DR and BDR in OSPF
OSPF, which stands for Open Shortest Path First, is a link-state routing protocol that calculates the shortest course or path to any destination inside the network using the Dijkstra algorithm. However, OSPF has several limitations, mainly in terms of non-broadcast multi-access (NBMA) networks such as Ethernet or Frame Relay. In these networks, more than one router can be connected to the same segment, and each router has to exchange routing information with every other router on the segment. This can cause a variety of network overhead and congestion and also slow down the convergence process. In order to solve such an issue, OSPF introduces the principles of DR and BDR, which stand for Designated Router and Backup Designated Router. In this blog, we will explain what DR and BDR in OSPF are, their functions, and their election process. Before getting into more details, let’s first understand what DR and BDR are in networking. The DR is the Designated Router on a segment, and it is the router with the highest priority among all the segment routers. The priority is a value between zero and 255 that may be configured manually or left at the default value of one. If two or more routers have the same priority, the router with the highest router ID (commonly the highest IP address) turns into the DR. The DR has major functions: The DR maintains a complete link-state database (LSDB) of the network segment, which contains all of the LSUs received from different routers. The DR additionally generates a network LSA for the network segment, which summarizes the records of all the routers connected to it. The network-LSA is flooded to all different OSPF routers inside the same area. The BDR is the Backup Designated Router on a segment, and it is the router that has the second highest priority amongst all of the routers on the segment and acts as a backup for the DR. The BDR is elected identically as the DR and chosen after the DR. The BDR has two important functions: The BDR is elected at the same time as the DR, but it does not perform any feature until the DR fails. Now that we have a better understanding of DR and BDR in OSPF. Let’s begin with the DR and BDR election process. The DR and BDR election is primarily based on criteria: the OSPF priority and the router ID. DR and BDR election process in OSPF takes place at some stage in the initialization phase of OSPF whilst routers form adjacencies with every other. The election method follows these steps: Now we have explained the DR and BDR election process in OSPF. A DR is needed for OSPF to reduce the wide number of adjacencies and LSA flooding in a multi-access network. The DR acts as a central node communication for OSPF routers. OSPF determines the DR and BDR based on priority. The router with the highest priority will be the DR, and the second highest priority will act as BDR. When two routers have the same priority, then router ID comes into action. The router with the highest router ID will be DR. DR stands for designated router, which is mainly used to connect all routers in a network segment. In contrast, ABR, which stands for area border router, is primarily used to connect OSPF areas. ABR (Area Border Router) connects different OSPF areas to the backbone area (area 0). ASBR (Autonomous System Boundary Router) connects the OSPF network to other routing domains. ABR and ASBR have different roles and functions in OSPF. In this blog post, I have explained the concepts of DR and BDR in OSPF and how they are elected in an OSPF network. We have also learned how to influence the election of DR and BDR by configuring each router’s priority and router ID. Join PyNet Labs’ most demanded OSPF BGP Combo Training. We hope you have enjoyed this blog post and learned something new about OSPF. If you have any questions or feedback, please feel free to leave a comment below.Introduction
What is DR?
What is BDR?
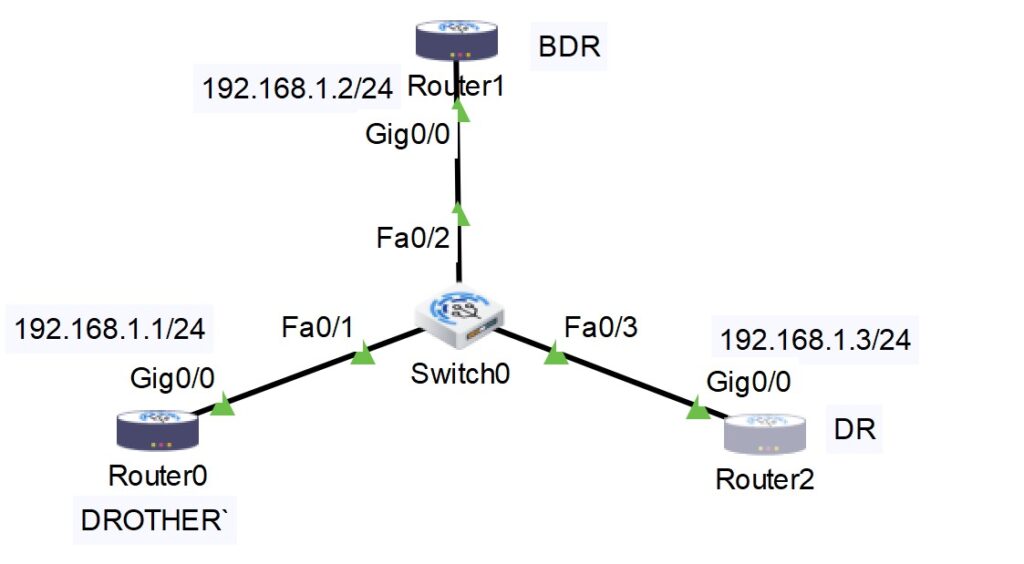
DR and BDR election process in OSPF
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – Why is a DR needed for OSPF?
Q2 – How does OSPF determine DR and BDR?
Q3 – What is Dr and ABR in OSPF?
Q4 – What is ABR and Asbr in OSPF?
Conclusion







