What is ARP – Address Resolution Protocol?

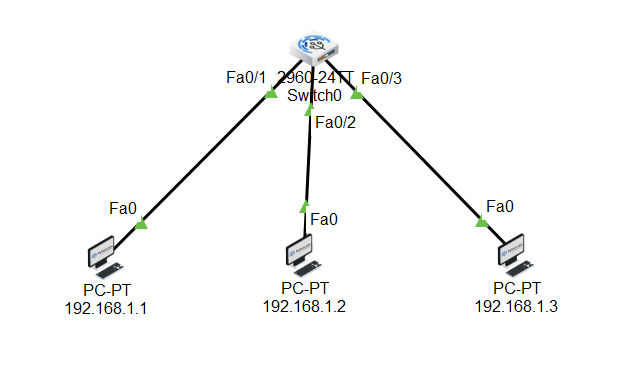
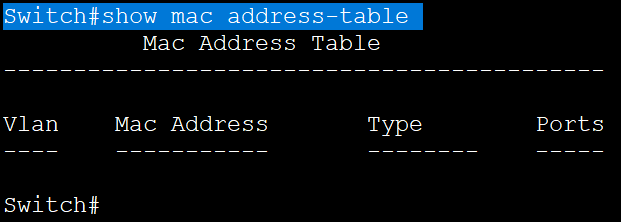
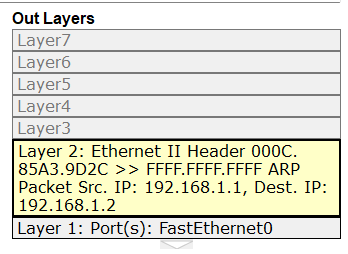
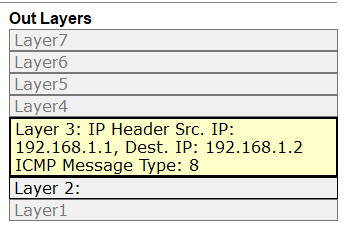
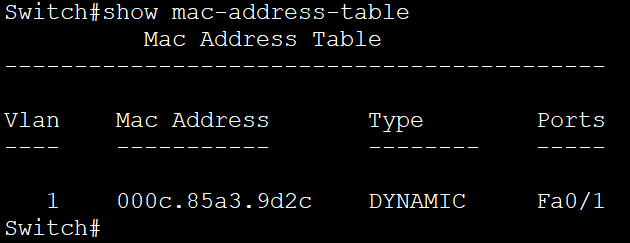
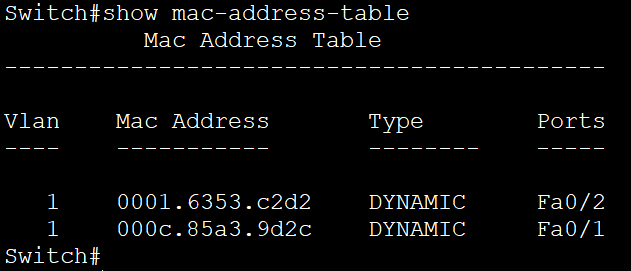
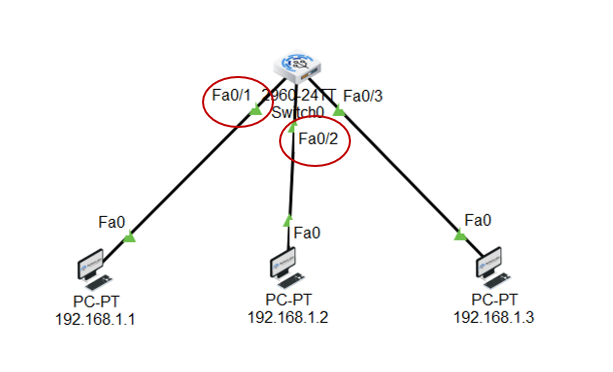
ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol but do you also wonder, what is ARP and how does ARP work? In this blog, we will be discussing these topics in detail. Have you ever imagined how the information or data is being shared over the internet? Any information exchanged from one source to destination with the help of IP, travels over the internet. We all know that an IP address helps to make the communication from source to destination. Have you ever wondered that IP Address is somewhat which works on routers but in today’s production networks, we have a network device (Switch) that connects all the multiple end devices to make the communication. Learn more about ARP in our upcoming CCNA Course. Now in the case of LANs, the devices are connected with a centralized network device known as a Switch, and the Switch is a device that doesn’t understand IP Addresses as it’s a layer-2 device of OSI, which works on frames. So, it works with the MAC address. In Local Area Networks, the communication is possible because of MAC Addresses, as these layer-2 switches can identify only the MAC Address. Now how they identify the MAC-Addresses of clients and how the communication is done, let’s see that. As discussed earlier, the full form of ARP is Address Resolution Protocol. It is a fundamental communication protocol used in computer networks, specifically in the Internet Protocol (IP)suite. It is mainly used to find the MAC-Addresses of the devices with the help of an IP Address. Whenever a device wants to send data to another device in the same local network, it needs to know the MAC address of that device. However, devices use IP addresses to identify each other. This is where ARP comes in. The primary purpose of the Address Resolution Protocol can be defined as to convert 32-bit addresses to 48-bit addresses and vice versa. The IP Addresses in IPv4 are 32-bits, while the MAC addresses are 48-bits. ARP is essential for the proper functioning of local networks because it enables devices to discover and remember each other’s MAC addresses dynamically. Without ARP, devices wouldn’t be able to communicate efficiently within the same network using IP-based protocols. ARP is a crucial protocol for local network communication and is used extensively in both small and large-scale networks. Understanding ARP’s behaviour and potential vulnerabilities is essential for maintaining network efficiency and security. To understand how does Address Resolution Protocol works, let’s take a scenario: In this scenario, we have switch and this switch is connected with 3 PCs with following IP’s as – Now, PC-1 (192.168.1.1) wants to communicate with PC-2(192.168.1.2). So, let’s verify the MAC Table in switch first by using the command. Switch#show mac address-table As you can see, no entries are there in MAC table of switch. Now, once the PC-1(192.168.1.1) drops a ping request to PC-2(192.168.1.2), the switch is going to store the MAC Address of PC-1(192.168.1.1) in its MAC table with the connected port number. Now, when the PC-1(192.168.1.1) sends a ping request, the switch will store the MAC Address of PC-1 in its MAC table. See the image to verify. And then, the switch, after storing the MAC of PC-1, will broadcast the frame in the network, and all the devices will reject, excluding the one whose destination is in a layer-3 header which is PC-2(192.168.1.2). When PC-2 replies to the switch, then the switch will store the MAC of PC-2. This is how ARP works. So, let’s discuss the requirement of the Address Resolution Protocol. You may also like – Multicast Communication End devices in the LAN communicate with the MAC addresses, not IP addresses. Once the MAC entries are there in the MAC table, the switch will not broadcast the traffic in the network. The communication will be in the form of unicasting. The purpose of Address Resolution Protocol is to find the MAC Addresses of connected clients in the network and create MAC entries so that the switch doesn’t need to broadcast again and again to find the destination. There are four types of ARP (Address Resolution Protocol), which are: It is used by the proxy servers on a network to answer the ARP queries for an IP address that is not available on that network. The proxy offers its own MAC address as the destination, and it routes the traffic to the intended destination via a tunnel or another interface. Gratuitous ARP is a special kind of Address Resolution Protocol reply which is not a response to an ARP request. It is used in advanced network scenarios and is useful to detect IP conflicts. Reverse ARP is used by a device in the local area network, which knows its MAC address but isn’t aware of its IP address. Reverse ARP requests the device’s IP address from the gateway router’s ARP table. As the name suggests, inverse ARP is the opposite of ARP. It uses the MAC addresses to find the IP addresses. These are the various types of ARP. With ARP (Address Resolution Protocol), messages to discover MAC addresses are shared and broadcast across all systems in the LAN. The diagram below shows the format of the message: Here is an explanation of all the fields of the ARP message format: ARP poison routing and ARP cache poisoning are other names for ARP spoofing. In this kind of malicious attack, a hacker sends fake ARP packets to the LAN of the target organization with the goal of connecting their MAC address to the IP address of a trusted server or device there. The link enables data to be transmitted from the victim’s computer to the attacker’s computer instead of the intended recipient. Attacks using ARP spoofing can be risky since confidential data may be transferred across machines without the victims’ awareness. Other types of cyberattacks are also made possible by ARP spoofing, such as the following: Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks are a sort of infiltrating when a hacker intercepts, relays, and modifies messages between two parties—who are unaware that a third party is involved—in order to collect information. To gain sensitive information, the attacker may attempt to take control of and manipulate the communications sent by one or both parties. A MITM assault is challenging to intercept and resist because these kinds of attacks use sophisticated software to mimic the style and tone of conversations, including text- and voice-based ones. When malware is spread and seizes control of a victim’s web browser, it is called an MITM attack. Although the attacker is not particularly interested in the browser itself, they are interested in the data that the victim shares because this information may contain usernames, passwords, account numbers, and other sensitive data that is shared in online conversations and discussions. The goal of a denial-of-service (DoS) assault is to prevent users from accessing systems, servers, and networks by flooding them with data. A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) assault is a larger-scale DoS attack that uses a large number of sources to flood a system with traffic. These kinds of attacks take advantage of network protocol flaws that are well-known. A weak network may be readily overwhelmed and rendered unusable when a high number of packets are sent to it. When a hacker steals a user’s session ID, hijacks their online session, and impersonates them, it is called session hijacking. The attacker can carry out whatever operation or activity that the user is permitted to carry out on that network once they have the session ID. When a person tries to log into a secure website or web service or obtain access to a system, authentication takes place. A session hijacker will interrupt the authentication process and intrude in real time since the session ID is saved in a cookie in the browser. Here are some advantages of the ARP Protocol: ARP has the following disadvantages: These are the advantages and disadvantages of Address Resolution Protocol. ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is commonly known as a communication protocol used to map an IP address to a physical MAC address on a local network. It enables devices to find the MAC address of another device based on its IP, ensuring proper data packet delivery within the network. ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) does not have its own IP address. It is used to resolve IP addresses to MAC addresses on a local network, enabling proper data packet delivery between devices within the network. ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) operates at Layer 2 of the OSI model. It is specifically used to map IP addresses (Layer 3) to MAC addresses (Layer 2) on a local network. ARP is essential for communication within a local network segment and is used to discover and maintain the MAC address corresponding to a specific IP address. ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is used in Local Area Networks (LANs) to resolve IP addresses to MAC addresses within the same network segment, operating at Layer 2 of the OSI model. It is not typically used in Wide Area Networks (WANs). In conclusion, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a fundamental communication protocol in computer networks. It enables devices to map IP addresses to MAC addresses on a local network, ensuring accurate data packet delivery. ARP plays a crucial role in establishing communication between devices within the same network segment. Understanding how ARP works and its various types is essential for network administrators to secure their networks and prevent potential security threats like ARP spoofing or ARP poisoning attacks. By grasping the significance of ARP and its mechanisms, network professionals can maintain the efficiency and security of their network infrastructures. Overall, a thorough understanding of ARP and its functionalities is vital for maintaining network efficiency and security, making it essential knowledge for network administrators and IT professionals alike. We hope you have found the information you were looking for. Please comment on any suggestions or updates in the comment box below; we appreciate your valuable feedback. If you like this blog, you can subscribe to our free newsletter to never miss out on any updates.Introduction
What is Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)?
How does ARP work?
What is ARP in Computer Networks useful for?
What are the types of ARP?
Proxy ARP
Gratuitous ARP
Reverse ARP
Inverse ARP
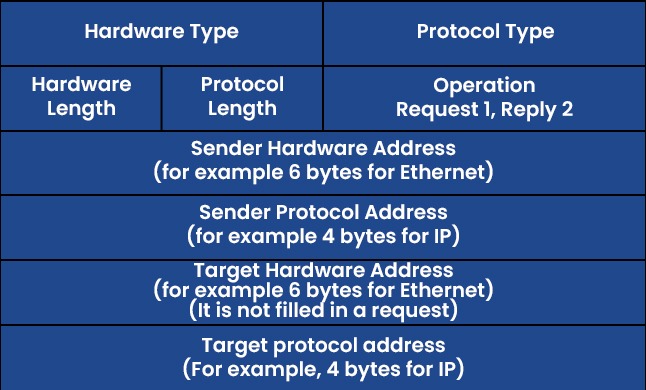
ARP Protocol Message Format
What is ARP Spoofing/ARP Poisoning Attack?
Attacks by a Man-in-the-Middle (MTM)
Denial-of-service-attack
Session Hijacking
Advantages of Address Resolution Protocol
Disadvantages of Address Resolution Protocol
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is ARP and why it is used?
Q2 – What is the ARP IP address?
Q3 – Is ARP layer 2 or layer 3?
Q4 – Is ARP a LAN or WAN?
Conclusion







