What is DHCP Snooping?
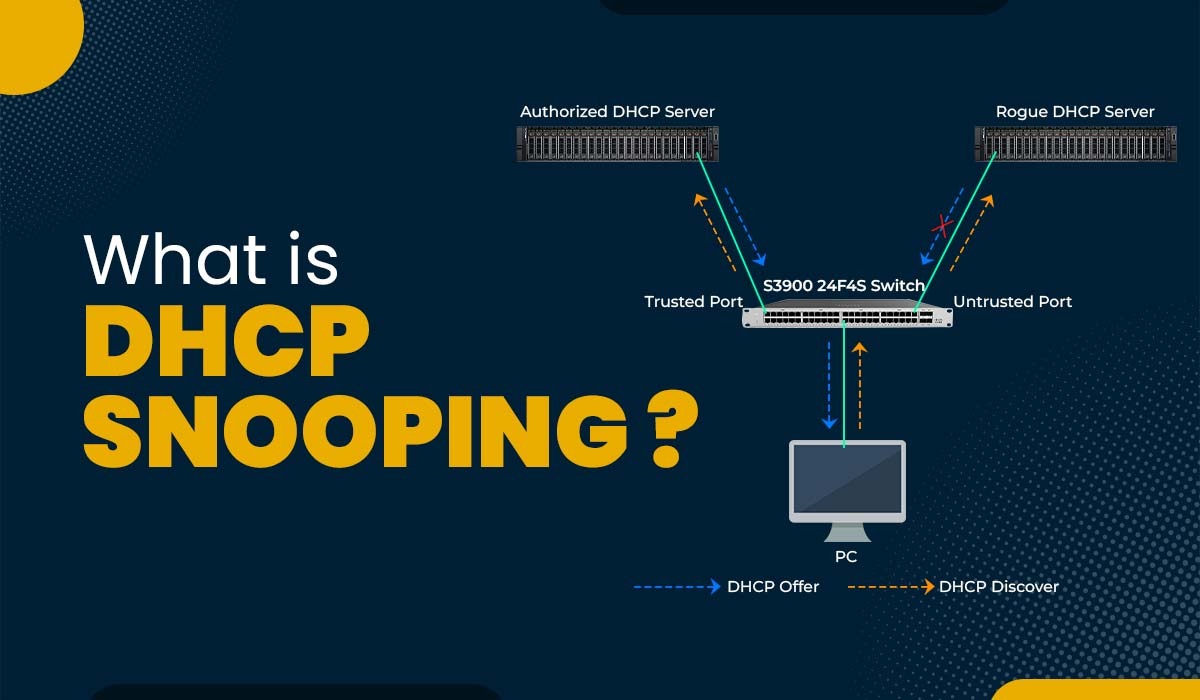
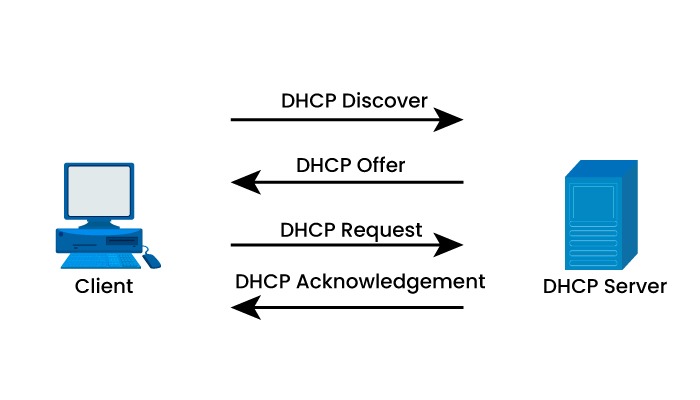
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network protocol that enables devices to obtain IP addresses and other network configuration details from a server. DHCP simplifies IP addresses as well as reduces the need for configuration. However, it also introduces security risks, such as DHCP spoofing and DHCP starvation. To safeguard the network against these threats, there is a security feature called DHCP snooping that can be implemented. In this blog, we will explain what DHCP snooping is, how it works, its configuration, and how it can prevent various attacks. Let’s start by first understanding what DHCP snooping is. DHCP snooping is a layer 2 security mechanism that filters and verifies DHCP messages exchanged between clients and servers. It operates on switches that connect end devices like PCs, laptops, and access points in order to prevent malicious servers from providing IP addresses to clients. Additionally, it maintains a database of IP address bindings and leases for each client, which aids in verifying the source of network traffic and preventing IP spoofing. DHCP Snooping is essential for every organization’s network because, with it, many end-user devices like PCs and laptops can automatically learn IP addresses. The host is creating an IP address lease for the DHCP server. It needs to be configured on Layer 2 switches where unauthorized hosts are connected to secure hosts in the organization’s network from making connections to unauthorized DHCP servers. But the question that arises is how it really works. Let’s understand in detail. To understand how DHCP snooping operates, it is essential to understand the DHCP process. The diagram below illustrates an exchange between a client and a server: The process involves the following steps: Now that we have a basic understanding of how DHCP works, and if someone wants to go into more details, one can go through the DHCP blog. Let’s understand how DHCP snooping works. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol snooping categorizes switch ports into two types: trusted and untrusted. Trusted ports are those that connect to authorized servers or other switches with snooping enabled. On the other hand, Untrusted ports connect to end devices like PCs, laptops, printers, etc. By default, all ports are considered untrusted unless otherwise configured. It operates by inspecting the messages that pass through the switch and applying rules based on the type of port and message. The actions taken by snooping for scenarios are summarized in the following table: As shown in the table, DHCP snooping allows any message from a trusted port to pass through without any modifications. This ensures communication between DHCP servers and clients without any disruptions. However, suppose an untrusted port receives a message that’s not a Discover or Request message. In that case, DHCP snooping drops it to prevent rogue servers from offering IP addresses or providing false information to clients. Additionally, any malformed message, or one that does not match the information, in the binding table is also dropped by snooping. Let’s move on to how the snooping can prevent some of the attacks and maintain the integrity of the data. DHCP snooping can prevent two common types of attacks that exploit the DHCP protocol. These are: DHCP spoofing is a type of attack where a malicious host pretends to be a server and offers fake or harmful IP addresses and network parameters to unsuspecting clients. This can lead to consequences such as: DHCP snooping comes into play to combat spoofing by identifying and blocking any offer or ACK message that originates from a port. This ensures that only authorized DHCP servers are allowed to provide IP addresses and network settings to clients. DHCP starvation refers to an attack in which a malicious host floods a server with fake MAC addresses through DHCP discovery messages, depleting the available IP address pool. This attack can lead to consequences such as: To mitigate starvation, one can make use of DHCP snooping, which restricts the rate of DHCP messages on untrusted ports. This prevents attackers from taking control of the system with requests, thereby preserving available IP addresses. It is a security feature that carefully filters messages. It effectively prevents servers from assigning IP addresses to clients. Enabling this feature is recommended if you wish to safeguard your network against attacks. DHCP snooping is an approach where we configure our switches to learn about DHCP traffic and intercept any malicious DHCP packets. An attacker who operates a DHCP server and the same subnet will likely respond more quickly to a client’s DHCP Discover message. In the event that the attacker is successful, he can designate the customer’s IP address as the man-in-the-middle attack’s default gateway. Create a topology as shown below: First of all, you should enable DHCP snooping globally. Click the switch and use the command below to enable the snooping. SW1(config)#ip dhcp snooping Before sending a DHCP discovery message to the DHCP server, the switch will add option 82 by default. It annoys those same DHCP servers, and they will drop the packets. After turning on DHCP snooping, if your client does not get the IP address, you should use the command below. SW1(config)#no ip dhcp snooping information option Select the WLAN for which you want to use the snooping. Sw1(config)#ip dhcp snooping vlan 1 Once you enable the snooping all interfaces are untrusted by default. Make sure that the interfaces leading to the DHCP server are trusted. SWl(config)#interface fa0/3 SWl(config-if)#ip dhcp snooping trust This is how you will be able to configure DHCP Snooping. DHCP snooping is a security feature that carefully filters messages. It effectively prevents servers from assigning IP addresses to clients. Enabling this feature is recommended if you wish to safeguard your network against attacks. When enabled, DHCP snooping establishes a binding table that keeps track of each client’s MAC address, IP address, VLAN information, and corresponding port. Only ports connected to trusted servers are marked as trustworthy. Allowed to send valid DHCP offers and acknowledgments. DHCP snooping is a security feature that filters DHCP messages from untrusted sources. A DHCP server is a device that assigns IP addresses to network devices. DHCP snooping is a security feature that functions at the layer 2 level and filters out messages originating from sources that are not trusted. DHCP snooping is a layer 2 security feature that filters and validates DHCP messages between clients and servers. It prevents rogue DHCP servers, DHCP spoofing, and DoS attacks by dividing the switch ports into trusted and untrusted types. In this blog, we have explained what DHCP snooping is in detail, along with its working. We also discussed how it can prevent common attacks to safeguard one’s data. DHCP Snooping is an advanced topic covered in Advanced Network Training that is CCNP ENCOR Training.Introduction
What is DHCP Snooping?
Need of DHCP Snooping
DHCP Snooping Works
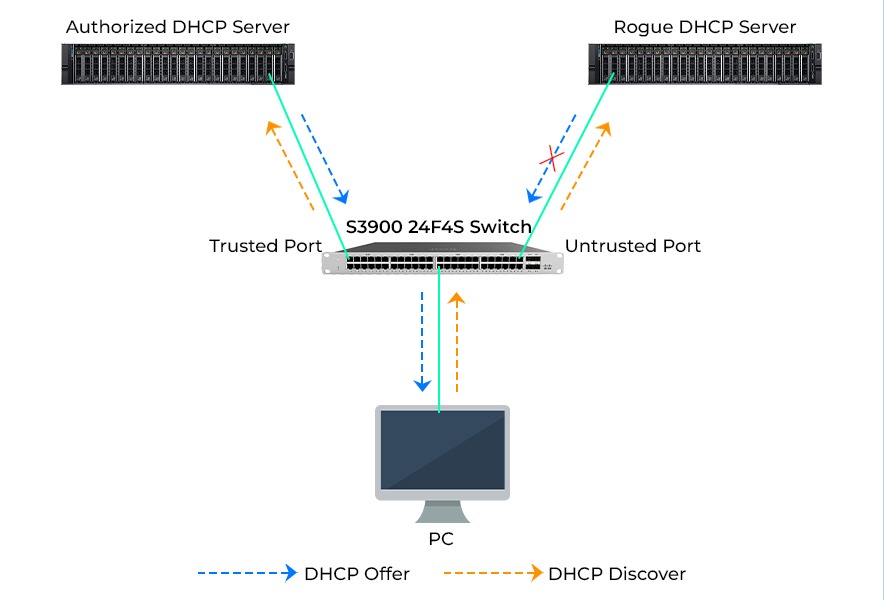
Port type Message type Action Trusted Any Forward Untrusted Discover Forward Untrusted Request Forward Untrusted Offer Drop Untrusted Ack Drop Untrusted Other Drop Common Attacks Prevented by DHCP Snooping
DHCP Spoofing
DHCP Starvation
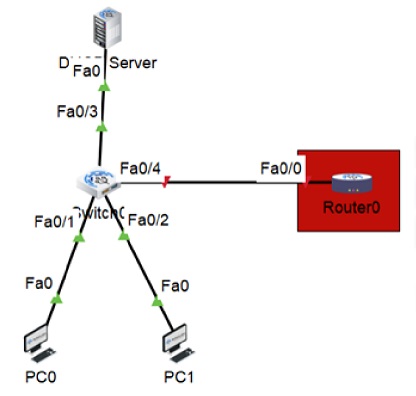
DHCP Snooping configuration
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Should I enable DHCP snooping?
Q2. What is the basic DHCP snooping?
Q3. What is the difference between DHCP snooping and DHCP server?
Q4. Is DHCP snooping Layer 2 or 3?
Conclusion







