What is Ansible, and What is it used for?

Automating tedious tasks makes developers’ responsibilities more manageable, allowing them to focus on other activities that benefit the organization and if we talk about automation, Ansible is a great strength. It is becoming extremely relevant among automation tools and has become the number-one choice for software automation in many organizations. It provides a centralized platform to automate configuration management and deployment processes, reducing manual errors and increasing efficiency, which has revolutionized the way IT infrastructure is managed and configured. Additionally, it also gained huge popularity in the CCIE DevNet track as it allows automating network infrastructure operations in an easy and efficient manner. In this blog, you will learn about what is Ansible used for, how it works and much more in detail, but before that let us understand what it actually is. Looking to land a high-demand DevNet role? Mastering these tools is a critical step. DevNet Expert training provides a comprehensive curriculum that dives deep into Ansible’s capabilities and its application in network automation. Ansible is an automation tool or platform that simplify the process of managing and deploying software applications and IT infrastructure and provides automation solutions to administrators, operators, and IT decision makers across various technical disciplines. It allows to save time at work while improving the scalability, stability and dependability of an IT infrastructure. It is introduced for IT specialists who use it for updates of workstations and servers, application deployment, cloud provisioning, intra-service orchestration configuration management and almost everything system managers do regularly. Furthermore, it is an agentless system that executes actions over a remote SSH or Windows remote management connection and has no additional security infrastructure, so it is easy to deploy. It uses a simple, human-readable language called YAML (YAML is not a markup language) to describe automation tasks in the form of playbooks. These playbooks define a series of steps or tasks that need to be executed on a remote system, known as a host. Unlike more simple management tools, its users can leverage Ansible automation to install software, automate daily tasks, provision infrastructure, improve security and compliance, and share automation across the enterprise. Ansible works by connecting to nodes and pushing out small programs known as ansible modules. It then implements these modules over SSH by default and then eliminates them when finished. The Ansible management node is the control node, which handles the complete implementation of the playbook. It is the node from which users are performing the installation, and the inventory file provides a list of hosts where the module needs to run. The management node allows SSH connections, and then it applies the module to the host machines and installs the product and once installed it removes the module. Now, let’s discuss what is Ansible used for. Some of the significant use cases of it in an organization are: Ansible is the most popular DevOps tool because it allows orchestration, automation, configuration, and IT infrastructure management. It provides customization and scaling according to demand and helps automate implementing internally created applications in production programs to make DevOps easier. In DevOps, it allows rapid deployments, IT architectures are coordinated, installations are reliable, and feedback loops move faster. Docker is a high-performance framework used to efficiently create and deploy containers on servers and local devices. With its straightforward design, Ansible offers a robust collection of capabilities and integral modules that allow it to create automation scripts that help create tasks and run them in preferred settings more easily. It is primarily used for automation and the first step to automate the operational service lifecycle of your application is to automate any hardware deployment. It can automate IT infrastructure on virtualization platforms, bare metal servers, and cloud servers. Additionally, it can automate the setup of multiple systems, databases, device storage devices, firewalls, and networks. Ansible is an easy, reliable, and continuous configuration management solution that provides granular infrastructure data that humans can read and process with computers. With just a password or an SSH (Secure Socket Shell) key, anyone can start monitoring machines. With Ansible, deployment of multiple applications becomes simple and quick, and there is no need to manually set up the application on each machine. It uses SSH to communicate with the remote network and execute all instructions when the module is launched from the control device. Moving on, let’s discuss its features. Some of the key features of Ansible are – Here’s a look at the many components that make up the Ansible framework. Modules are critical software that Ansible distributes from one command computer to all nodal network points or remote hosts. They are predefined instructions that are applied directly to the remote host. Playbooks run modules that maintain applications, packages, and files. Ansible invokes all modules to deliver updates or perform the required activity and disconnects them after completion. It has over 450 modules for specific tasks. It contains hundreds of built-in modules and code that run when a playbook is launched. A playbook consists of plays, consisting of various tasks, consisting of modules. Playbooks are task-specific user guides for Ansible. Playbooks direct the workflow because the tasks written in them are executed in the order they are written. They are simple text documents built in YAML, a data serialization language that humans understand. They are at the heart of what makes it so popular because they explain the tasks the user needs to perform quickly without the need to remember terminology. In addition to being able to describe settings, they can also organize the steps of any manually organized task and operate tasks concurrently or sequentially. Plugins are small pieces of code that extend the functionality of a website. Ansible comes with many of these, but user can create their own. Plugins in this case are a specific type of module and before running the module on the nodes, the plugins are run. The inventory includes all the nodes or hosts that need to be taken care of, along with their IP addresses, databases, server details, and other information. All machines (controls and nodes) used with Ansible are listed in a single, easy-to-read file containing this comprehensive data. After registering the inventory, one can assign parameters to multiple hosts through a simple text-based format. One can use an application programming interface or API to extend Ansible’s connection options. It includes extending callbacks and other functionalities in addition to using SSH for transmission. Its API serves as a medium for public and private cloud applications. Hosts are nodal structures that take advantage of the data model unique to the Ansible Automation Engine and can cross multiple hardware platforms without much difficulty. A private or public cloud is a collection of remotely located servers that a person can use to collect, organize, and process information. Instead of keeping the data on a local server, these systems are hosted on the Internet. It deploys cloud resources and instances, connects them to the database, and can handle jobs remotely. CMDB is a database that serves as a data repository for IT systems. By deploying Ansible-CMDB code, users can automatically transfer the results of Ansible’s data-collection tasks to a static HTML summary page. Here are some benefits associated with ansible – It offers a lot of benefits, but like any tool, it also has its drawbacks. Some of the drawbacks associated with Ansible are – The primary purpose of Ansible is to automate provisioning, application deployment, configuration management, orchestration, and many other IT processes. Ansible allows to streamline automation and configuration management across the enterprise by supporting six critical use cases: Because it provides an automation tool that is simple, powerful, and agentless. Also, powerful functions in many IT domains do not require special coding skills. Ansible uses 4 GB of memory per 100 forks to avoid potential resource conflicts. Ansible is an open-source tool for provisioning, application deployment, and configuration management that allows saving time, money, and effort by automating tasks across multiple servers. It is essential for developers and operations engineers to understand tools like these. Therefore, in this blog, we have discussed it in-depth, like what it is, how it works, what is Ansible used for, its features, its architecture, and its advantages and disadvantages.Introduction
What is Ansible?
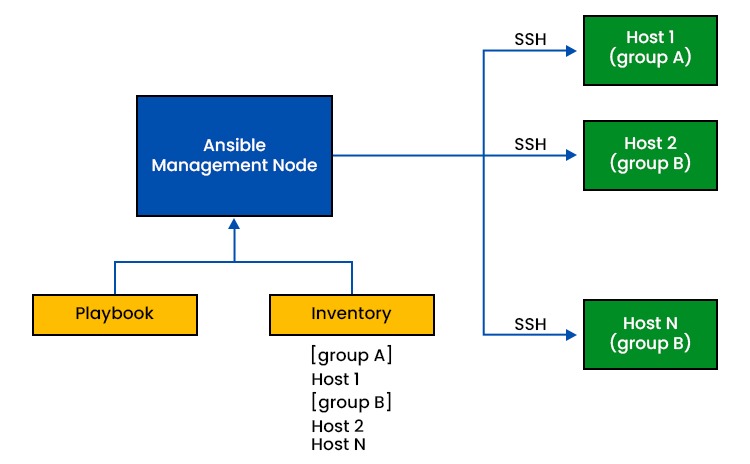
How Ansible Works?
What is Ansible used for?
Ansible for DevOps
Managing Docker Containers
For Automation
Configuration Management
Installing Web Applications
Ansible Features
Ansible Architecture
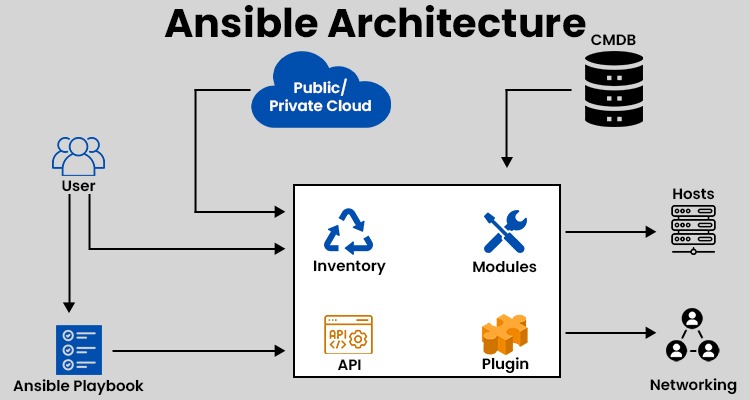
Modules
Playbook
Plugins
Inventories
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
Host and Networking
Cloud
Configuration Management Database (CMDB)
Benefits of Ansible
Drawbacks of Ansible
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is the main purpose of Ansible?
Q2 – What issues does Ansible solve?
Q3 – Why Ansible is the best?
Q4 – How much memory does Ansible use?
Conclusion