What is Routing Table in Networking?

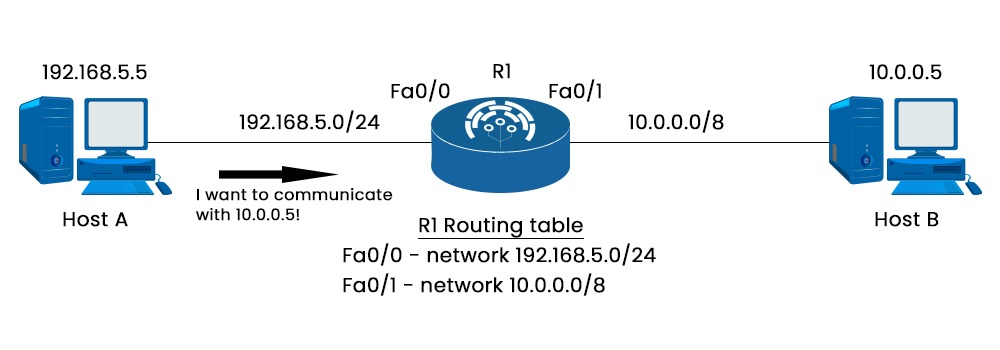
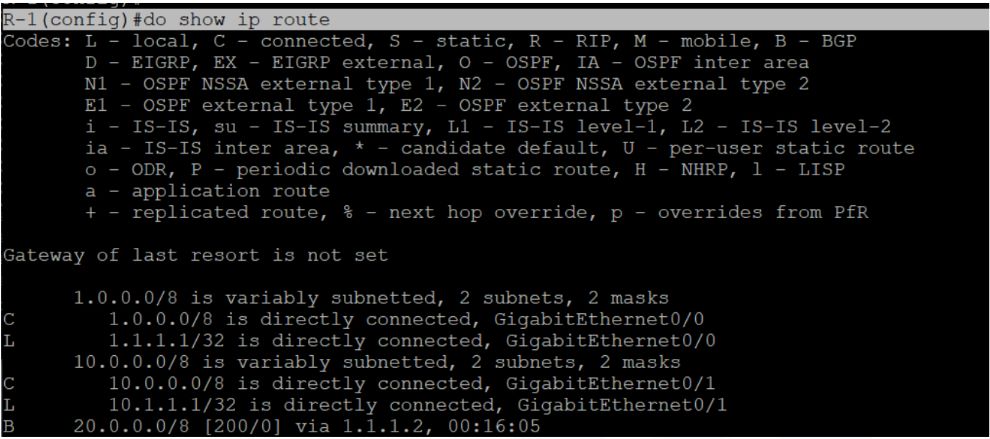
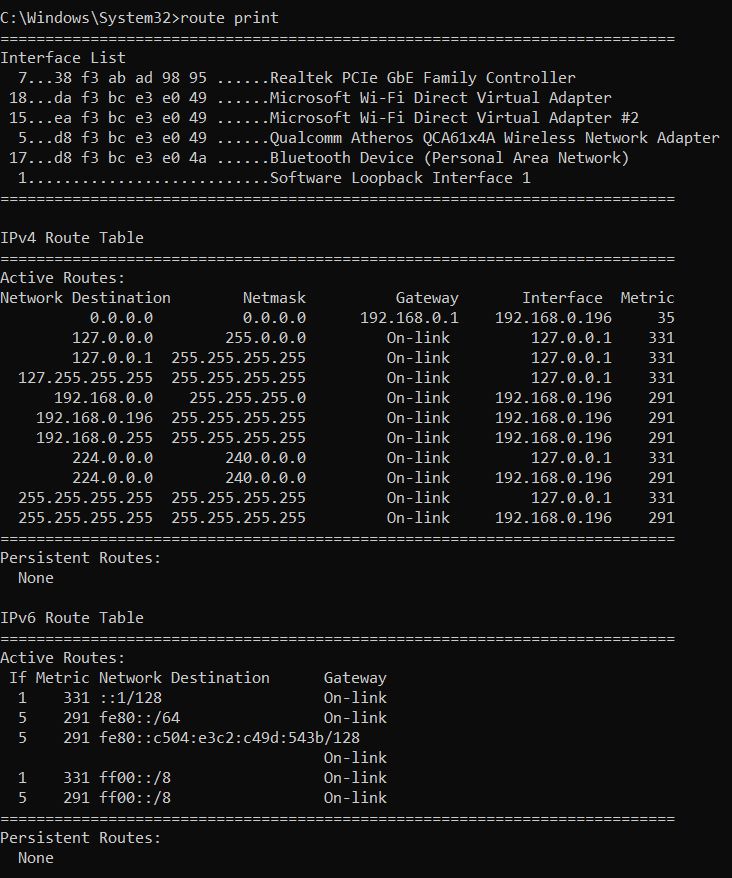
Routing is a fundamental concept in the field of data communication networks. Routing allows the transmission of data from a specific source address to a designated destination address across a network that is interconnected. Routing takes place at the network layer, specifically Layer 3, within the framework of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model. But how does a router know where to send a packet? The answer is: by using a routing table. But what is routing table? The routing table comprises the routing entries, also known as routes, which the router acquires through different means. The router has the capability to acquire routing entries through either static or dynamic means and subsequently manage its own routing table. In this blog, we will focus on the basic functioning of the routing table in networking, its components, and its working. A routing table is a data structure that allows the storage and access of necessary data regarding routes leading to designated IP destinations. The established pathways are afterwards utilized to transmit packets across network links in order to reach the right destination. Routers and switches utilize route tables in order to determine the best route for forwarding data packets within a network. In simple terms, a routing table in networking is like a map that helps routers and switches make decisions about where to send data packets. Each entry in the routing table contains information about the network addresses and the corresponding next-hop or outgoing interface for forwarding the packets. Routing tables in networking are dynamic and can be updated based on changes in the network topology or network conditions. This allows network devices to adapt to changes and find new paths if the previous routes become unavailable or congested. Now that we have an overview of what is routing table let’s move on to understand its working, but before getting into the details of its working, we must first understand the components of routing table entries and routing table routes. A route to a certain network is often represented by an entry in a routing table. A routing table consists of multiple entries, each of which contains the following information: Mainly there are three types of routes in the routing table in networking, these are: Let’s understand the three routes mentioned above in detail. In the case of static routing, all the routes are added manually and won’t change unless one intends to modify them. Advantages of Static Routing Disadvantages of Static Routing In the case of dynamic routing, routes are learned or updated by routing protocols. Routing protocols exchange routing information with other routers and automatically adjust the routing table based on network changes. Advantages Disadvantages Default routing is a method of configuring a router to forward packets to a single destination when there is no specific route for the destination in the routing table. Advantages Disadvantages The routing table in networking contains data that is utilized to determine the optimal path for a packet to traverse in order to reach its final destination. Every packet contains both the source and destination IP addresses. Upon receiving a packet, the network device or router examines the IP packet’s contents and compares it with the entries listed in the routing table. The selection of the most suitable entry for the destination is employed to determine the subsequent routing of the packet. Let’s further understand with the help of an example. The picture above depicts a network consisting of two PCs and a router. Host A is focused on establishing communication with Host B. Host A must utilize the router as the default gateway since it and the receiving host are on separate subnets. The router gets the packet, looks at the IP address, and analyzes its routing database to determine which interface to send it out. The router’s routing table can be shown with the help of the “show ip route” command. C 1.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, GigabitRthernet0/1 The above statement indicates that every packet intended for the 10.0.0.0/8 network will be transmitted through the Fa0/1 interface. And three types of routes that we discussed above are used to populate the routing table. These are static, dynamic, and default routing. It’s important to remember that the routing tables don’t just apply to Cisco devices. The “route print” command can also show you the routing table in your Windows. Below we have provided the image. We hope this explanation was helpful to understand how routing table in networking works. A routing table is a data structure that stores information about the possible destinations for network packets. It contains a list of routes, each with an associated address or prefix, and a next hop or gateway that indicates where to send the packets that match the route. The purpose of a routing table in networking is to help routers and other network devices to forward packets efficiently and correctly to their intended destinations. A routing table in networking has three types of routes: static, dynamic, and default. Routing is the process of directing network traffic from its source to its destination by determining the optimal path based on routing tables, allowing efficient communication between devices in a network. It works by examining the destination IP address of packets and using the routing table to determine the next-hop or outgoing interface for forwarding the packets towards their intended destination. This blog assists you in understanding what is routing table, its components, and its working. A routing table in networking is a vital component of a router that enables it to perform routing efficiently and effectively. A routing table stores information about different routes to network destinations and helps a router determine the best path for a packet based on various criteria. Understanding the significance of routing tables helps us appreciate the underlying mechanisms that enable the vast interconnectedness of modern networks.Introduction
What is Routing Table?
Routing Table Entries
Network Destination Netmask Gateway Interface Metric 101.25.67.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.2 eth3 1 default 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.1 eth0 0 192.25.67.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.3 eth5 10
Routing Table Routes
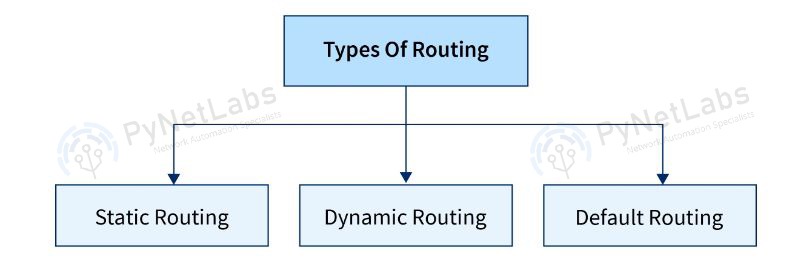
Static Routing
Dynamic Routing
Default Routing
How Does Routing Table Works?
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is the routing table?
Q2 – What is the use of router table?
Q3 – What are the 3 types of routes in routing table?
Q4 – What is routing and how it works?
Conclusion







