Difference between Broadcast and Multicast

One of the fundamental concepts in computer networking is transmission, which is the process of sending data from one device to another over a network. Transmission can be classified into different types based on how the data is addressed and delivered to the intended recipients. The main difference between broadcast and multicast is that during the broadcast, the packet is sent to all of the hosts that are connected to the network, but during the multicast, the packet is sent only to the hosts that are supposed to receive it as the intended receivers. In this blog post, we will talk about the two different transmission techniques, namely broadcasting, and multicasting, and also discuss multicast vs broadcast in detail. Broadcast and multicast are two methods of transmitting data over a network. Below we have outlined some basic differences between the two. These are the basic difference between Broadcast and Multicast, we will take a closer look at these differences later on. Let’s first understand broadcast and multicast in detail. The term “broadcast” refers to a data transmission method that allows all network hosts to use the same channel for exchanging information. When one host sends a packet across a network via broadcast, it is received by every host in the network. When a host sends data across a network, it includes the destination host’s address in the packet’s address field. At this point, all the other hosts on the network have received the packet because it was broadcast. Each host verifies the packet’s address after receiving it. The destination host processes the packet if it has its address. The packet is dropped otherwise. For example, when you turn on your computer and connect to a network, it may send a broadcast packet to request an IP address from a server. This way, the server can assign an IP address to your computer without knowing its specific address. One of the common examples of broadcast is wireless networks. To understand the difference between Broadcast and Multicast, one should take a look at their advantages and disadvantages. Here are some advantages of broadcast – Here are some disadvantages of broadcast – Multicasting refers to a transmission technique wherein multiple copies of a single packet are distributed to a specific group of hosts within a network who have expressed interest in receiving the said packet. It is a one-to-many communication method. The multicast transmission sends data to only those devices that are interested in receiving it. As you can see in the above figure how network routers send and receive a packet via different interfaces. Router R1 sends the packet that is received from the source via interfaces 1 and 2. Similarly, router R2 sends the packet received from R1 to the interested members (in this case, both members are interested). Furthermore, R3 sends the received packet from R1 to the interested member (in this case, only one member is interested). Multicast is useful when sending the same data to many devices, but not everyone, such as streaming video or audio. For example, when you watch a live video on YouTube or Netflix, you may receive a multicast packet from a server that contains the video data. This way, the server can send the same data to multiple viewers without duplicating it. Some advantages of Multicast are – Some of the disadvantages of multicast are – Now, let’s move on to the difference between Broadcast and Multicast in Detail. Below we have explained the basic difference between the two – This was the detailed comparison of Broadcast vs Multicast. Now, you can easily decide which one is right for you. When a packet is sent to all the devices that are connected to the network is known as a broadcast. Whereas when a packet is sent to a specific device (those who are interested) that is connected to a network is known as multicast. In the case of broadcast, the packets are sent to all the devices, which can further result in clogging or overloading of the network. Whereas multicast only sends data to devices that needs the data, improving privacy, speed, etc. Video conferencing applications are one of the examples of multicast. Unicast and multicast are two different methods of transmitting data over a network. Unicast sends data from one source to one destination, while multicast sends data from one source to multiple destinations. Which one is better depends on the type and purpose of the transmitted data. While both broadcast and multicast are used to reach a big audience, still there is a key difference between the broadcast and multicast. When communicating with a specific group of people, multicast is preferred, whereas broadcast is more often utilized for reaching a large audience.Introduction
Broadcast vs Multicast
Factors Broadcast Multicast Basic One-to-all One-to-many Transmission The sender transmits data to all receivers in the network, regardless of their interest. The sender transmits data to a group of receivers who have joined the multicast group. Management No group management is required. Group management protocols are needed to join and leave multicast groups. Bandwidth Wastes bandwidth as data is sent to uninterested receivers. Saves bandwidth as data is sent only to interested receivers. Traffic Generates more network traffic as data is replicated at every router. Generates less network traffic as data is replicated only at branching points. Process Simple and easy to implement. Complex and requires more processing power. Security Less secure as data is exposed to all receivers. More secure as data is delivered only to authorized receivers. What is Broadcast?
Advantages of Broadcast
Disadvantages of Broadcast
What is Multicast?
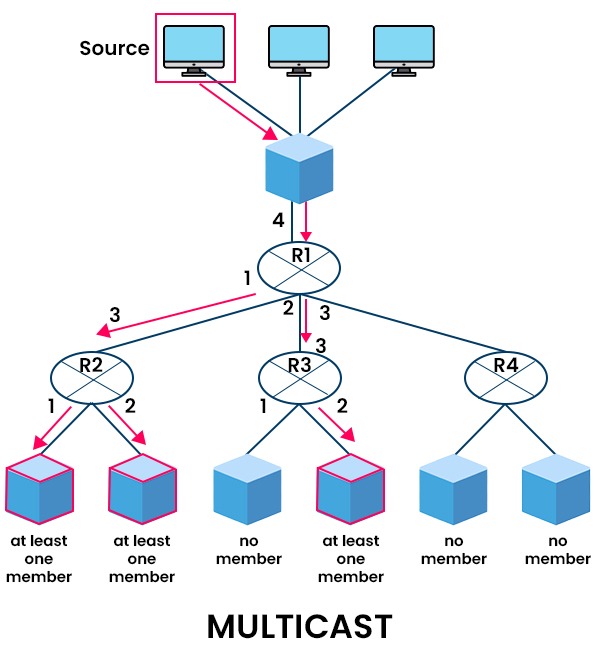
Advantages of Multicast
Disadvantages of Multicast
Difference between Broadcast and Multicast
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is the difference between broadcast and multicast IP?
Q2 – Why multicast is better than broadcast?
Q3 – What is an example of multicast?
Q4 – Which is better unicast or multicast?
Conclusion







