What is VPN in Cyber Security and its Types?

Nowadays, everyone relies heavily on digital platforms, whether for business purposes or some important transactions. With the increase in digital presence, protecting personal data from hackers is crucial. VPN in cyber security is one approach to stop third parties from obtaining vital data for their benefit. In this blog, we will discuss what a VPN really is, its history, the need for a VPN, how it works, types of VPN in cyber security, benefits and drawbacks of using a VPN. Let’s first understand the basic meaning of VPN. VPN in cyber security stands for Virtual Private Network. It is a technology that creates a virtual network over the internet by encrypting your data and hiding your IP address. Your device connects to a distant server managed by a VPN provider when you use a VPN, and this server then serves as the pathway for all of your internet traffic. Online identity and actions are kept secret in this manner from anybody who is possibly spying or attempting to steal sensitive data. In the 1990s, VPN was developed as a secure connection for distant employees to corporate networks. Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP), developed by Microsoft in 1996, was the first VPN protocol. Later, L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol), which had additional security measures, replaced PPTP. Internet Protocol Security, or IPsec, was first launched by IETF in 1998 and quickly became the standard for VPNs. For IP packets, IPsec offers reliable encryption and authentication. OpenVPN, an open-source VPN protocol that employs SSL/TLS encryption, was developed in 2001. One of the most reliable and flexible VPN protocols currently available is OpenVPN. Firewalls and network address translation (NAT) may be avoided using OpenVPN, which can operate on any port. We now have a basic understanding of VPN and its history. Let’s see how VPN works. A VPN functions by establishing a secure tunnel between your device and a distant server. The tunnel is encrypted with a key that only you and the server can access. In this manner, nobody will be able to see or manipulate your data as it passes through the tunnel. As you can see in the picture below, how VPN really works. Now, the question that arises is how an encryption tunnel works. Let’s understand in detail. Encryption tunnel works via a combination of algorithms as well as protocols to protect the data. When we talk about the protocols, it defines how the data is packaged, transmitted, and verified. In the case of algorithms, it defines how data is scrambled and unscrambled. As you can see in the picture above, the encryption tunnel has two endpoints, namely, the client’s device and the VPN server. Whenever a user tries to connect to the VPN, the user’s device usually initiates a handshake with the VPN server. This process is commonly known as exchanging cryptography keys and parameters that are further utilized in establishing the encryption tunnel. After the handshake process, the encryption tunnel is established. It is finally possible for the user’s device and the VPN server to exchange data securely. Now that we have a good understanding of the working of VPN in Cyber Security. Let’s understand the types of VPN. There are different types of VPN in cyber security as per various requirements and objectives. Among the most common ones are: With Remote access VPN, we can connect from a distance to a private network, such as a business or home network. In this manner, we may use the network’s resources—like files, printers, and software—just as if we were physically present there. Employees who work from home or travel regularly and others who wish to access their personal network from any location typically utilize remote access VPNs. A site-to-site VPN connects two networks that are located at separate locations, as opposed to a remote access VPN, which enables individual users to connect to a network and utilize its services. Site-to-site VPN builds a virtual link between two or more networks by connecting them over the internet. The networks can safely and effectively exchange resources and data in this manner. Businesses that wish to cooperate with partners or customers or have several offices or branches spread throughout the country often utilize site-to-site VPNs. Mobile VPN is designed especially for portable devices like smartphones and tablets that regularly switch between networks or their network connections. No matter how good or accessible the network is, mobile VPNs provide the device with a reliable and secure connection. People who travel often utilize public Wi-Fi networks or require mobile access to sensitive data and frequently use mobile VPNs. We have explained how VPNs work and the different types of VPNs that are used. Let’s focus on the benefits and limitations of using a VPN in Cyber Security. Here are a few uses of VPN – Yes, the VPN is secure as it uses cryptography, which guarantees the user’s security and privacy and provides all the three features of the “CIA Triad”. If the underlying network infrastructure alone cannot provide security, the VPN protocol allows connected systems to provide the right level of protection. Here are various protocols that provide secure and encrypted data: Users and businesses may benefit from VPNs in a variety of ways, including: Even if VPNs are made to play an essential part in modern business, they are not a perfect solution. VPNs have some limitations that affect both their user and business cybersecurity, such as: VPN services are legal in many countries and always remain legal if not used for illegal activities like online fraud, cyber theft, or downloading copyrighted content in certain countries. Therefore, the legality of a VPN also depends on the country and its geopolitical relations with other countries. For example, according to a Bloomberg report, China will ban all VPN services. Some users use VPNs to access websites restricted under the “Great Firewall” of China. It is done to prevent rival countries’ data leaks and protect security systems. Virtual Private Network, or VPN, is a technological advancement that provides safe online connections to private networks. There are mainly 3 types of VPNs. These are – VPNs are used because it makes it difficult for hackers, snoopers, or even govt. agencies to access or modify data as per their benefit. In order to do that, a VPN provides a secure tunnel and also hides the user’s IP address, which might disclose their location and identity. Some of the uses of VPN are: People who value their online privacy and security need a VPN. A VPN encrypts their internet traffic and hides their IP address from prying eyes. VPN in cyber security is a technology that establishes a secure connection over the internet using data encryption and IP address masking. It may provide us with a lot of benefits as well as some limitations. Because of this, we should use a VPN responsibly and for the intended goals. In this blog, we have discussed what is a VPN, how VPN works, its advantages and disadvantages.Introduction
What is a VPN?
History of VPN
How VPN works?
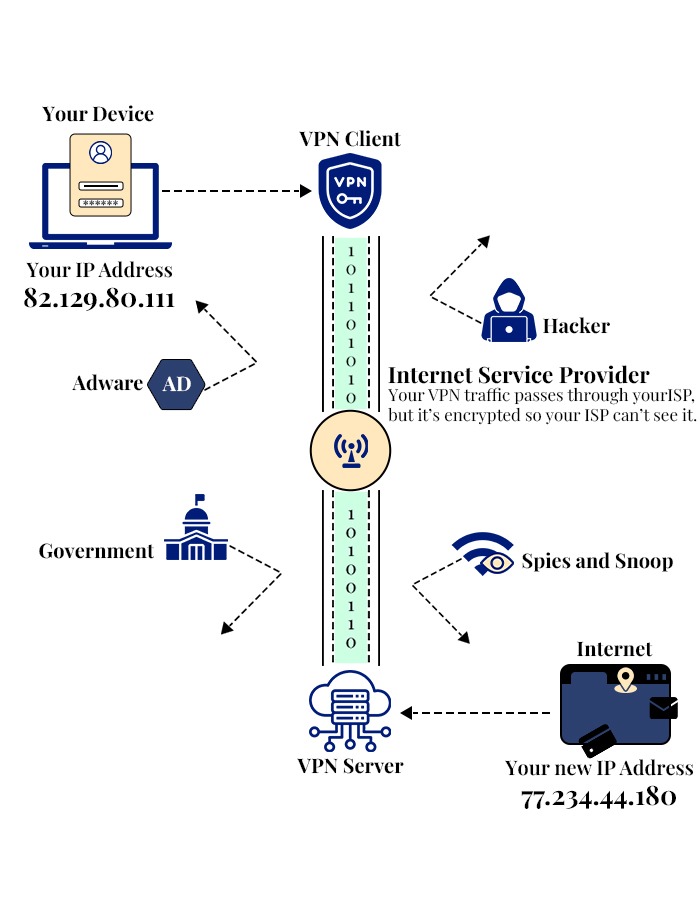
How does the encryption tunnel work?
Different types of VPN in Cyber Security
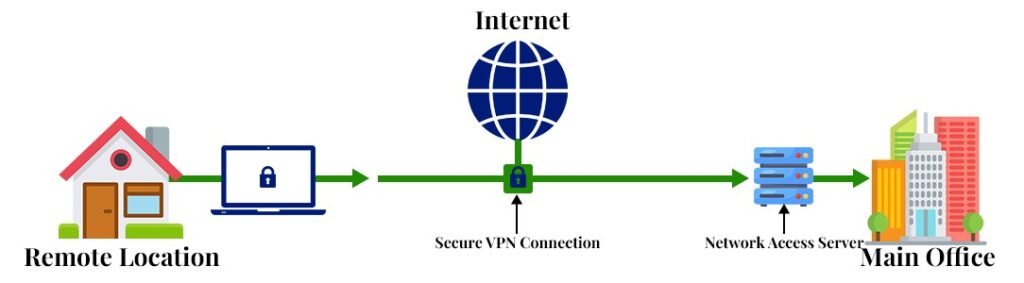
Remote access VPN
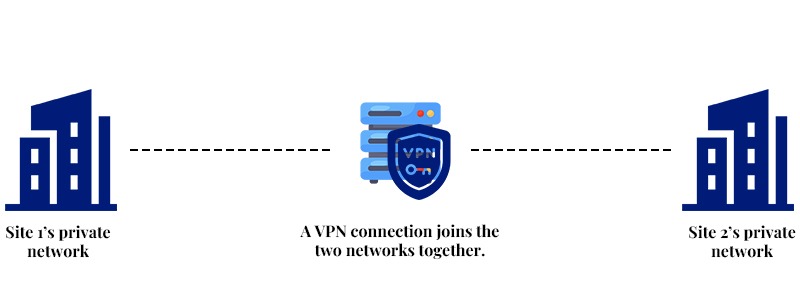
Site-to-site VPN
Mobile VPN
What is VPN in Cyber Security used for?
Is VPN Secure?
VPN Protocols
Benefits of using a VPN
Limitations of using a VPN
Is VPN legal or illegal?
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is VPN and its type?
Q2 – Why VPN is used for security?
Q3 – What are 3 uses of VPN?
Q4 – Who needs a VPN?
Conclusion







