What is Ethernet in Computer Networks?
Ethernet is a technology that enables devices to communicate over a wired network. It is widely utilized in area networks (LANs) where computers, printers, scanners, and various other devices are interconnected both with each other and with the internet. Ethernet is also employed in wide area networks (WANs) where multiple LANs are linked over distances. In this blog, we will discuss about the Ethernet in computer networks, its history, its purpose, and how it is different from Internet. Ethernet serves as a standard that defines how data is transmitted and received across a network. It utilizes CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection) protocol, meaning that every device on the network listens for signals before transmitting data and pauses if it detects any collision with the data of another device. Ethernet in Computer Network operates in two layers of the OSI model: the physical layer and the data link layer. Ethernet employs a data unit known as a frame that comprises three parts: header, payload, and trailer. The header carries information such as source and destination address, while the payload contains the transmitted data. Lastly, the trailer holds a checksum to validate the integrity of the data. Ethernet supports several network protocols and technologies that improve its functionality such as Internet Protocol (IP) for addressing and routing packets in interconnected networks, and the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) for reliable, connection-oriented communications between devices. Although wireless networks have replaced Ethernet but wired connections are more secure and less susceptible to interference than wireless networks. This is the main reason why so many organizations continue to use Ethernet. Ethernet was developed in the early 1970s by a team of engineers at Xerox PARC under the supervision of Robert Metcalfe. He was inspired by the ALOHAnet wireless network. When discussing its commercial use, it was introduced in 1980 and standardized by IEEE in 1983 as 802.3. Ethernet has evolved to support various functionalities such as higher speeds, more device connectivity, and longer distance connectivity while maintaining backward compatibility. Below, we have shown the evolution of Ethernet. Now that we have a basic understanding of Ethernet in computer networks, let’s now discuss the purpose of Ethernet. Ethernet serves as an efficient means of transmitting data. This transmission of data takes place between computers or devices within a network. It facilitates data communication through frames that contain source and destination addresses, data payload, and error detection codes. Additionally, Ethernet supports the broadcasting and multicasting of data to recipients. Furthermore, Ethernet is compatible with different types of data and protocols like IP (Internet Protocol), TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), UDP (User Datagram Protocol), HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), FTP (File Transfer Protocol), SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), and others. This technology also ensures network scalability and flexibility by supporting topologies such as bus, star, ring, tree, mesh, and hybrid configurations. When we discuss the application of Ethernet in Computer Network, there are many. Some of these are file sharing, web browsing, email services, video conferencing, online gaming experiences, streaming media platforms, cloud computing services, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Let’s discuss the different types of Ethernet in detail. Different types of Ethernets are utilized to connect devices and allow data transfer. Below, we have discussed the most common types of Ethernet. This particular type of Ethernet network employs cables known as twisted pair or CAT5. It usually allows data transfer at a speed of around 100 Mbps. Fast Ethernet utilizes both fiber optic and twisted pair cables to enable communication. It can be further categorized into three types. These are: Gigabit Ethernet is an upgraded version of Fast Ethernet and is more prevalent in today’s networks. It enables data transfer at a speed of 1000 Mbps or 1 Gbps. Similar to Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet also utilizes fiber optic and twisted pair cables for communication. Advanced cables like CAT5e or CAT6 are often used to transfer data at speeds up to 10 Gbps. 10 Gigabit Ethernet is an advancement from Gigabit Ethernet. It is mostly used in high-performance networks such as data centers or backbone networks. It allows data transfer at a blistering speed of 10 Gbps or 10,000 Mbps. It relies on fiber optic cables such as single-mode or multimode fibers for communication purposes. It can be further classified into four types. These are: A switch ethernet is a device used to connect devices like computers, printers, and servers using Ethernet cables. Its main function is to filter data packets based on the destination device’s MAC address. It supports data transfer at 10Mbps to 100Mbps for fast Ethernet and 1000Mbps to 10Gbps for the latest Internet. Let’s now understand the functioning of Ethernet in computer network. Below, we have discussed the functioning of Ethernet in computer network. This is how Ethernet in Computer Networks works. Here are the different standards of Ethernet: Here are the key elements of Ethernet Connection – Some of the advantages of Ethernet are – Some disadvantages associated with Ethernet are – Many students get confused between the Internet and Ethernet. Let’s compare them. Below, we have explained the difference between the two in a tabular form based on different factors. Ethernet is used to help devices communicate with each other within a network. Ethernet Stands for Ethernet Local Area Network Standard. It supports different data transfer rates, some of which are 10Mbps, 100Mbps, 1000Mbps, or up to 10 Gbps. An Ethernet cable is a type of network cable that connects devices such as computers, routers, and switches. It allows data transmission over a wired network. Standard Ethernet is a LAN technology that uses 10Base5 coaxial cables and operates at 10 Mbps. It provides service up to the data link layer. Ethernet is a computer networking technology that allows data transmission between devices in a network using cables or wireless signals. Over time, Ethernet has evolved to achieve speeds and capacities in order to meet application requirements and adapt to various environments. In this blog, we have explained the Ethernet’s history, types, and functioning.Introduction
What is Ethernet in Computer Networks?
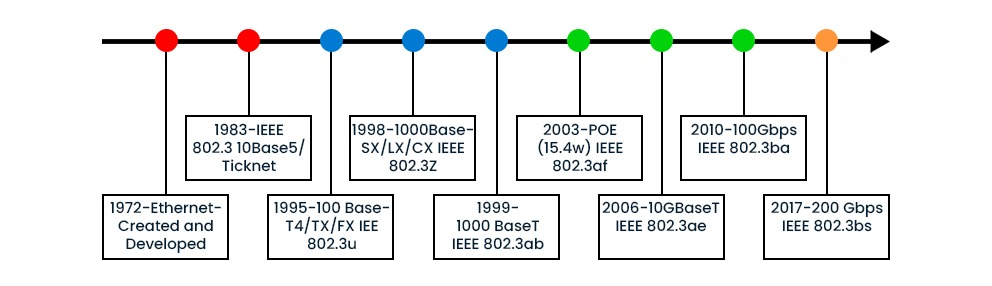
History of Ethernet
Why use Ethernet in Computer Network?
Types of Ethernet in Computer Networks
Fast Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet
10 Gigabit Ethernet
Switched Ethernet
How Does Ethernet Work?
Ethernet Standards
Key Elements of Ethernet Connection
Advantages of Ethernet in Computer Network
Disadvantages of Ethernet in Computer Network
Difference Between Internet and Ethernet
Factors Internet Ethernet Scope Global Local Medium Various, such as fiber optic, satellite, wireless, etc. Cables, such as twisted pair, coaxial, fiber optic, etc. Speed Depends on the bandwidth and latency of the connection Depends on the type and quality of the cable and the network card Security Less secure, as data can be intercepted or modified by hackers or malicious software More secure, as data is transmitted within a closed network and can be encrypted or authenticated Cost Higher, as it requires paying for an internet service provider (ISP) and a router Lower, as it only requires buying cables and switches Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is Ethernet used for?
Q2. What is the full form of Ethernet?
Q3. What is the Ethernet cable?
Q4. What is standard Ethernet?
Conclusion







