packet inspection. If a packet contains malware but successfully completes the appropriate TCP handshake, it would effectively bypass any security measures in place. Because of this reason, these types of firewalls don’t provide enough protection to businesses. Advantages – Disadvantages – Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs) are now the most popular form of firewall due to their increased security compared to traditional firewalls like packet-filtering and stateful inspection. An NGFW is a firewall that does deep packet inspection in addition to other capabilities, such as application awareness and control, cloud-delivered threat information, enhanced network visibility, and integrated intrusion prevention. Advantages – Disadvantages – We have thoroughly discussed firewall and its types; below, we have explained in detail the firewall deployment architecture. Firewalls can be categorized into three categories on the basis of deployment, these are: Each computer runs a program called a software firewall, which controls what programs and ports may communicate with each other on a network. One of the major advantages of using a software firewall is its significant utility in establishing defense in depth through the separation of individual network endpoints. The only issue with these types of firewalls is that not all devices are compatible with a single software firewall. Advantages – Disadvantages – Hardware firewalls are the physical barriers installed between your network’s gateway and your internal systems. These are highly effective in providing perimeter security. It can be achieved by intercepting any malicious traffic originating from external sources before it can reach the network endpoints of the company. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of exposing the network to potential threats. Advantages – Disadvantages – A cloud firewall is a type of network security system that monitors and controls the incoming and outgoing traffic of a cloud-based service or application. The key advantage of cloud-based firewalls is their simplicity in expanding with your company. The cloud server may have more processing power added to it so that it can filter more traffic as your demands increase. Advantages – Disadvantages – The first step in ensuring a company’s secure development in the dynamic digital era is realizing the advantages that firewall protection can provide. Some of the advantages are: Firewalls are a network security tool that may allow or block data packets depending on predetermined policies. They are generally used to safeguard network nodes from unwanted data traffic and applications. Types of firewalls: The most common 3 types of firewalls are: Proxy server firewall, Next-gen firewalls (NGFW), and Stateful inspection firewall. Proxy or next-gen firewalls are among the best as they are the most secure firewall compared to all others. Common uses of firewalls are: When a computer is linked to the internet, it needs additional security measures, such as a firewall. It is crucial to maintain system security in order to protect from cyber threats and hackers. In this blog, we have explained firewall and its types and advantages that they can provide for better security.Introduction
What is Firewall?
Purpose of Firewalls
Different Types of Firewalls
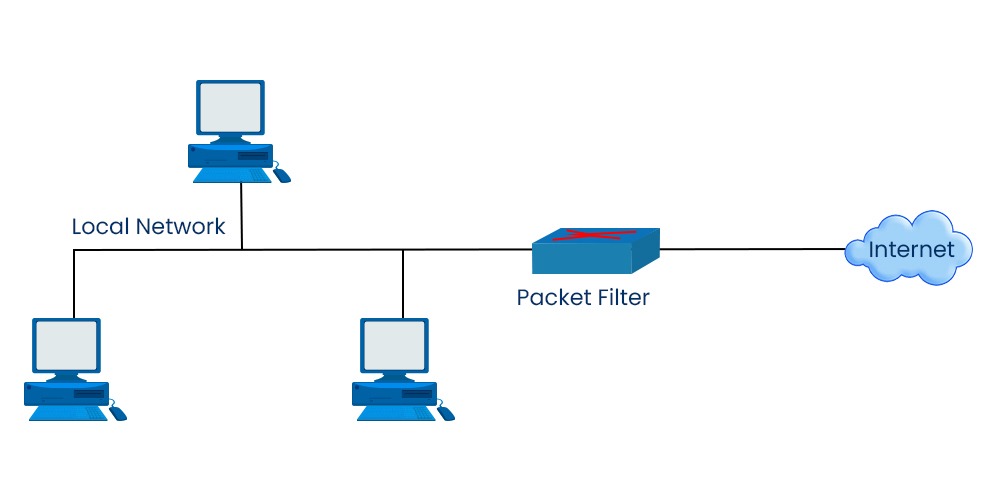
Packet filtering Firewall
Proxy Service Firewall
Stateful Inspection Firewall
Circuit-level Gateways Firewall
Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW)
Software firewalls
Hardware firewalls
Cloud firewalls
Advantages of using various types of Firewalls
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is firewall and its type?
Q2 – What are the 3 types of firewalls?
Q3 – Which type of firewall is best?
Q4 – What are the uses of firewalls?
Conclusion







