Difference between Routing and Routed Protocols
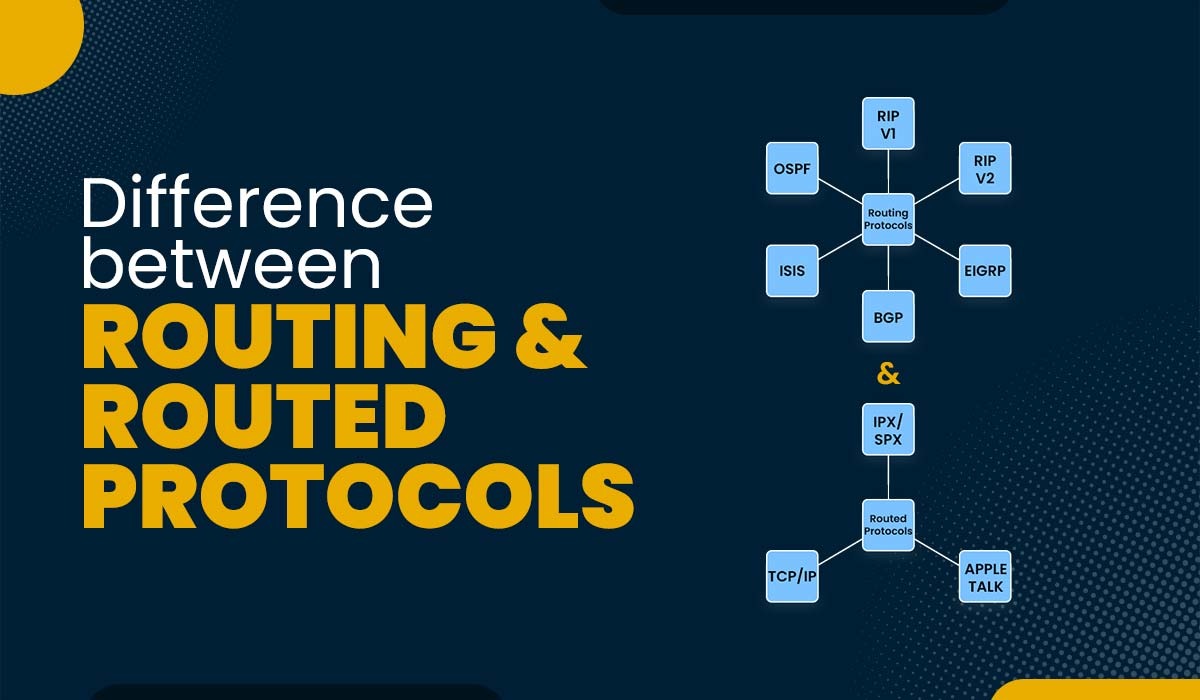
Routing and routed protocols are two critical principles in computer networking that confuse many students. Both are associated with the network layer of the OSI model, which is responsible for offering logical addressing and routing packets across different networks. Both have specific features and traits. In this blog, we will explain routing protocol vs routed protocol in detail as well, and we will try to understand both separately, along with examples. Before getting into more details, let’s first understand routing and routed protocols. A routing protocol is a set of policies or algorithms routers use to exchange information about the networks they are connected to. This information helps routers decide the best route to transmit packets to their destination. Routing protocols function on the network layer of the OSI reference model and use route update packets to communicate with each other. Routers run various routing protocols to exchange updates and assist in finding the best paths to a destination in a network. When a new network is added, routing protocols can learn about it and recognize when a network is unavailable. We now have a basic understanding of what routing protocols really are. Let’s move on to the types of routing protocols. Mainly, there are two types of routing protocols. These are: In static routing, the routes are manually configured by means of the network administrator and do not change based on network conditions. This type of routing is simple, stable, and rapid, but it isn’t scalable or adaptable to network modifications. Static routing is best suited for small networks with a fixed topology. In dynamic routing, the routes are automatically updated based on modifications inside the network topology or metrics, including hop count number, bandwidth, delay, and so on. This sort of routing is complex and efficient, but it consumes greater resources and bandwidth. Dynamic routing is best suited for big, complicated networks with a variable topology. Let’s now discuss the examples of routing protocols for better understanding. Below, we have discussed various examples of routing protocols with their characteristics. We now have a detailed understanding of routing protocols and their types and examples. Let’s discuss the advantages and disadvantages of routing protocols. Some of the advantages of routing protocols are: Some of the disadvantages of routing protocols are: We have explained the routing protocol in detail; let’s now understand the routed protocols. A routed protocol is a protocol that includes the process of carrying user information or data from one host to any other throughout the network. It operates on the network layer of the OSI model and offers logical addressing and encapsulation to the data packets. A routed protocol relies upon a routing protocol to find the best route to its destination. Routed protocols make use of a technique for addressing that may address a specific network and a host within that network. Let’s see some of the examples of routed protocol. Below, we have discussed some examples of routed protocols with their characteristics. Here are some advantages of routed protocols – We now have an understanding of what routing and routed protocols are. Let’s move on and discuss the difference between routing and routed protocols. Below, we have compared Routing Protocol vs Routed Protocol in a tabular form to explain the difference between the two. These are the main differences between Routing and Routed Protocols. In summary, routed protocols deal with the content and structure of data packets, while routing protocols deal with the rules and algorithms that routers use to decide how to forward these data packets from one network segment to another. Routing protocols ensure that data packets from one network can traverse multiple networks to reach their destination by determining the most efficient path. Routing protocols are simply the algorithms used by the router in order to communicate with each other by sharing information about the best route to the destination. In comparison, a routable protocol is a network protocol that can be routed between networks within an internetwork in order to route the packets. The three types of routing protocols are: A routed protocol is a type of network protocol that can be sent over a router. It has an address field that specifies the destination of the packet. Examples are IP, IPv6, and AppleTalk. OSPF is a link-state routing protocol that is based on SPF, i.e., shortest path first algorithm. Both routing and routed protocols play a crucial role in network communication. In this blog, we have discussed the basic differences between the two, along with their types and examples. To understand the limitations and their scope of use, we also have discussed their advantages and disadvantages.Introduction
What are Routing Protocols?
Types of Routing Protocols
Static Routing
Dynamic Routing
Examples of Routing Protocols
Advantages of Routing Protocols
Disadvantages of Routing Protocols
What are Routed Protocols?
Examples of Routed Protocols
Advantages of Routed Protocols
Difference between Routing and Routed Protocol
Factors Routing Protocol Routed Protocol Purpose To determine the best routes for data packets To carry data packets between end devices Addressing Use logical addresses (such as IP addresses) to identify networks Provide logical addresses (such as IP addresses) to identify end devices Operation Operate at the network layer of the OSI model Operate at the network layer or higher layers of the OSI model Types It can be static or dynamic Can be routable or non-routable Example RIP, EIGRP, OSPF, BGP, etc. IP, IPX, AppleTalk, etc. Hardware/Software Implemented in network devices, primarily routers. Typically implemented in end systems or hosts (e.g., computers, servers). Scalability The choice of routing protocol can impact network scalability and routing efficiency. The scale of the network is mostly independent of the routed protocol in use. Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is routing protocol and routable protocol?
Q2. What are the 3 types of routing protocols?
Q3. What is meant by routed protocol?
Q4. Is OSPF a routed protocol?
Conclusion







