What is Proxy ARP in Networking?
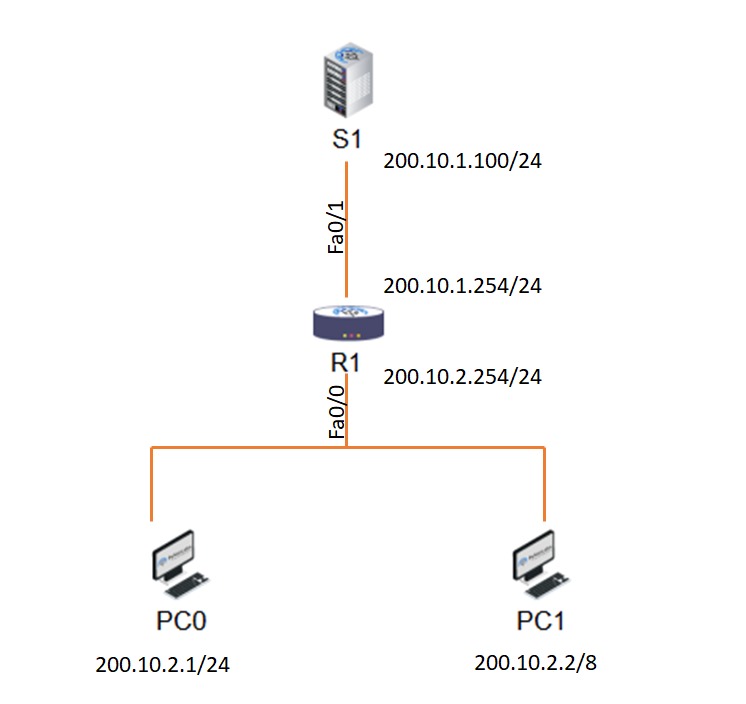
If Someone is interested in networking, they must have heard the term Proxy ARP. But what does it really mean, and how does it work? Proxy ARP is a technique that allows a device to respond to the ARP requests on behalf of another device. This can be useful in situations where the devices want to communicate but are separated from the same network segment, i.e., on different subnets. In this blog, we will explain what Proxy ARP is, its purpose, how it works, along with its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s begin by first understanding what a Proxy ARP is. Proxy ARP or Proxy Address Resolution Protocol is an extended version of ARP in which a device (usually a router) replies to the ARP requests for a given IP address that is not part of the local network. The router acts as a proxy for the destination device to which the host wants to communicate and provides its own MAC address as the reply. The sender then sends the packet to the router’s MAC address, and from there, it will be forwarded to the actual destination. Let’s understand with the help of an example. Suppose there is a device named A that wants to send a packet to another device named B. In order to send a packet, device A needs to know the MAC address of the device B. For this, device A broadcasts an ARP request on the network asking for a specific IP address (10.1.1.1). Device B, if it has the IP address, responds with an ARP reply by informing that it has an IP address (10.1.1.1) and MAC address (0053.FFFF.9999). But as we all know, ARP only functions within the same subnet. If devices A and B are on different subnets, they need to use a router to communicate. Device A sends the packet to its default gateway (the router), which then forwards it to device B’s subnet. In this case, device A does not need to know device B’s MAC address, but only its default gateway’s MAC address. Note: Proxy ARP can help devices on a network reach remote subnets without the need to configure routing or a default gateway. One of the purposes of Proxy ARP is to allow communication between devices that are not part of the same subnet but have incorrect (incorrect subnet masks) or incomplete (missing default gateways) routing information. It can also be used in order to provide connectivity for devices that do not have any routing intelligence or do not support routing protocols. Further, it can be useful in different scenarios. Some of these are: Now that we have a basic understanding of Proxy ARP along with its different purposes. Let’s now discuss how Proxy ARP works. Below, we have explained the functioning of Proxy ARP with the help of a topology. In the above topology, we have two subnets, i.e., 200.10.2.0/24 and 200.10.1.0/24. There is a router in the middle connected to both of these subnets. On the bottom side, we have two hosts (PC0 and PC1); on the top side, we have a server named S1. This is where Proxy ARP comes into action. We now have a detailed knowledge of how it operates. Let’s now discuss its advantages and disadvantages. One of the main advantages of Proxy ARP is that it can easily be added to a single router on a network and doesn’t affect the routing tables of other routers. Below, we have discussed some other advantages of it. Apart from all the advantages that we have discussed, Proxy ARP also has some drawbacks. Let’s understand them in detail. The main disadvantage of Proxy ARP is that it can lead to security and performance issues on the network. Some of these are discussed below. Yes, disabling proxy ARP is necessary for security reasons. One can intercept traffic on your network with proxy ARP enabled. The command for disabling Proxy ARP is no ip proxy-arp. In order to enable IP proxy ARP, one can use the command ‘ip proxy-arp’ in interface configuration mode. With the help of this command, the router will respond to ARP requests on behalf of other hosts. ARP, or Address Resolution Protocol, is mainly used to map network layer addresses to link layer addresses. With the help of ARP, different devices can communicate on the same network. Proxy ARP is when a device responds to ARP requests on behalf of another device. Gratuitous ARP is a broadcast request in order to get information regarding the IP address of the router. In this blog, we have explained how proxy ARP works. It is a technique that allows communication between two devices on different subnets. We also have discussed the purpose, advantages, disadvantages, and functioning of Proxy ARP. We understand that it can be helpful in some situations, but along with that, it also has some drawbacks. Hence, it is always suggested to use it whenever necessary.Introduction
What is Proxy ARP?
Purpose of Proxy ARP
How Does Proxy ARP work?
Advantages of Proxy ARP
Disadvantages of Proxy ARP
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Should I disable proxy ARP?
Q2. How do I enable IP proxy ARP?
Q3. What is ARP used?
Q4. What is the difference between proxy ARP and gratuitous ARP?
Conclusion







