What is BGP in Computer Networks?
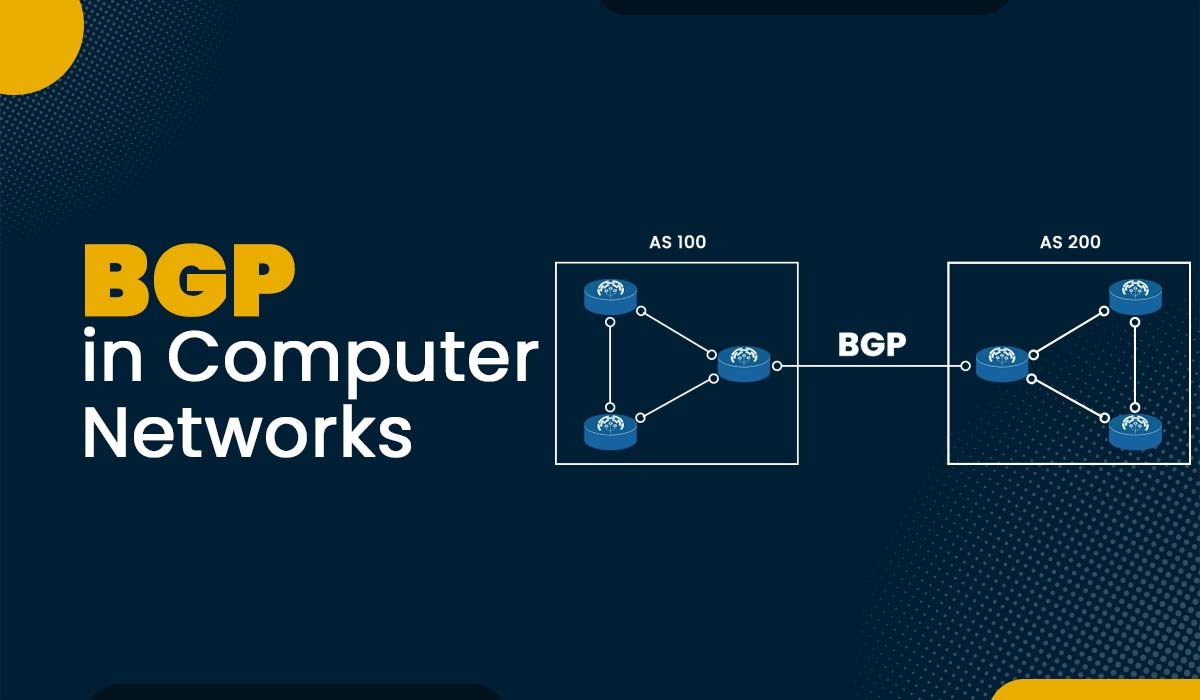
There are many different routing protocols used in computer networks that allow communication between various devices. BGP in computer networks is one of the most important protocols used to exchange data between different AS (Autonomous Systems). It’s the standard protocol for communication between ISPs and also between businesses and ISPs. BGP contains complete routing information to all destinations. BGP uses the routing data to track which networks are reachable and broadcasts that data to other BGP systems. BGP stands for Border Gateway Protocol, and it’s a type of EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocol), and to be precise, it’s a type of Path-Vector Routing Protocol. We have shown in the figure below: The main purpose of BGP is to choose the best path for sending data across the internet. While surfing the web, data is sent over many networks before arriving at its final destination. BGP analyzes all potential data transmission pathways and chooses the most efficient one. For example: When a user in India wants to access a website based on servers in the United States, BGP ensures that the two locations can communicate quickly and effectively. Apart from the application of BGP for large-scale networks that we already have discussed, BGP is used in various technological domains. Let’s discuss the role of BGP in today’s technology in detail. Software-defined networks (SDNs) use the BGP to regulate traffic routing in response to network conditions dynamically. And in the field of cloud computing, BGP serves the purpose of interconnecting virtual networks and guaranteeing accurate traffic direction to designated destinations. Since BGP can be used to monitor network traffic and block harmful activities, it is also playing a larger role in the fight against cybercrime. Security experts may defend their networks from attack by studying BGP routing data to find signs of attack. BGP’s ability to route data between devices and networks makes it more crucial in the IoT industry. BGP provides a flexible and effective means of transmitting data between networks and the ever-growing number of Internet-enabled gadgets. Before getting into the working of BGP protocol in networking, let’s understand what autonomous systems are. In order to supervise organizations like ISPs, universities, and governments, autonomous systems were implemented. These systems consist of several independent networks, yet they are managed as a single entity. Major companies’ network infrastructures often consist of many smaller networks that are geographically separated yet linked via a common operating environment. Each of your computers and other devices connected to the internet is linked to an AS. IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) is mainly responsible for managing autonomous systems. When two or more independent systems need to be connected, they use BGP to handle the routing of packets between them. BGP uses the AS to identify a system uniquely. This is of utmost significance for routing and administering routing tables for autonomous systems and other networks around their borders. BGP in Computer Networks uses a routing table to manage data packets and allows routers to exchange data with each other. The BGP process on the router is responsible for generating routing table information which is further based on various factors such as: TCP connection and TCP port 179 are utilized by BGP in order to exchange data and messages. Using the routing table and the attributes of the best possible paths, BGP selects the most efficient one for data transmission. Some of these attributes are AS path, next hop, IGP metric, and origin, which influence the routing decisions of the routers. BGP routers use a complex algorithm called the BGP decision process to select the best route for each destination network based on these attributes. Routers that support BGP protocol in networking may generate graphs that map networked pathways within or between autonomous systems by exchanging information about available or new paths. This maintains the reliability of information flow in networks, boosts network stability, and avoids loop formation. BGP in computer networks plays a crucial role in the functioning of the Internet by performing various vital functions. These functions include managing route information, selecting the most efficient route, providing redundancy measures to prevent routing errors, offering security through authentication mechanisms, and allowing communication between different network types. BGP maintains an accurate routing table by constantly adding new routes and updating the existing ones. BGP utilizes this table for deciding how to transmit data from one network to another. BGP in computer networks determines the most effective route for data transmission based on a number of factors, including distance and latency. In most cases, BGP routers will have many potential pathways to choose from and prioritize the one with the best performance. The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) relies on a series of algorithms referred to as the BGP Decision Process to identify and reduce routing path loops. This process helps optimise packets’ transmission by selecting the most efficient route, thereby minimizing bandwidth consumption and avoiding unnecessary diversions. The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) utilizes a preconfigured password or key to authenticate messages exchanged between routers. This measure helps guarantee that only authorized entities are able to engage in the exchange of information while simultaneously preventing malicious actors from preventing the flow of traffic. EBGP is used to exchange routing information between different autonomous systems (AS), while IBGP is used to exchange routing information within the same AS. Below we have discussed the basic difference between EBGP and IBGP in a tabular form. These are the differences between the two BGP types. Here are some benefits of BGP in Computer Networks- Here are some disadvantages of BGP Protocol in Networking – BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is used in the internet infrastructure to facilitate routing and exchange of routing information between different autonomous systems (ASes). Mainly there are two types of BGP. These are: BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) uses a message-based format for communication, with messages exchanged between routers in the form of variable-length packets containing different types of BGP messages such as Open, Update, Keepalive, and Notification. BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) operates through six stages: Idle, Connect, OpenSent, OpenConfirm, Established, and Active. These stages represent the progression of a BGP session from initialization to full routing table exchange and stable connectivity. BGP in computer networks is the protocol that connects different networks on the Internet and enables them to exchange routing information. BGP is a dynamic and flexible protocol that can adapt to network topology and traffic conditions changes. We hope that this post has given you a better understanding of BGP protocol in networking and its role in the Internet. You can also check out – BGP Interview Questions and Answers BGP is one of the most important protocols in networking. If you want to learn more about the networking protocols, you can take the OSPF BGP Combo Course or CCNA Training.Introduction
What is BGP in computer networks?
Role of BGP Protocol in Today’s Technology
SDN and Cloud
Cybersecurity
IoT (Internet of Things)
Autonomous Systems
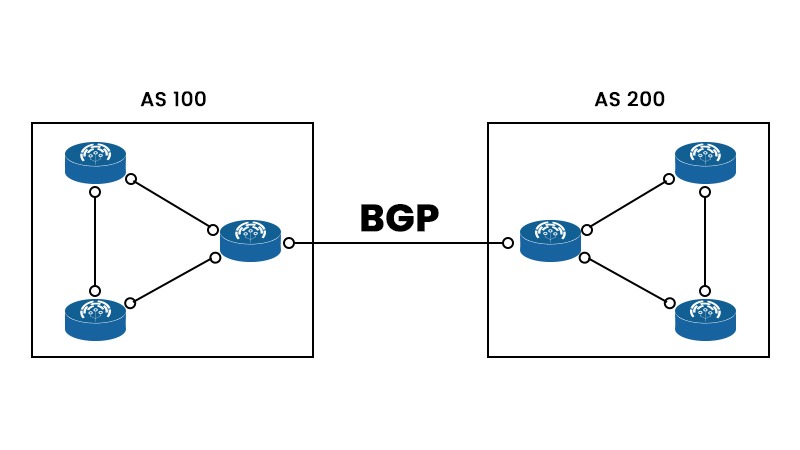
How does BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) works?
Functions of Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
1. Maintaining Route Information
2. Selecting the best route
3. Detecting loops in routing paths
4. Providing security
BGP Route Information Management Functions
Difference Between External BGP and Internal BGP
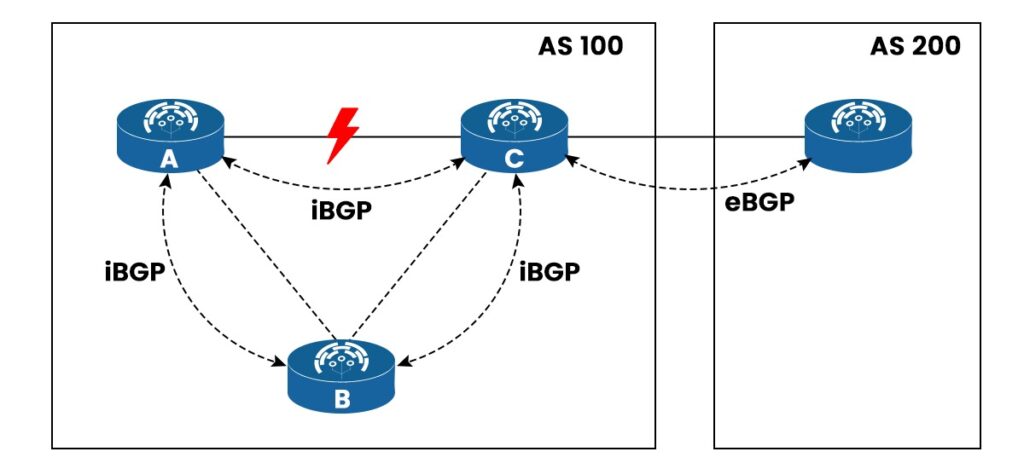
Factors EBGP IBGP Administrative Distance (AD) The default administrative distance in the case of EBGP is 20. The default administrative distance in the case of EBGP is 200. TTL (Time-To-Live) EBGP peers by default set TTL to 1. IBGP peers by default set TTL to 255. Loop prevention AS-path attribute is checked for the presence of its own AS number. In the case of the IBGP, Split-horizon is used for loop prevention. Topology No need for full mesh topology. Full mesh topology is required in IBGP. Attributes EBGP modifies some attributes, such as AS_PATH and NEXT_HOP, when sending routes to another AS. IBGP preserves the attributes received from eBGP and does not change them when sending routes within the same AS. Advantages of BGP
Disadvantages of BGP
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – Where is BGP used?
Q2 – How many types of BGP are there?
Q3 – What is the BGP format?
Q4 – What are the 6 stages of BGP?
Conclusion







