Transmission Media in Computer Network and Its Types

The modern global environment is constantly evolving. Data Communication and networking technologies have revolutionized many aspects of modern life. They now depend on computer networks for almost everything. Computers and other types of telecommunication devices may represent data as signals. They are transferred as electromagnetic signals from one device to another. Electromagnetic signals may travel from one sender to another through a vacuum, air, or other transmission media. This blog aims to provide you with an overview of the transmission media in computer networks and types of transmission media. Before moving any further, you should take a look at our CCNA Course. Transmission Media is a method of establishing a communication medium to transmit and receive information in the form of electromagnetic signal waves. Since different physical components operate it, it is put under the physical layer while being worked on by physical elements from the physical layer. A LAN, or local area network, is the physical setup where a transmitter and receiver communicate utilizing a Transmission medium. Copper-based or fiber-based transmission media are used to carry either electric or optical signals. The transmission medium is also known as a communication channel. Media Terminology Now, that we have a good knowledge of Transmission Media, it is time to indulge ourselves to the types of Transmission Media. Depending on the nature and quality of the transmission, the following types of transmission media may be broken down into two categories. This type of media uses cables to transmit signals across the network. Wired media, often known as guided media, is a form of transmission medium. It has a finite range in the communication system and is also known as a Bounded transmission media. With the use of physical wiring connections, the qualities of the transmission signals may be concentrated and contained inside a specific, constrained channel. Transmission speeds are one of the most striking features of this kind of communication. The copper media uses cables that use copper conductors inside the cable that is used to transmit electrical signals. The core is made up of copper conductors. Its purpose is the signal transmission. To prevent the copper conductor from overheating, an insulator is utilized. A metal conductor is braided around the insulator. It aids in blocking out any unwanted noise or allowing for any unwanted cross-talk between electrical signals. The setup is entirely covered in a protective plastic layer. Its Features – 2. Twisted pair This cable has eight insulated wires. These are paired in groups of 2 and are twisted together based on a color code. The twisting is done to decrease interference caused by the adjacent wires. One wire in the pair may send signals to the receiver, while the other serves as a ground reference. The twisted pair is further divided into two parts, i.e., shielded and unshielded. a. Shielded twisted pair These twisted pair cables are covered in a braided shield which acts as a shield from outside interference. b. Unshielded twisted pair These twisted pair cables do not have a braided shield. The 4 pairs are simply covered in a plastic insulator for safety. Color Codes – Straight through cable You might also like – Hub vs Switch vs Router Crossover cable In addition, optical fiber, a physical medium, has also become the standard for long-distance communications. Optical fibers are transparent, flexible wires composed of glass (silica) or plastic that are just a little thicker than a human hair. It acts as a waveguide, allowing light to travel between the fiber’s two ends. Fiber optic communications rely heavily on optical fibers because they allow for greater bandwidths (data rates) and transmission over greater distances than traditional modes of communication. It contains strands of glass fibers inside an insulated casing. The route for light is provided by the core, located in the center. The core is surrounded by cladding that reflects light to prevent loss of signal and allow the passage of light. 2. Multi-mode That’s all from Wired Transmission Media, let’s move on to Wireless Transmission media. Unguided media, also termed as unbound transmission medium, is a method of transmitting data without the need for cables. Physical geography has no bearing on these media. Unguided media are also known as wireless communication. It is a wireless transmission media channel that does not need a physical medium to connect to network nodes or servers. Wireless LAN is also called WLAN. It has become very popular in modern times. It uses radio frequency waves to transmit information from one device to another. Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) is a brand name. The IEEE 802.11 standard defines the protocols that enable communications with Wi-Fi-enabled wireless devices. Check this out – VLAN Trunking Protocol That’s all from the Wireless Transmission Media. Now, that we have uncovered everything from Transmission Media and types of transmission media, it is time to conclude this article. Transmission Media carries the information through LAN in the form of bits. It mainly carries information between the sender and the receiver therefore known as communication channels. Examples include twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, fiber optic cables, wireless technologies (like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth), microwave transmission, and satellite communication. The choice of transmission media depends on factors like distance, bandwidth requirements, and susceptibility to interference. Here are the 4 types of transmission media – Twisted Pair, Coaxial Cable, Fiber Optic Cable, and Wireless Transmission. Guided media refers to transmission media that provide a physical path or conductor for transmitting signals. It includes media like twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, and fiber optic cables, where the signals are guided along the transmission path. Unguided media, on the other hand, refers to transmission media that do not provide a physical path for signal transmission. Instead, the signals are propagated through the air or space using wireless technologies such as radio waves, microwaves, and satellite communication. Unguided media do not rely on a physical medium to transmit signals and are sometimes referred to as wireless or free space communication. Here are a the types of unguided media – Radio Waves, Microwaves, Infrared, Light Waves, and Satellite Communication. While constructing a network, transmission media are crucial because they ensure that data is transferred and received without interruption. A network can only be fully set up and functional with a medium to transmit the data inside the network. This blog is mostly concerned with transmission media and its types. Nonetheless, the transmission rate, cost, ease of installation, and distances covered are all considered while deciding on a medium. We hope this blog has helped you learn about ‘Transmission Media’.Introduction
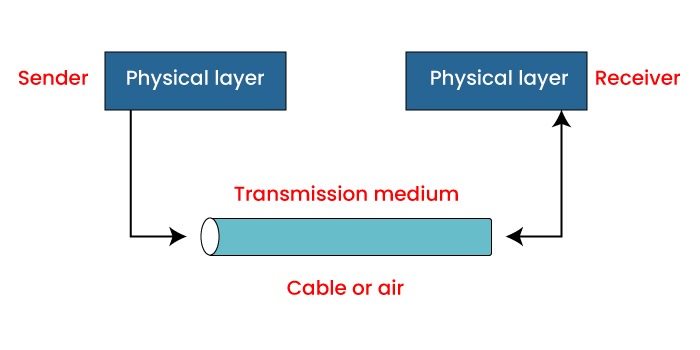
What is Transmission Media?
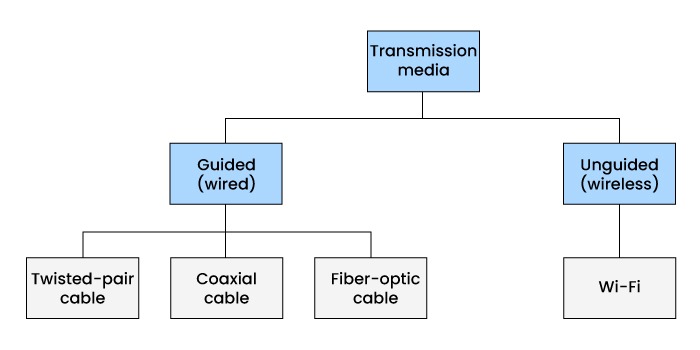
Types of Transmission Media
Guided or Wired Transmission Media
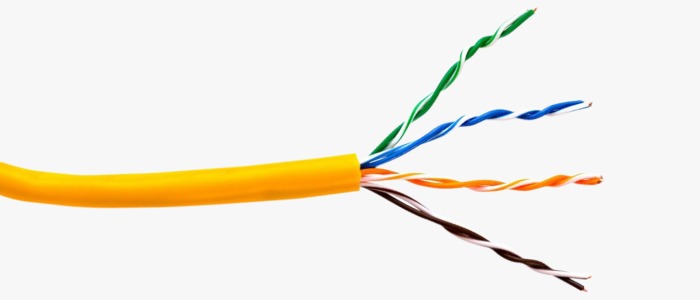
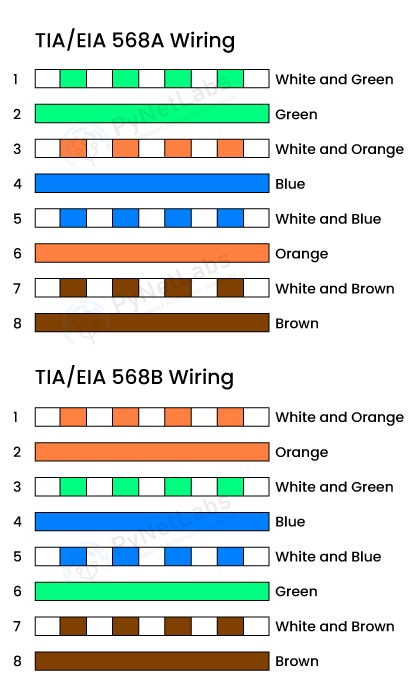
A. Copper
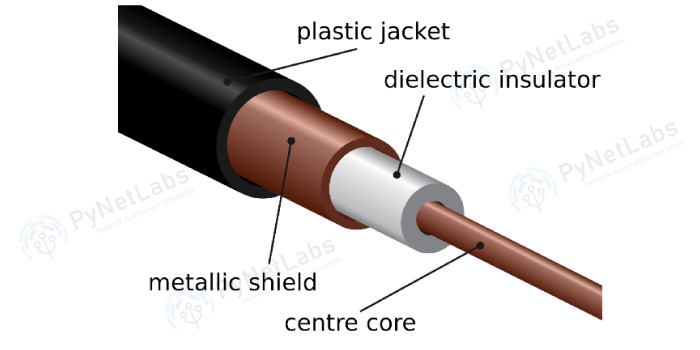
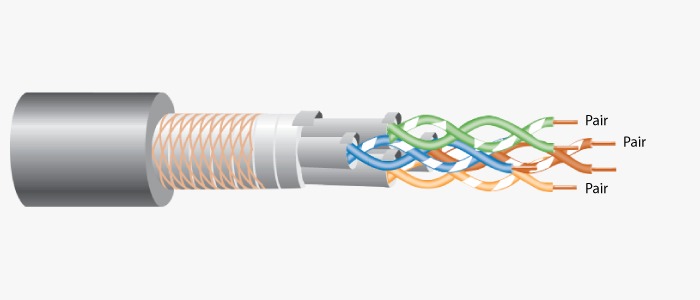
Ethernet Type Bandwidth Cable Type Maximum Distance 10Base-T 10Mbps Cat 3/Cat 5 UTP 100m 100Base-TX 100Mbps Cat 5 UTP 100m 100Base-TX 200Mbps Cat 5 UTP 100m 100Base-FX 100Mbps Multi-mode Fiber 400m 100Base- FX 200Mbps Multi-mode Fiber 2Km 1000Base-T 1Gbps Cat 5e UTP 100m 1000Base-TX 1Gbps Cat 6 UTP 100m 1000Base-SX 1Gbps Multi-mode Fiber 550m 1000Base-LX 1Gbps Single-mode Fiber 2Km 10GBase-T 10Gbps Cat 6a/Cat 7 UTP 100m 10GBase-LX 10Gbps Multi-mode Fiber 100m 10GBase-LX 10Gbps Single-mode Fiber 10Km
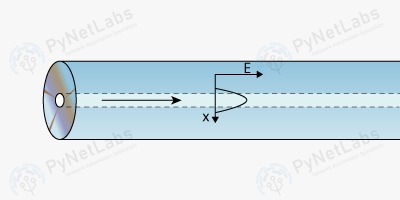
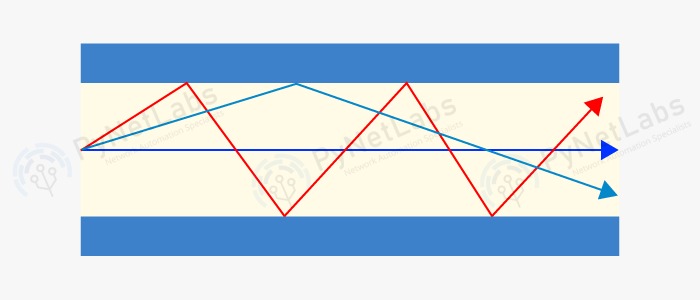
B. Fiber Optics
Unguided or Wireless Transmission Media
WI-FI
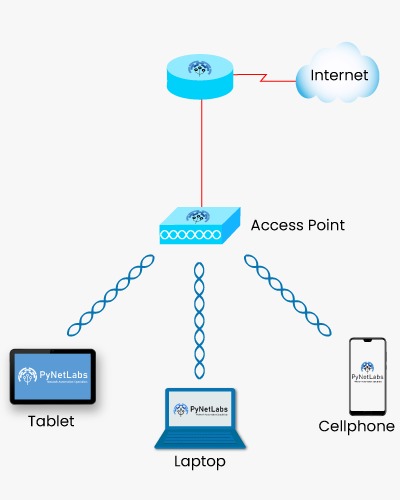
Standard Year Released Frequency (GHz) Speed Range (Indoor) Range (Outdoor) 802.11 1997 2.4 2Mbps 20m 100m 802.11a 1999 5 1.5-54Mbps 35m 120/5000m 802.11b 1999 2.4 11Mbps 35m 120m 802.11g 2003 2.4 54Mbps 38m 140m 802.11n 2009 2.4/5 600Mbps 70m 250m 802.11ac 2013 2.4/5 450/1300Mbps 35m – 802.11ax 2019 2.4/5 10-15Gbs 30m 120m Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is the transmission media?
Q2 – What are 4 types of transmission media?
Q3 – What is guided and unguided media?
Q4 – What are the types of unguided media?
Conclusion







