FTP – File Transfer Protocol
File transfer is one of the most common and essential tasks in computer networks. Whether downloading a file from a website, uploading a file to a cloud service, or sending an email attachment, file transfer is involved in some way. But have you ever wondered how file transfer works and what are the protocols and mechanisms via which file transfer takes place over the internet? In this blog, we will explain the most widely used file transfer protocol, i.e., FTP in computer networks. FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol. The TCP/IP network allows the transfer of files between two computers through a widely accepted network protocol. FTP came in the early 1970s and has been updated since then. The current version of FTP is defined in RFC 959. FTP is widely used for transferring web pages, software updates, and other data over the Internet. It can also be used for downloading files to computer from other servers. Even while moving data between systems is relatively easy and uncomplicated, there are situations when it can go wrong. For instance, These issues are solved by the FTP protocol by creating two connections between hosts. Data transfer takes place over one connection, and the control connection occurs over a different connection. FTP in computer networks operates on a client-server model. The client requests to access the file stored on the server, and the server responds to the client’s request and sends the respective file. The client and the server communicate using two types of connections. These are – The client and server communicate to send and receive commands through the control connection. FTP uses a control connection to transmit information such as user name, password, remote directory change commands, file retrieval, storage instructions, etc. It is initiated via port 21. The data connection allows the transfer of file data between the client and server. It is initiated via port 20. FTP works via two different modes. These are: A typical FTP protocol works as: FTP is designed to transfer files over networks with different operating systems, file systems, or architectures. Users using FTP in computer networks are able to access and alter files located on distant computers without worrying about the specifics of how the data are being moved or stored. FTP Protocol is used for a variety of purposes, some of these are: There are several varieties of file transfer protocols available. Some of these are: SFTP stands for The SSH File Transfer Protocol. SFTP is a layer above SSH that provides all the security and authentication capabilities of SSH. This protocol is rapidly replacing FTP/S and has already overtaken legacy FTP. It provides the full range of features available via these protocols with high reliability and higher levels of security. TFTP is a simplified version of FTP that uses UDP instead of TCP for data transfer. Not all programs can use TCP because of its complexity and the features they don’t require. Regarding client-server interactions, TFTP’s simple structure and low cost make it suitable. TFTP is limited to File Transfer only and does not permit authentications. TFTP is mainly used for bootstrapping network devices or transferring small files. File Transfer Protocol Secure (FTPS) is the secured variant of FTP, similar to Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. Transport Layer Security (TLS) and secure socket layer (SSL) safeguard these protocols. Using FTPS, companies may establish encrypted connections with their clients, partners, and end-users. FTPS can encrypt either the control connection only (explicit FTPS) or both the control and data connections (implicit FTPS). Hypertext Transfer Protocol, or HTTP, is a popular way to exchange data in the corporate world. This protocol is very easy to implement for server-to-client and client-to-client file transfers. The HTTP protocol is vulnerable to firewall-related challenges. However, compared to FTP, it is fundamentally insecure and lacks the ability to ensure data security and regulatory compliance. This protocol is implemented in situations where security concerns are not a factor. Here are the FTP Commands – These are the commands of File Transfer Protocol. An FTP client is a software that allows sharing of files by creating a connection between both the host computer and the remote server through the server’s domain, IP address, username and password. It enables the transmission of data and files in both directions between two computers that have a TCP network or Internet connection. It works on a client/server model where the host computer acts as the client and the remote FTP server acts as the central server. Below are some of the following FTP clients: There are three common ways to use FTP: FTP protocol has several advantages as a file transfer protocol, such as: FTP can transfer large files The feature of FTP protocol to transmit a vast number of files, regardless of their size, is its most useful feature. When you need to transfer terabytes of data all at once, FTP can manage the task both effortlessly and quickly, avoiding inefficiencies and lost time in the process. FTP can transfer multiple directories at once Enhance your workflow efficiency by transmitting multiple directories simultaneously without the need for frequent monitoring of the transfer progress. Additionally, you can transmit individual files or directories as needed. It is possible to continue working while the transfers occur in the background. You have control over your transfers FTP in Computer networks allow the user to resume a disrupted transfer in case of a lost connection without initiating the process. Certain FTP clients offer the capability to schedule data transfers, allowing users to determine the degree of automation they desire. You can use FTP for WordPress management FTP is also essential for working with WordPress sites. Because it establishes a direct link to the site’s files, you can perform things like installing and deactivating WordPress plugins and themes by hand or make modifications to the core WordPress files. Likewise, FTP may be used to identify and fix typical website problems, including incompatibility with external resources, conflicts between themes, and internal server failures. There are several disadvantages of using FTP (File Transfer Protocol). Here are some of the key drawbacks: The File Transfer Protocol was never meant to be a secure channel for sensitive data. That’s why we don’t encrypt anything. It is not necessary for a hacker to decipher encryption in order to see or modify data during an FTP transmission. If the provider’s system is hacked, the data might be intercepted and used even if you utilize FTP cloud storage. Since FTP data moves at a slower pace, it is more vulnerable to attacks such as spoofing, sniffer, and brute force. Hackers can examine an FTP transmission with the help of a port scan. Clear-text passwords, which are not encrypted, are one of FTP’s most serious security flaws. With FTP, you may send data over the Internet. The use of FTP requires access to the Internet. When a file is downloaded, it is sent from a server to the receiving device, but when it is uploaded, it is sent from the receiving device to the server. For transport purposes, FTP only relies on the usage of the transmission control protocol (TCP) rather than the user datagram protocol (UDP). File Transfer Protocol (FTP) allows data exchange between computers connected through a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) network, such as the Internet. The establishment of an FTP connection between two machines in Linux can be achieved through the utilization of the command “ftp.” FTP in computer networks is a prominent protocol for transferring files over a network. FTP operates on the client-server model and uses two separate channels for communication: a control channel and a data channel. In this blog, we have covered the basic definition of FTP, its working, the purpose of using FTP, different types of FTP, its advantages, and challenges. We hope you liked it. FTP – File Transfer Protocol is an integral part of CCNA Course. So, if you want to learn more, you can also check out the CCNA Course. Do let us know about your experience in the comment box.Introduction
What is FTP Protocol (File Transfer Protocol)?
How FTP Protocol works?
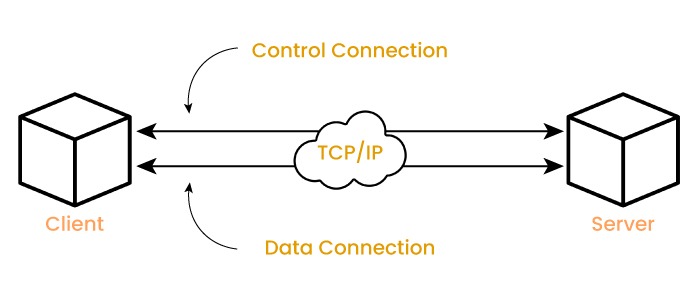
Control Connection
Data Connection
Purpose of FTP in computer networks
Types of FTP Protocol
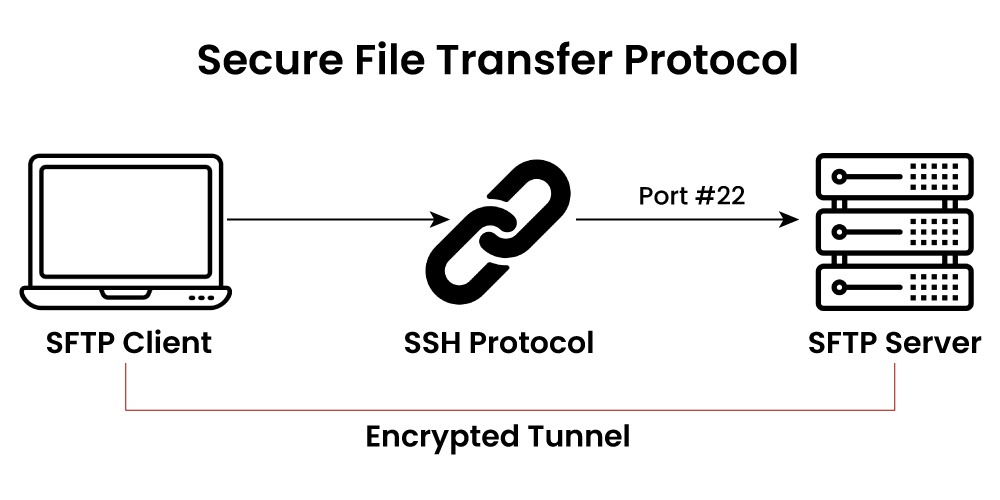
Secure FTP (SFTP)
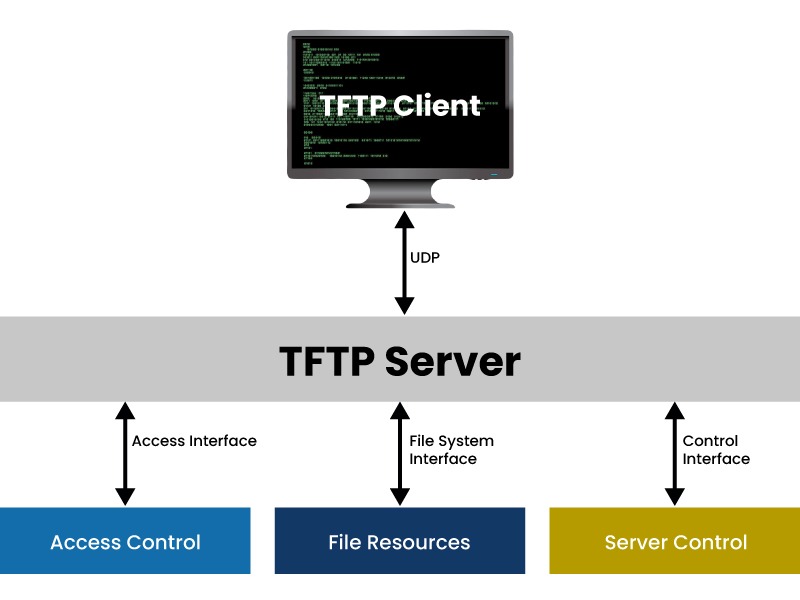
Trivial FTP (TFTP)
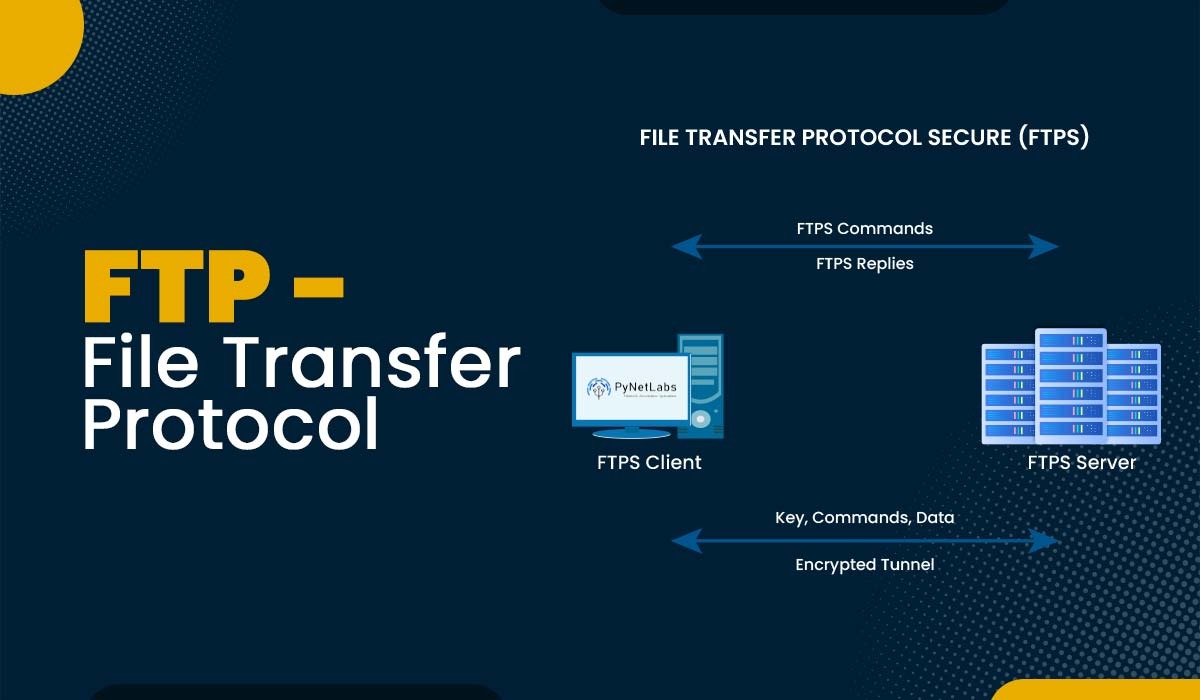
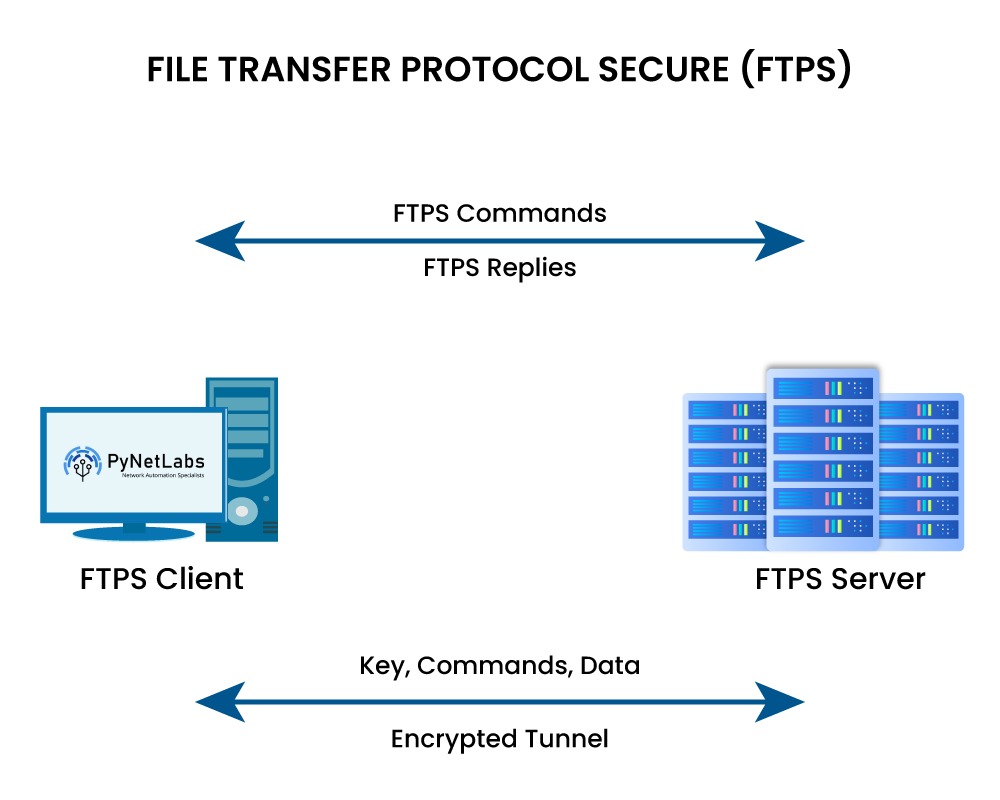
File Transfer Protocol Secure (FTPS)
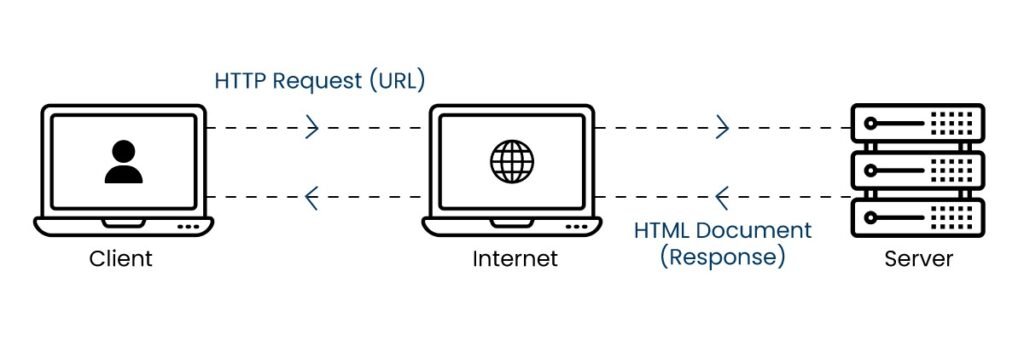
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
File Transfer Protocol Commands
FTP Commands Description ! It allows shifting between operating systems and FTP. ? It allows to print information about FTP commands. append It allows joining two files together. ascii It allows converting the file share mode to ASCII and is the default mode for many FTP programs. binary It fixes file share mode to binary. bell This command is used to alert by bell sound when any command is executed. bye It allows to exit and terminate the FTP session. cd It allows modification of the remote system’s directory. close It allows terminating FTP connections to remote systems. dir It allows to receive a list of contents in a remote directory. delete It allows deleting a file from the currently open remote directory. debug It allows activating and turning off debugging mode, and this command does not require a remote system connection. disconnect It allows terminating the FTP session. FTP It allows access to the FTP interpreter. get It allows to creation of duplicate data (one file) from the server to the client device. hash It allows a client to request a cryptographic hash of a file from the server-side FTP process. help It allows local help information to be presented. This command does not need a remote system connection. lcd It allows changes to be made to directories on your local system. literal It shares the argument with the remote system. ls It allows to present a list of names of files in the current remote directory. mdelete It allows deleting most files at once. mdir It allows listing the contents of multiple remote directories. mget It allows duplicating multiple data files from a remote computer to a local computer. mkdir It allows the creation of a new directory within an existing remote directory. mls This command shows a list of file names in multiple server directories. mput It allows multiple files to be duplicated from a user device to a server device. open This command allows the creation of a link with another computer system. put This command allows to duplication of a file from a user device to a server device. pwd It allows finding out the path name of the local directory of the remote system. quit It allows the FTP session to be terminated (like bye). quote It shares the argument with the remote system. recv It allows the recovery of files from a remote machine. remotehelp It allows for presenting remote system information. rename This command allows changing the name of a system file. rmdir It allows removing a directory from a local remote directory. send This command allows sending files. status This command allows to show the current state of the system. type It allows specifying the file share type. user This command shares the details of the new user. verbose It allows to turn verbose on/off. FTP Clients
How to use File Transfer Protocol
Advantages of File Transfer Protocol
Disadvantages of FTP Protocol
Security Challenges of FTP
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – How Does FTP Work?
Q2 – Does FTP Use TCP or UDP?
Q3 – What is FTP used for?
Q4 – What is FTP in Linux?
Conclusion







