What is Broadcast Domain in Networking?
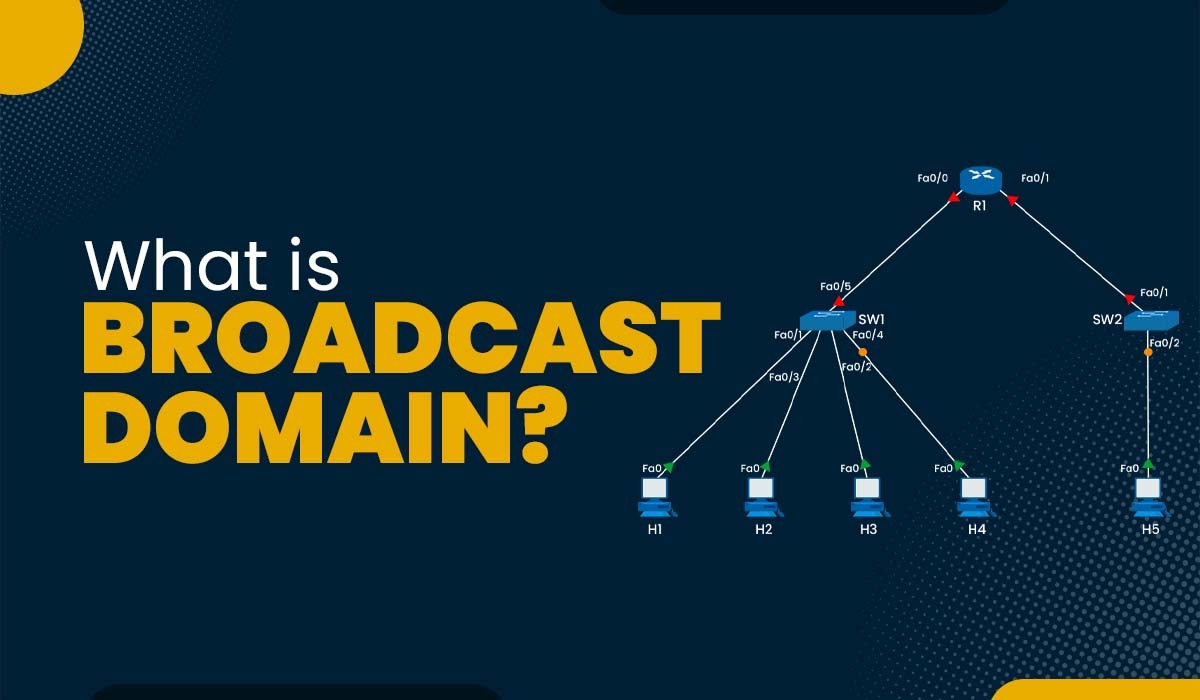
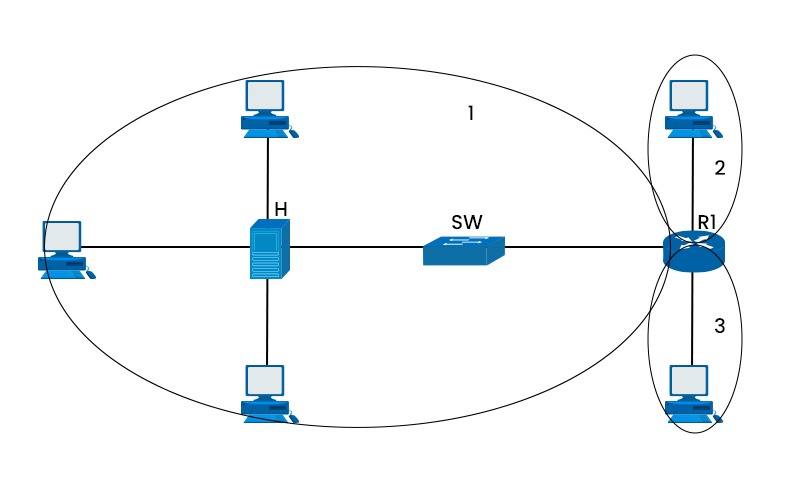
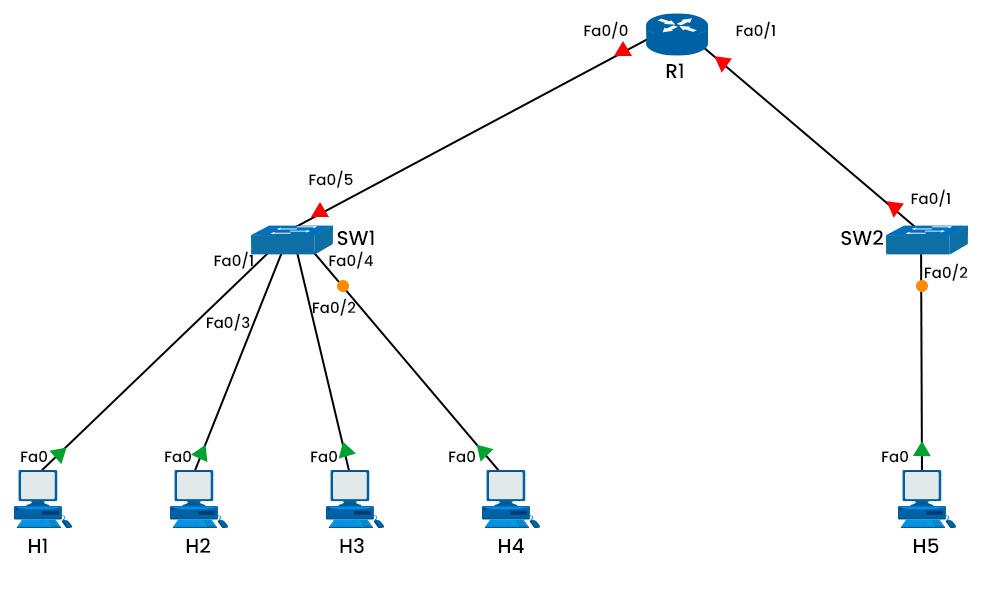
The study of networking covers a wide range of topics and technologies. A logical subdivision of a computer network where all nodes may interact with one another by sending and receiving broadcast messages is known as the broadcast domain. Regardless of their destination address, broadcast messages are unique data packet types distributed to all network devices. In this blog, we will explain what is a broadcast domain, how it works, and its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s begin by understanding what it really is. A logical subdivision of a computer network known as a “broadcast domain”. It allows all nodes to communicate with one another through broadcast at the data link layer. Using physical addresses known as MAC (Media Access Control) addresses, the data link layer moves data between nearby nodes in the same network segment. It may be bridged to another LAN segment, or it may be located on the same LAN (Local Area Network) segment. The network devices that can forward or block broadcast messages establish a broadcast domain. Switches and routers are the most common devices that may establish or separate broadcast domains. Switches are devices that connect multiple nodes in the same network segment and forward data packets based on their MAC addresses. Switches will route broadcast messages to every interface except the one from which they originated. This indicates that all ports on a switch are in the same broadcast-domain by default. In order to forward data packets depending on their IP (Internet Protocol) addresses, routers connect various network segments. Routers cannot forward broadcast messages from one network segment to another. This indicates that every interface on a router is a member of a unique broadcast domain. As you can see, there is an example of a broadcast domain with three others. One can easily understand that all ports on a hub or switch are contained within a single broadcast domain, i.e., 1, while all ports on a router are assigned to a separate broadcast domain, i.e., 2 and 3. Note: Another way to create or separate it on a switch is with the help of VLANs. Each VLAN has its own broadcast domain; thus, without a router or other device that can route traffic between them, VLANs cannot interact with one another. Many might confuse broadcast domains with subnets. Let’s understand the fundamental difference between these two. Below we have explained the basic difference between the two. We now have a basic understanding of the broadcast domain in networking. Let’s move on to its working. Let’s look at an example of a network with three switches and four hosts to show how it works. This network has two broadcast domains, one on the left side of R1 and the other on the right side. No broadcast frames are sent between the two domains by router R1. Let’s imagine that H1 and H2 desire to connect via their respective IP addresses. H1 must use ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) to learn H2’s MAC address because it is unaware of it. ARP is a protocol that employs broadcast to ask for a device’s MAC address if it matches a specified IP address. H1 will issue an ARP request to H2 using the destination IP address of H2 and the destination MAC address of FF:FF:FF:FF:FF. Every device to the left of R1, including SW1, SW2, H3, and H4, will get this ARP request. Due to its matching IP address, only H2 will respond with an ARP reply that includes its MAC address. The destination MAC address of the unicast frame with the ARP response will be H1. From the ARP request and reply frames, the switch SW1 will determine the MAC addresses of H1 and H2 and store them in its MAC address table. The MAC addresses of H3 and H4 will likewise be determined by the switch SW2 from their traffic. Only the ports with the destination MAC addresses will receive unicast frames from the switches using their MAC address tables. Since ARP frames are broadcast at the data link layer, the router R1 will not receive or transmit any of them. However, R1 must be used as the default gateway if H1 is interested in communicating with H5 using their IP addresses. In such a situation, H1 will issue an ARP request to R1’s left interface, asking for its MAC address. R1 will respond with its MAC address and then use its routing table to direct the IP packets from H1 to H5. We have explained how it works; let’s understand its advantages and disadvantages. Some of the advantages of a broadcast domain are: Apart from all the advantages, there are also some disadvantages too. These are: These are the advantages and disadvantages of Broadcast domain in computer networks. An example of it is every port on a switch in a switched Ethernet network has a different collision domain, although all ports on the same switch are by default in the same broadcast domain. One of the main functions of it is effective network communication. It allows several devices to receive the same message concurrently. A collision domain is where devices can collide on a network, whereas, a broadcast is where devices can receive broadcast messages. They are different network segments. A VLAN broadcast domain is a group of devices that can receive each other’s broadcast messages. It is created by configuring VLANs on switches. The broadcast domain in networking is one of the crucial concepts. It vary in size and form depending on network devices and connections. It offers advantages as well as disadvantages for network communication; thus, it should be properly planned and maintained for performance and security. In this blog, we have covered what is a broadcast domain in detail, along with its working. We have also explained some of the advantages and disadvantages that are associated with it.Introduction
What is a Broadcast Domain?
Broadcast Domain vs Subnet
Factors Broadcast Domain Subnet Layer Layer 2 (Ethernet) Layer 3 (IP) Address MAC address IP address Forwarding Switches forward broadcast frames to all interfaces in the same broadcast domain Routers forward packets to the destination subnet based on the routing table Separation VLANs can create multiple broadcast domains on a switch Subnetting can create multiple subnets within a network How does Broadcast Domain work?
Advantages of Broadcast Domain
Disadvantages of Broadcast Domain
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is a broadcast domain example?
Q2 – What is the function of broadcast domain?
Q3 – What is the difference between collision and broadcast domain?
Q4. What is a VLAN broadcast domain?
Conclusion







