What is Bus Topology in Computer Network?

Computer networks play a vital role in allowing communication, data sharing, and resource utilization across devices. Within these networks, network topologies define how devices are interconnected. Various types of network topologies exist, such as point-to-point, mesh, star, ring, tree, and hybrid. Each topology has its own advantages and disadvantages. In this blog post, we will specifically focus on the bus topology – one of the oldest network topologies. We will look into its purpose and provide examples to explain its functioning principles while discussing both its advantages and disadvantages. All these network topologies are very important for network engineers to connect their networks. That is why, these topologies are covered in the very beginning of your networking journey, i.e., CCNA Training. Let’s move on and understand what bus topology really is. Bus topology refers to a network arrangement where all devices are connected to a cable known as the “bus,” which serves as the medium for data transmission. Each device directly connects to the bus cable, forming a structure. Consequently, any data transmitted by one device becomes accessible to all devices that are part of the network. To ensure transmission without signal interference or disruption, the bus cable incorporates two endpoints called “terminators.” These terminators prevent signals from bouncing back within the system. Note: The bus is mainly a passive type of network. This means that it does not amplify signals. It simply transmits them across devices. Now that we have a basic understanding of Bus topology. Let’s discuss its purpose in networking. Bus topology is commonly employed in simple networks that have relatively low traffic and require minimal security. Below, we have discussed some of the purposes of using it. Let’s now look at some bus topology examples in networking. One of the most common examples of bus topology in computer networks is Ethernet. When we talk about Ethernet, it is simply a standard protocol that defines how data is transmitted or received in a network. It makes use of coaxial or twisted pair cables to connect devices in a bus topology. As we all know, every device has a unique MAC address that helps identify it on the network. When a device wants to send data to another device, it simply broadcasts the data by adding the destination MAC address on the bus. After that, all the devices that are part of the bus topology receive the data, but the one who has the associated MAC address accepts it. Another example of bus topology is the CAN (Controller Area Network) bus used in vehicles. With the help of the CAN bus, various sensors, actuators, and controllers communicate without a central computer. Now, if we talk about how it works, it’s simple. Each device has an identifier that assists in determining its priority on the network. In order to send data, the device first checks if the bus is free and then sends its identifier with the data. In cases where two devices try to transmit the data at the same time, the one with the highest priority wins. We have explained some bus topology examples. Let’s now understand the functioning of Bus topology before getting into its advantages. In a bus topology, data is sent as packets or frames along a coaxial or twisted-pair cable. These packets or frames contain a header with information like source and destination addresses as well as the type of data being transmitted. Below, we have explained its working in detail. There are several advantages associated with using bus topology: Apart from the advantages that we just discussed, bus topology also has some disadvantages. These are: Three advantages of bus topology are: There are different network topologies, each having some advantages and disadvantages. The five network topologies are: An example of a bus network is Ethernet. Bus topology is simple and economical by which one can make devices to communicate in a computer network. In this blog, we have explained what it is, real-life examples for better understanding, its purpose, working along with its advantages and disadvantages. Any suggestions or queries are most welcome. Please share it in the comment section below.Introduction
What is Bus Topology in Computer Networks?
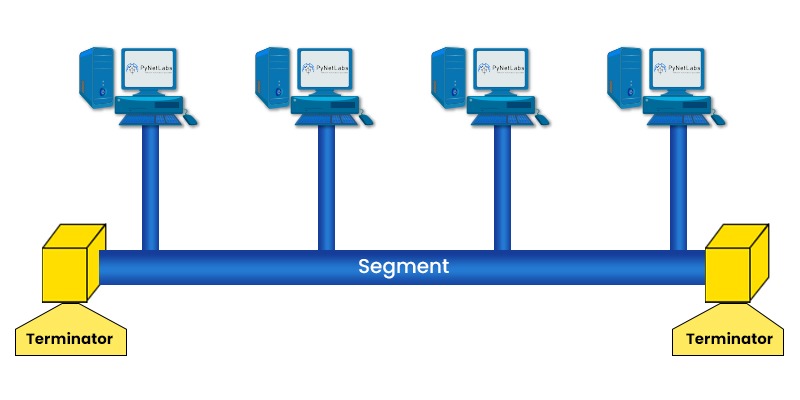
Purpose of Bus Topology in Networking
Bus Topology Examples
How Does Bus Topology Work?
Advantages of Bus Topology in Networking
Disadvantages of Bus Topology is Networking
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are 3 advantages of bus topology?
Q2. What are the 5 network topologies?
Q3. What is bus ring and star topology?
Q4. What is an example of a bus network?
Conclusion







