What is the difference between Packet and Frame?

In computer networks, data is sent between devices using protocols and layers. Each layer has its way of packaging and handling data. There are two types of data units: packets and frames. Packets are used in the network layer, while frames are used in the data link layer. But what is the fundamental difference between packet and frame? In this blog, we will discuss the difference between the two and define the frame and the packet in detail. Before getting into more details, let’s first understand the difference between Packet and Frame. Below, we have explained the difference between packet and frame in a tabular form based on different factors. Now, that we have a basic understanding of the difference between packet and frame. Below we have explained what a frame and packet really are. Frames are the building blocks of the OSI model data link layer. This layer facilitates data transfer between neighboring nodes within a network, such as two computers connected by a cable or wireless link. The data link layer also encompasses functions like error detection, correction flow control, and medium access control. A frame comprises three components: a header, a payload, and a trailer. The header carries details like the source and destination MAC addresses. The sender and the source MAC addresses represent the addresses of devices on the network. Meanwhile, the payload contains the transmitted data, like an IP packet or an ARP request. The trailer includes a checksum or cyclic redundancy check (CRC) that helps identify any errors in the frame. The format and size of a frame depend on the type of data link protocol that is used, such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, etc. For example, an Ethernet frame can have a maximum size of 1518 bytes, while a Wi-Fi frame can have a maximum size of 2346 bytes. Below, you can see the frame format. Another data unit is commonly known as a packet within the network layer of the OSI model. The network layer allows the transmission of data across different networks like the Internet. The network layer carried out responsibilities such as routing, logical addressing, fragmentation and reassembly congestion control, and quality of service. A packet comprises two components: a header and a payload. The header stores details such as source and destination IP addresses representing the addresses of devices on the network. On the other hand, the payload contains the data being transmitted, like a TCP segment or an ICMP message. The format and size of packets vary depending on the network protocol employed, such as IPv4 or IPv6. For instance, an IPv4 packet can have a size of 65535 bytes, while an IPv6 packet can reach up to 65575 bytes in size. Below, we have shown the packet format for better understanding. Below, we have explained the frame vs packet in detail and some examples. One of the main difference between Packets and Frame is that a packet is a unit of data at the network layer that contains network addresses and payload, while a frame is a unit of data at the data link layer that includes physical addresses and error-checking bits. Some of the other difference between packet and frame are: These are the difference between Packet and Frame. Frames are data units with headers and trailers. Packets are data units with headers only. Bits are binary digits that transmit data. A packet is a unit of data that travels across a network. It contains information such as the source, destination, and content of the message. A packet is a data unit that usually travels across different networks. Frame is the one who carries the packet on a physical link. Therefore, a packet can be larger than a frame. Frame loss happens when a frame is either dropped or discarded by a network device due to many reasons, such as congestion. Meanwhile, packet loss happens when a packet is dropped by the network or, for some reason, gets corrupted during transmission. Both these not only affect the performance but also the quality. In this blog, we have discussed frame vs packet in detail. Now, we have a basic understanding that the packets are utilized within the network layer while frames operate within the data link layer. Apart from that, we have discussed that the frame contains physical addresses, whereas packets contain logical addresses. In addition to this, we also have shown the frame and packet format. Understanding the difference between packet and frame is crucial as it provides insight into the transmission of data across layers and protocols within computer networks. Additionally, this knowledge helps in the identification and resolution of network issues while optimizing network efficiency. Choose CCNA Course to learn the two topics in depth.Introduction
Frame vs Packet
Factors Frame Packet OSI Layer A frame is a data unit at the Data Link Layer A packet is a data unit at the Network Layer Addressing Uses physical (MAC) addresses of source and destination devices Uses logical (IP) addresses of source and destination devices Correlation Encapsulates packets Encapsulates segments Fields Contains preamble, type, data, and CRC fields Contains source IP, destination IP, TTL, identification, protocol type, version, options, and data fields Function Responsible for error detection and correction, flow control, and media access control Responsible for routing, fragmentation, and reassembly of data across networks What is Frame in Computer Network?
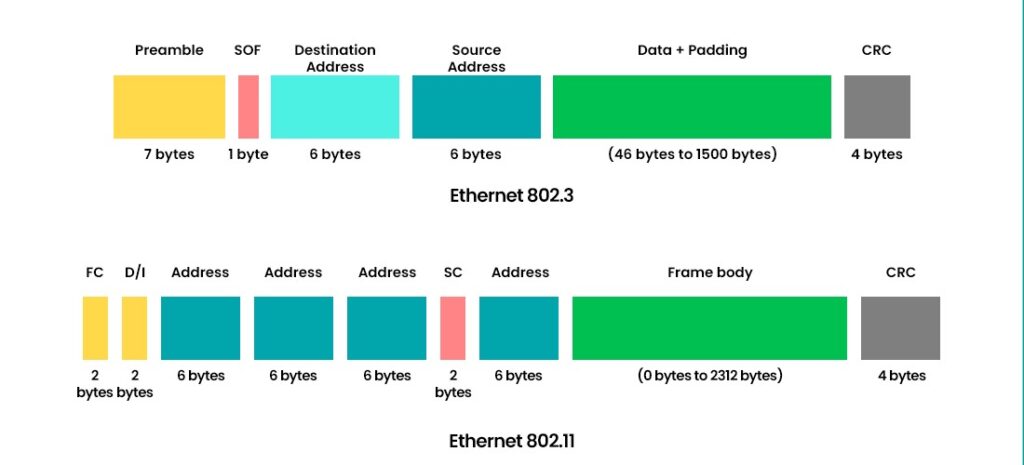
What is a Packet in Computer Networks?
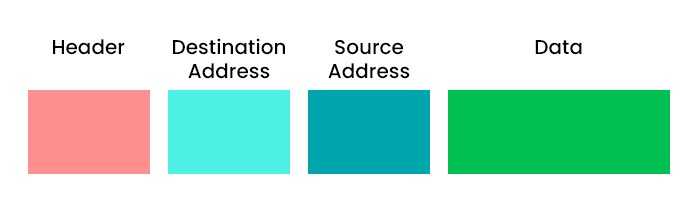
Difference Between Packet and Frame
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the difference between frames vs packets vs bits?
Q2. What is called Packet?
Q3. Is a packet larger than a frame?
Q4. What is the difference between frame loss and packet loss?
Conclusion







