What is ASBR in networking?
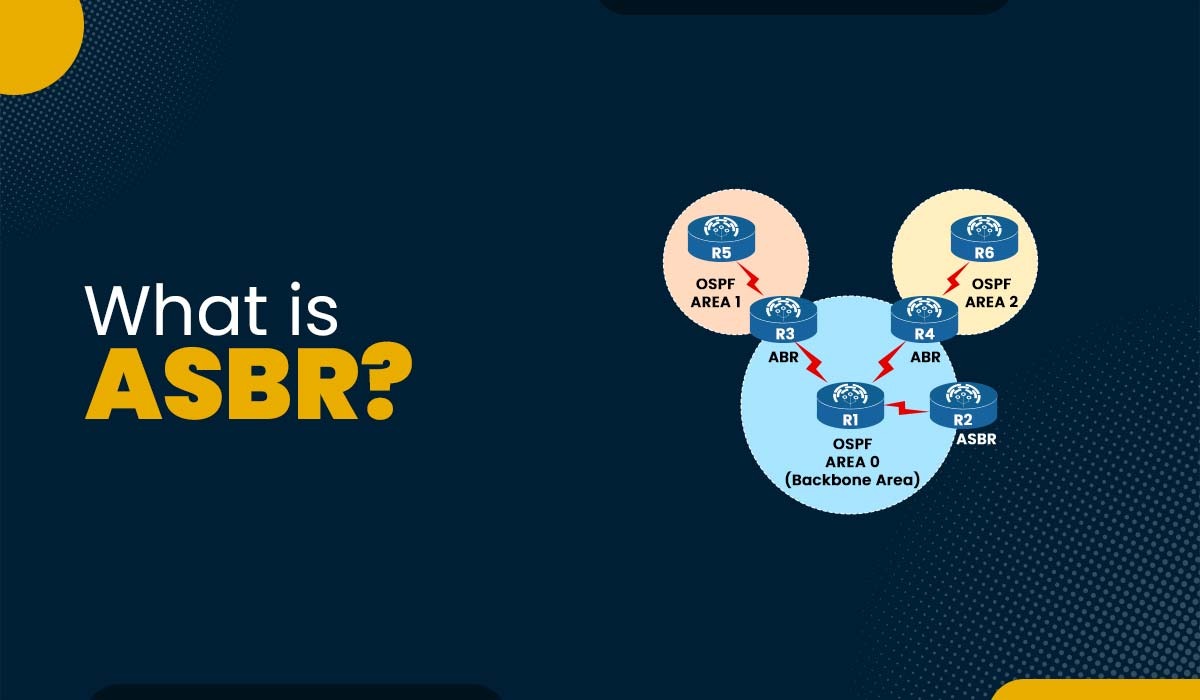
If you have knowledge regarding OSPF, you already know that it is a routing protocol that is mainly used to divide a network into different areas. Each area has its separate topology as well as the information regarding the routing. This makes it less complicated and also results in less overhead. If someone wants to connect their OSPF network with a different network that uses different protocols like EIGRP, BGP, and many others. How can one exchange the routes between these networks? That’s where ASBR comes into action. In this blog, we will explain what ASBR in networking is, its purpose, and how it functions, along with its advantages and disadvantages. Before getting into more details, let’s first understand what ASBR is. ASBR stands for Autonomous System Boundary Router. It is a router that runs multiple protocols and serves as a gateway to routers outside the OSPF domain and those operating with specific protocols such as EIGRP, BGP, and many others. The ASBR is capable of importing and translating different protocol routes into OSPF through a method called redistribution. Route Redistribution allows the ASBR to advertise external routes to the OSPF network and vice versa. For example, when you have an OSPF network that connects to another OSPF network that belongs to a different autonomous system (AS). An AS is a group of networks that tends to share the same routing policy and administration. In this case, you may want an ASBR to redistribute routes among the 2 OSPF networks, given that they’re considered external to each other. The purpose of ASBR is to permit communication among different autonomous systems or routing domains. An autonomous system is a group of networks underneath a common administration that share a common routing policy. For instance, an ISP may additionally have its personal autonomous system that uses BGP in order to communicate with other ISPs, and its clients use OSPF to communicate within their very own networks. An ASBR can connect these two autonomous systems and allow them to exchange routes. Hence, ASBR is of great importance in filling the communication gap between two different areas using different protocols. We now have a clear understanding of what ASBR in OSPF is and its purpose. Let’s move on to the functioning of ASBR. An ASBR functions by running a couple of routing protocols on its interfaces and performing redistribution among them. For instance, if an ASBR has an interface connected to an OSPF area, it’ll run OSPF on that interface and participate in the OSPF process. If it has another interface connected to a non-OSPF network, it’ll run any other protocol on that interface, such as with EIGRP, BGP, or static routes. The ASBR will then redistribute routes from one protocol to any other, primarily based on its configuration. For instance, if the ASBR desires to redistribute EIGRP routes into OSPF, it will take the EIGRP routes from its routing table and inject them into the OSPF LSDB (link-state database) as external LSAs (link-state advertisements). These external LSAs will then be flooded to all OSPF routers within the same area because of the ASBR. Similarly, if the ASBR desires to redistribute OSPF routes into EIGRP, it will take the OSPF routes from its routing table and inject them into the EIGRP topology table as external routes. These external routes will then be advertised to all EIGRP neighbors of the ASBR. The ASBR can also filter or summarize the routes it redistributes based totally on its configuration. For instance, if the ASBR desires to redistribute only particular EIGRP routes into OSPF, it can use an access list or a prefix list to match those routes and deny others. If the ASBR desires to redistribute only a summary of OSPF routes into EIGRP, it can use a summary-address command to create a single combination route for multiple subnets. We have explained the functioning of ASBR in networking. Let’s now discuss its advantages and disadvantages. Some of the advantages of using an ASBR are: Apart from all the advantages, there are also some disadvantages to using ASBR. These are: These are the advantages and disadvantages related to Autonomous System Boundary Router. ASBR, or autonomous system boundary router, is used to exchange routing information with routers that belong to different areas using different routing protocols. ASBR is a router that is usually connected to various autonomous systems via multiple protocols. In BGP, ASBRs use MP-BGP to advertise labeled VPN routes between ASes. One can quickly identify the ASBR in OSPF. If a router has one interface in the OSPF domain and another in any other routing protocol domain (e.g., RIP or EIGRP), it is considered to be an ASBR. ABR stands for Area Border Router. It connects different OSPF areas and advertises summary routes to them. In this blog post, we have learned about ASBR in networking. We have seen that an ASBR is a router that connects different routing protocols and autonomous systems using redistribution and type 5 LSAs. We have also discussed the purpose, function, advantages, and disadvantages of using an ASBR. We hope that this blog post has helped you understand what is ASBR in networking and how it works.Introduction
What is ASBR in Networking?
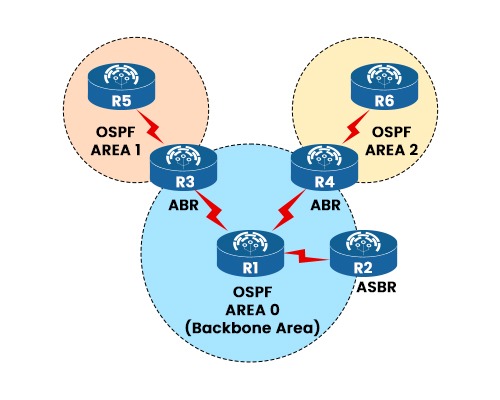
Purpose of Autonomous System Boundary Router
How does ASBR function?
Advantages of Autonomous System Boundary Router
Disadvantages of Autonomous System Boundary Router
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is ASBR used for?
Q2 – What is ASBR in BGP?
Q3 – How to identify ASBR in OSPF?
Q4 – What is the role of ABR in OSPF?
Conclusion







