TCP vs UDP – What’s the Difference?
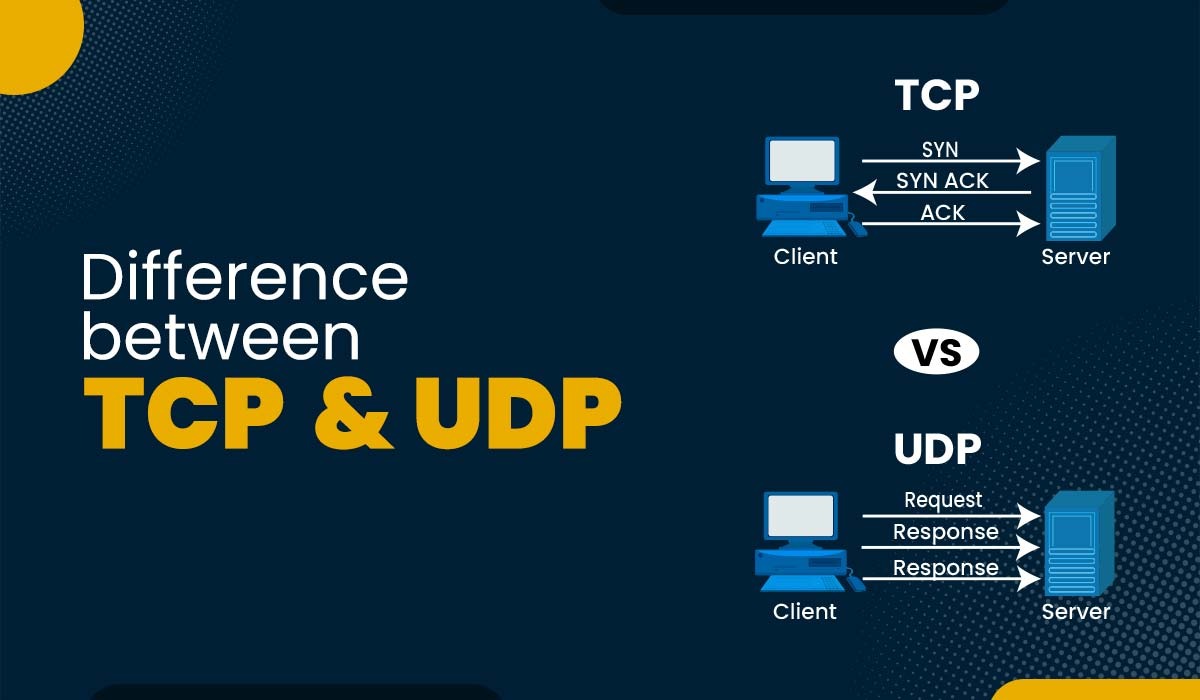
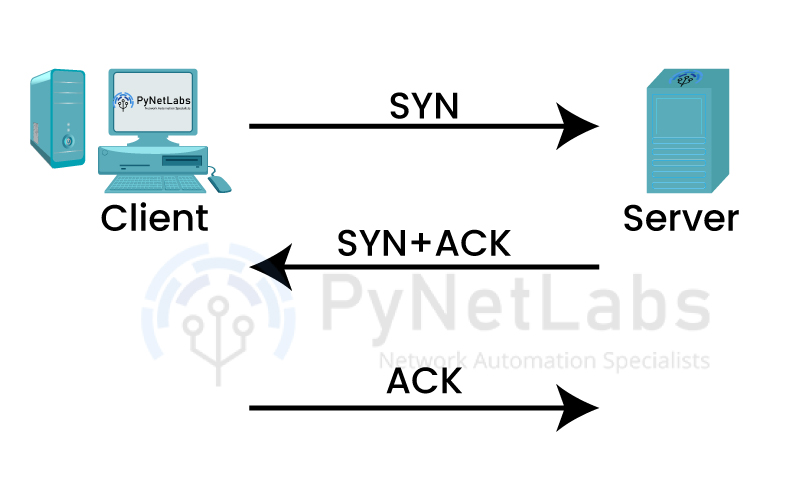
In the world of networking and communication protocols, two fundamental players stand out: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol). TCP vs UDP is a timeless comparison that holds significant importance in understanding how data travels across the internet. These two protocols form the backbone of internet communication, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. We will begin by diving into the basics of TCP and UDP, explaining how they function and what sets them apart. Through this article, you will gain insights into their individual strengths and weaknesses. So, without further ado, let’s understand the difference between TCP and UDP. Here are the top difference between TCP and UDP Protocol – In order to compare TCP vs UDP better, we will first take a look at each protocol and then discuss the difference between TCP and UDP in detail. TCP, short for Transmission Control Protocol, is a connection-oriented protocol that ensures reliable and ordered delivery of data packets between devices. It provides error detection, flow control, and congestion control mechanisms to guarantee the successful transmission of data. TCP establishes a connection between a sender and a receiver before transferring data, ensuring that packets arrive in the correct order and without errors. It retransmits lost or corrupted packets and acknowledges the receipt of data, making it highly reliable. Here are some features of TCP – TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is used in various applications and scenarios where reliable and ordered data transmission is essential. Here are some common use cases for TCP: User Datagram Protocol is a transport layer protocol used to transmit data. UDP, unlike TCP, has less overhead for establishing, maintaining, or terminating a connection; hence, it is faster than TCP. In UDP, the data is continuously sent to the recipient irrespective of whether it was received or not. UDP can be considered a lightweight protocol because of its lesser responsibilities while delivering data. It is unreliable because there is no acknowledgment after receiving the data successfully, which means the sender won’t know if the data was lost during communication or received by the recipient. Some of the features of UDP are – Here are a few disadvantages of using UDP (User Datagram Protocol): Now, let’s understand some key difference between TCP and UDP Protocols – TCP is called a connection-oriented protocol because it requires a logical connection to be established between the two devices to exchange the data. This connection is built by doing a three-way handshake. This process can be understood with the example of a telephone call where both the users have to get connected first over a session before they can exchange the messages or ideas. On the other hand, we have UDP, which is connection-less as it doesn’t go through any process and can directly send the data to the recipient. TCP is a reliable protocol as it provides the reliability of the delivery of packets to the receiver as a connection is built before data transmission. On the other hand, with UDP, we don’t get any surety whether the data was delivered or not; hence, we call it unreliable. TCP guarantees data delivery in the same sequence as the sender sent it. If the segments are received in the wrong order, TCP reorders them. In UDP, there is no such guarantee of the order of segments when they reach the destination. TCP is considered a heavy-weight protocol because of all the responsibilities it performs. The connection establishment requires the exchange of 3 packets before any data can be exchanged. TCP also handles reliability and congestion and is a heavy-weight protocol with a header size of 20 bytes. UDP is lightweight as there are no such needs for connection establishment. UDP doesn’t handle the ordering, reliability, etc., while data delivery; hence it ends up being a lightweight protocol with a header size of 8 bytes. The speed of TCP is slower than the UDP as in UDP; there’s no error recovery mechanism. It is a best-effort protocol which simply means that it will not guarantee the delivery of data. TCP works with flow control, ensuring that many packets are not transmitted over the connection to the receiver, whereas the UDP doesn’t follow a flow control mechanism. These are the main difference between TCP and UDP, explained in detail. TCP ensures reliable, ordered data delivery by establishing a connection, performing error correction, and retransmitting lost packets. UDP, on the other hand, is a connectionless protocol that prioritizes speed and low overhead but does not guarantee reliable delivery or perform error correction. TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is a suite of communication protocols used for transmitting data over networks. TCP is a reliable, connection-oriented protocol that ensures ordered and error-free data delivery, while UDP is a connectionless protocol that offers faster, lightweight communication but does not provide reliability guarantees. TCP is used for applications that require reliable and ordered data delivery, such as web browsing and file transfer, while UDP is used for real-time applications that prioritize speed, such as video streaming and online gaming. TCP is generally used more than UDP due to its reliability and error correction mechanisms, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. However, UDP is favoured in real-time applications where speed is crucial and minor data loss is acceptable, such as video streaming and online gaming. Now we have discussed TCP vs UDP in detail. In conclusion, TCP and UDP are two essential protocols used for data transmission in computer networks. TCP ensures reliable and ordered delivery of data packets, making it suitable for applications that require data integrity. UDP, on the other hand, provides faster and lightweight communication, prioritizing speed over reliability. Understanding the difference between TCP and UDP allows you to select the appropriate protocol for different use cases, optimizing performance and reliability based on your specific needs. TCP and UDP are a part of advanced network training, if you want to learn more about these protocols, you can learn it with CCNP ENCOR Training by PyNet Labs. If you still have some doubts about the topic TCP vs UDP then, here is the video you must consider watching –Difference between TCP and UDP in Tabular Form
Parameters TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) UDP (User Datagram Protocol) Connection Connection-oriented protocol Connectionless protocol Reliability Reliable delivery of data with error detection and correction Unreliable delivery of data without error detection or correction Ordering Guarantees in-order delivery of data No guarantee of in-order delivery of data Congestion Includes congestion control mechanisms No built-in congestion control mechanisms Packet Structure Contains header and payload information Contains minimal header information Use Cases Suitable for applications requiring data integrity and accuracy Suitable for applications that prioritize speed and efficiency What is TCP?
Features of TCP
Advantages of TCP
Disadvantages of TCP
Where TCP is used?
What is UDP?
Features of UDP
Advantages of UDP
Disadvantages of UDP
Where UDP is used?
TCP vs UDP
1. Connection
2. Reliability
3. Ordering of Messages
4. Weight
5. Speed
6. Flow-control
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is the difference between TCP and UDP?
Q2 – What is TCP IP and UDP protocol?
Q3 – Why is TCP and UDP used?
Q4 – Is TCP or UDP used more?
Conclusion







