What is a Subnet and How Subnetting Works?

The management of a network on a major scale is not easy. As networks continue to grow in size and complexity, network engineers are faced with the challenge of determining optimal routes for handling the substantial volume of traffic flowing through them. Subnetting is one of the solutions developed, but the question is, what is a subnet? A subnet is a logical subdivision of an IP network that allows network traffic to travel more efficiently. In this blog, we will focus on what is subnetting in computer networks, how it works, benefits and challenges associated with it. Before getting into more details, let’s first understand what a subnet really is. A subnet, or subnetwork, is a smaller network inside a larger one. Subnets, in particular, are smaller networks that are created when one IP network is divided into numerous networks. The goals of creating subnets in a network are to make it faster, more efficient, and more secure. Now, the question that comes into everyone’s mind is why we need a subnet. Congestion, delays, and bottlenecks will arise if an excessive amount of traffic uses the same path via your network, leading to inefficient backlogs. As networks expand, the need for more routers must be met; this is where subnetworks come in. Network traffic will choose the quickest path possible, avoiding less direct but more time-efficient paths. Subnets are always confused with VLANs, learn the difference between Subnet and VLANS. Let’s now understand subnetting in detail. Subnetting is the process of dividing a network into multiple smaller networks. This smaller network is known as a subnet. Implementing this solution results in improved routing efficiency, enhanced network security, and reduced broadcast domain size. Let’s understand subnetting with the help of an example. As we can see in the image, there is one network with 10.1.0.0/8. The following problems arise when all hosts on the network belong to the same subnet: The network that we discussed above can be subnetted as shown below: Now we can see that two different subnets are created for different departments, one for Sales, i.e., 10.1.0.0/8, and one for Operation, i.e., 10.2.0.0/8. A new broadcast domain has been created for the devices in each subnet. As a result, we’ll be able to implement packet filtering on the router and greatly minimize network traffic. Learn the difference between Subnetting and Supernetting. As we already know, subnetting divides a single network into multiple small networks for better functioning. Routers allow data transfer across networks, whereas each subnet will enable devices to exchange data among themselves. Subnet sizes are set according to the network technology in use and the number of connections required. Each company is free to create as many and as large of a subnet as it sees fit, up to the limits of the IPv4 address space allocated to it. Let’s understand the process of subnetting in detail with the help of an example. An IP address consists of two parts, i.e., network prefix (also known as network ID) and Host ID. Below we have seen it with the help of an image. To determine a subnet, it is necessary to utilize a subnet mask. This mask is computed by replacing all Network ID bits with ‘1’ and allocating a specific number of bits in the Host ID for the purpose of generating the subnet. The purpose of the subnet mask is to help with the routing of data packets from the internet to their intended subnet networks. The subnet mask serves the purpose of indicating the specific portion of an address that is designated for use as the Subnet ID. For the subnet mask, we have shown in the form of the image below. The broadcast address of a subnet is determined by setting all the remaining bits of the Host ID to ‘1’ after reserving certain bits to represent the subnet. The broadcast address is utilized to broadcast a message to all hosts within a given network. Below we have shown the broadcast address with an image. Subnetting is essential because it helps manage excessive usage of network IDs. It allows the company to develop its network channel efficiently for smooth and faultless data sharing over the network channel. To understand this clearly, here are some reasons why subnetting is necessary: Here are some uses of Subnetting – Although a subnet mask and an IP address look similar, there is still a big difference. Common examples of subnet masks include 255.255.255.0, 255.255.0.0, and 255.0.0.0. The address is a 32-bit value used to differentiate between a network address and a computer host address within an IP address. In order for TCP/IP to function properly, the utilization of a subnet mask is necessary. The function of this tool is to determine whether a computer or any other device, specifically whether it is connected to a remote network or a local subnet. Subnetting offers various benefits, some of which are: When a device transmits a packet, it will be received by all network devices, thereby imposing a load on the network. In the absence of appropriate context, broadcast packets have the potential to inundate devices within the network, resulting in spam-like behavior. This may result in a decline in network performance. Subnets can be utilized to restrict the range of intranetwork broadcast messages exclusively to a designated subnet. This functionality allows effective communication among devices within a subnet and, in the event that a destination address is not within the subnet, transmits a packet for routing outside the subnet. This approach helps to minimize network congestion and network issues. With the help of subnets, it’s possible to limit network breaches as one can isolate the compromised subnetwork. Hence, it assists in enhancing overall security by protecting sensitive data. Using subnets with variable lengths, we can allocate more or fewer addresses to each segment depending on their needs, allowing us to accommodate new devices or networks without wasting or running out of addresses. Apart from all the benefits that we discussed, Subnetting also have some drawbacks, let’s discuss them in detail. A subnet is a subdivision of an IP network that allows devices to communicate efficiently and securely. A network inside a network is defined as a subnet. It is also known as a subnetwork. Subnetting divides a network into smaller segments, each with its own address range and broadcast domain. This improves network performance, security, and manageability. Two types of subnets are FSLM (fixed length subnet mask) and VLSM (variable length subnet mask). No, 255.255.255.0 is a subnet mask. It’s a class C network with a range of 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.0. This blog covers what is a subnet in detail; we have also explained the working of subnetting with the help of examples. Still, if there is a doubt or any suggestions you want to share, feel free to comment below. If you are also looking for more networking knowledge, you can join PyNet Labs’ CCNA Online Course to dive deeper into subnets and other important topics.Introduction
What is a Subnet?
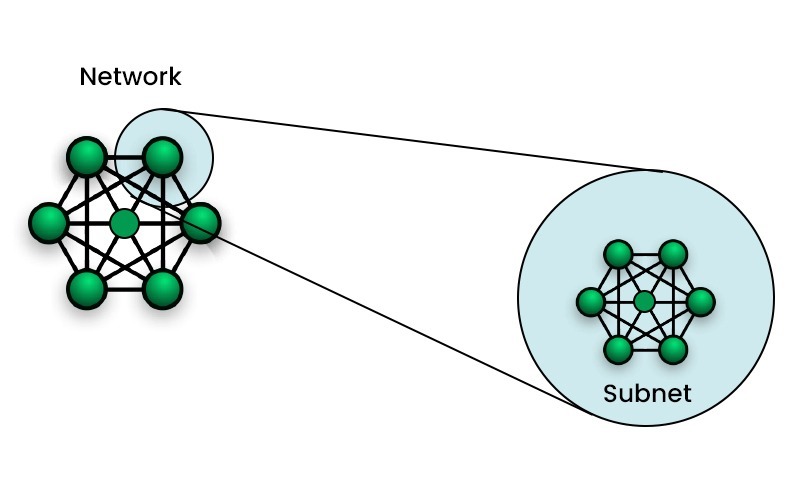
What is Subnetting in Computer Networks?
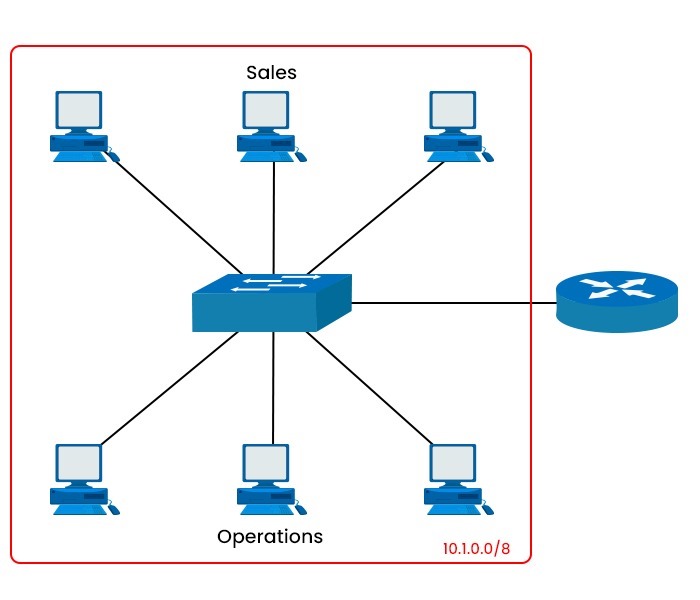
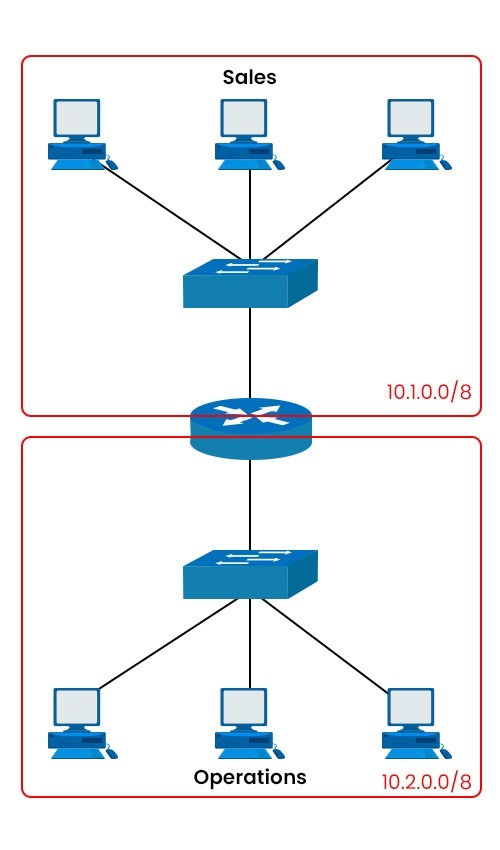
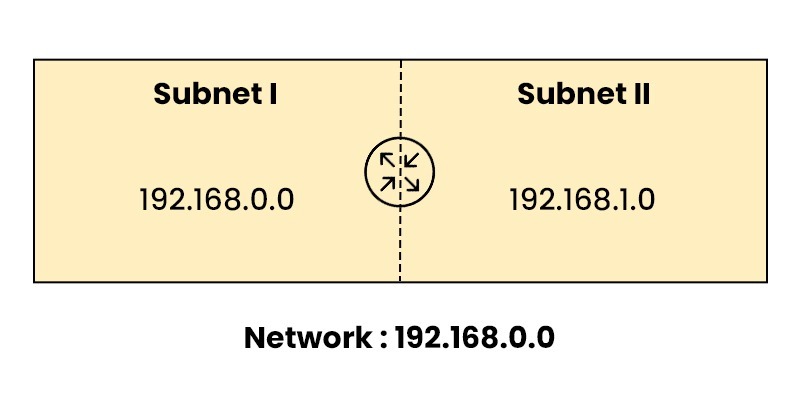
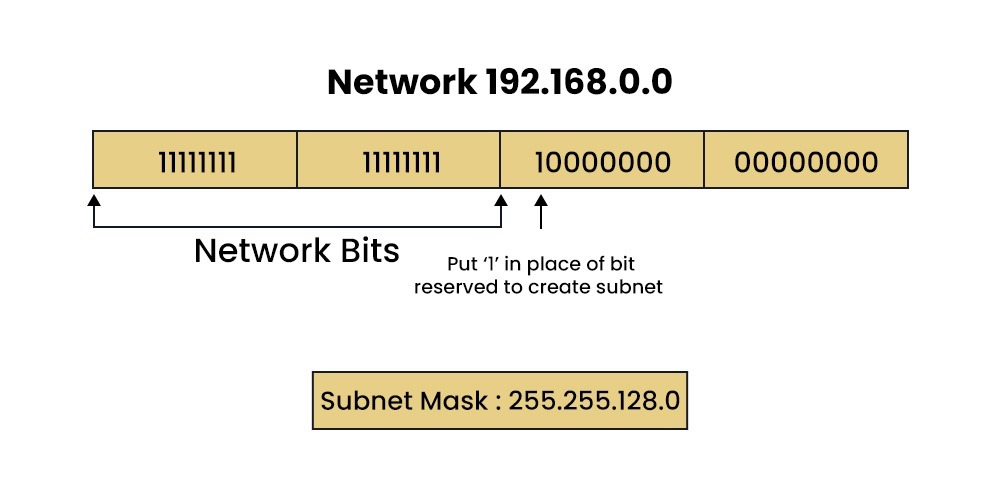
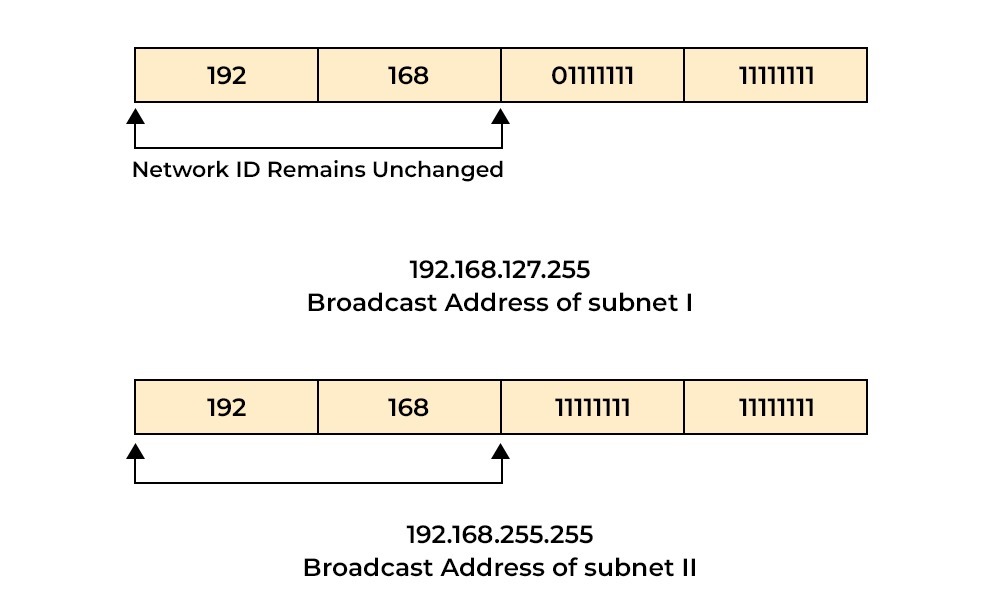
How Does Subnetting Work?
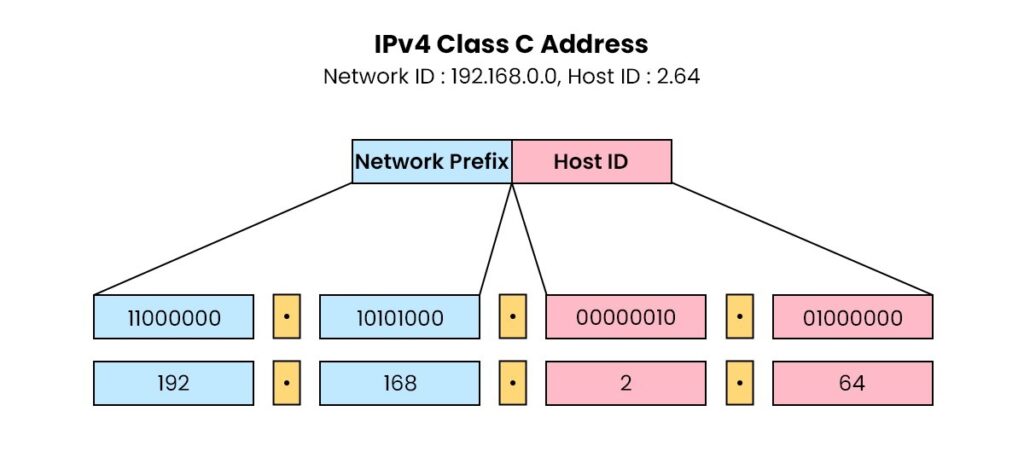
Why is subnetting necessary?
Uses of Subnetting
What is Subnet Mask?
Advantages of Subnetting
Disadvantages of Subnetting
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What do you mean by subnet?
Q2 – What is subnet and why it is used?
Q3 – What are the 2 types of subnet?
Q4 – Is 255.255 255.0 a subnet?
Conclusion







