Wireless Network Security

Wireless Network Security is to protect a wireless network from unauthorized or malicious access and damage to any data or computer using wireless networks. It is a complex process that involves designing and implementing security measures to ensure the security of wireless networks. It is generally done using wireless devices that encrypt and secure all wireless communication. The standards we use in wireless networks are defined in IEEE as 802.11, like wired ethernet standards are defined as 802.3. Wi-fi is a wireless networking technology that enables network devices to connect and exchange data over the Internet using RF (Radio Frequency). The process of designing, implementing, and ensuring security on a wireless computer network is called Wireless network security. It adds protection for a wireless computer network, also referred to as a subset of Network Security. It involves the implementation of various security mechanisms, such as encryption, authentication, access control, and intrusion detection, to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data transmitted over wireless networks. Wireless network Security is essential for preventing unauthorized access to your data. Wi-Fi networks use radio waves to transmit data therefore they are particularly vulnerable to cyberattacks. This means that Wi-Fi signals can potentially interrupt and access the data being sent. Cyberattacks are becoming very common these days and can cause huge consequences on security of wireless network. Hackers can access all the sensitive information such as credit card details or any other passwords. They can also take full control of your devices, which will cause identity theft and lead to big financial losses. To protect all your devices from these risks, it is very crucial to have wireless network security for saving and protecting your data. You can easily keep all your personal information safe from hackers, by taking few safety measures to secure your device. We have to configure wireless networks keeping a few things in mind, which are: Maximum routers support three things on WAN interfaces: There are many different techniques that serve to improve the security of wireless networks. The most common techniques are listed here: Various encryptions are used for the security of wireless networks like WEP, WPA, and WPA2. These three encryptions protect the data over wireless networks. So, how do these protocols protect the data? All these encryption standards use cipher for encryption of data which are as follows – Before selecting the encryption method, you must make sure that all the devices must support the authentication method you are applying. As these encryption methods come in two categories or variants – The working is same as discussed above. But advance encryptions will work using some algorithms here in the case of WPA2. Here are some best practices for Wireless Network Security – Two-factor authentication provides an extra layer of security by requiring users to enter a username, password, and a unique code generated by an authenticator app. Enabling this feature on the wireless router’s configuration page and using apps like Google Authenticator or Authy enhances protection against unauthorized access. Passwordless authentication, such as Cloud RADIUS, offers even more robust security, preventing network breaches even if passwords are compromised. This best practice is essential in ensuring only authorized users can access the network, bolstering overall security measures. One of the other practices for security of wireless networks is using a strong password with 8 to 10 characters long consisting of a combination of upper- and lower-case alphabets, numbers, and special characters/symbols and it must be changed with some interval of time to keep it secure. In this practice, data is encrypted before sending to the destination. This encrypted data can only be accessed by authorized users which helps to highly sensitive data from unauthorized individuals/hackers. It can be implemented by the use of encryption software, hardware, or services. In any organization, employees must be aware of the importance of the encrypting data and also know how encryption is done. Another best practice for wireless network security is to enable WPA3 security. The newest and safest wireless security protocol is WPA3. It offers more robust security than WPA2 and ought to be utilized whenever practical. Make careful to search for routers that support this most modern security standard when buying a router. Because earlier protocols were more vulnerable to attack, it’s crucial to make sure WPA3 is activated. Another excellent practice for wireless network security is using a VPN. A VPN makes it more difficult for someone to gain access to the connection by encrypting all traffic between a device and the VPN server. Since public Wi-Fi networks are frequently less secure than private ones, this is especially crucial while utilizing them. Use only VPNs from reputable providers, and emphasize to staff how crucial it is to use a VPN when working remotely. One of the excellent practices for wireless network security is to turn off SSID broadcasts. Any individual within the wireless network’s range can see the network name when SSID broadcast is enabled. By going to the wireless router’s configuration page and turning off the SSID broadcast feature, you can disable SSID broadcast. This makes it more challenging for all unauthorized users to connect to the network. If someone is within the network’s range and uses a wireless network scanner, they can still see the SSID, but it won’t be as simple to access. So, this is everything you need to know about Wireless LAN and the Security of Wireless Networks. Also, you can watch this video to understand more of this topic. The security of a wireless network involves measures such as encryption (e.g., WPA2/WPA3), authentication, access control, and intrusion detection. These safeguards protect data confidentiality, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure the integrity of wireless network communications. The five elements of a wireless network security solution are authentication, encryption, access control, intrusion detection and prevention, and security policies/procedures. These components work together to verify user identities, protect data, restrict access, detect intrusions, and establish guidelines for maintaining network security. Wireless network security is important to protect sensitive data, maintain privacy, prevent unauthorized access, and safeguard against cyberattacks and data breaches. It ensures the integrity and reliability of the network and helps organizations comply with regulatory standards. Four security threats to wireless networks include eavesdropping, unauthorized access, rogue access points, and denial of service (DoS) attacks. These threats can compromise data privacy, network integrity, and disrupt normal network operations. In conclusion, the security of wireless networks is most importance in today’s interconnected world. As discussed in this blog, wireless network security refers to the measures and protocols put in place to protect data, maintain privacy, and prevent unauthorized access in wireless communication. Implementing the best practices, such as strong encryption, secure authentication, network segmentation, and regular monitoring, can significantly protect the wireless network and prevent potential cyberattacks. If you are curious to learn more about such topics, consider joining PyNet Labs’ CCNA 200-301 training program where you are going to have 10X higher Interaction with Industry Expert Trainer and lifetime access to regular class recordings. To register for our CCNA training program, you can connect with us on Call, WhatsApp, Telegram, Viber, or Signal at +91 9821215002, or write us at [email protected].Introduction
What is Wireless Network Security?
Why is Wireless Network Security Important?
Configuration of Wireless Network
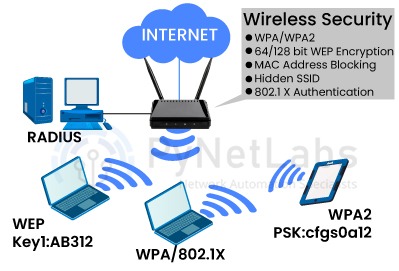
Techniques used for Wireless Network Security
Encryptions used in Wireless Networks for Security
Encryption Protocols Standards for encryptions Cipher WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) WEP RC-4 WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) TKIP Protocol (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) RC-4 WPA2 CCMP + TKIP (Counter Mode Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code) AES (Advance Encryption Standard)
Best practices for Wireless Network Security
1. Enabling Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
2. Using A Strong Password
3. Encrypting Data
4. Enabling WPA3 Security
5. Use of a VPN
6. Turning off SSID Broadcast
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is the security of a wireless network?
Q2 – What are the five 5 elements of wireless network security solution?
Q3 – Why is wireless network security important?
Q4 – What are any 4 security threats to wireless networks?
Conclusion







