Difference between EIGRP and RIP
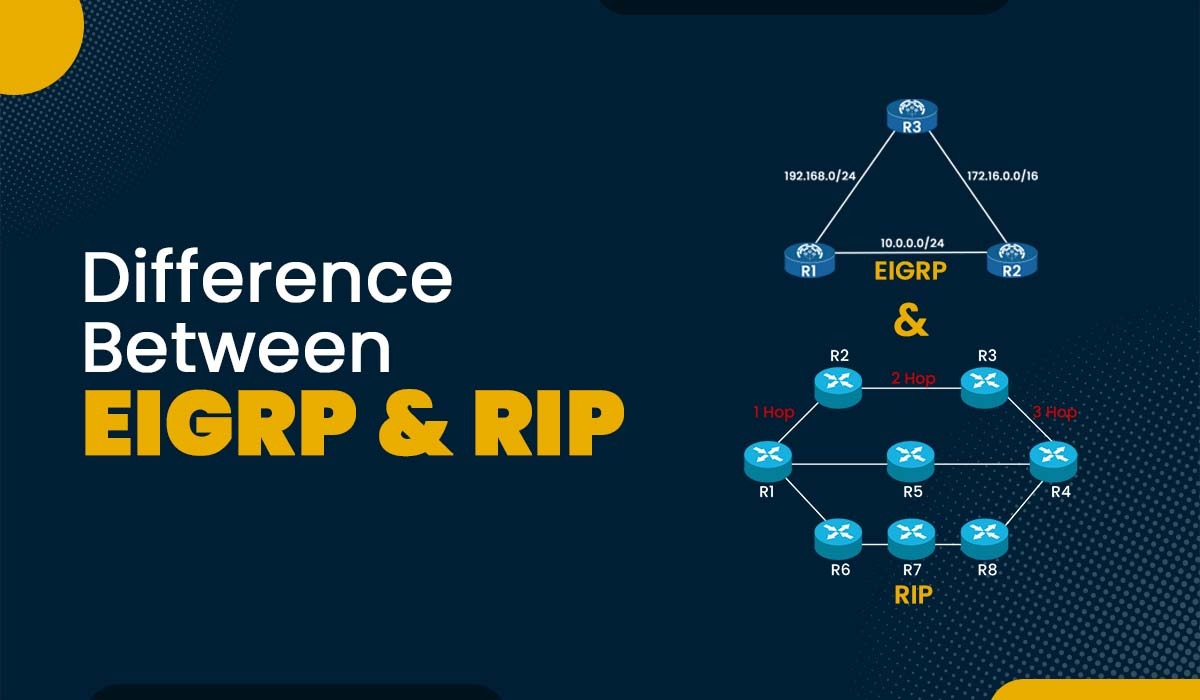
In a network, routers communicate with one another via different routing protocols available. Routing protocols help routers in order to choose the best path to a destination and also maintain the routing table. There are several types of routing protocols each with different functionalities, some of which are path vector, link state, and distance vector. In this blog, we will explain the basic difference between EIGRP and RIP, two well-known distance vector routing protocols. Before getting into the difference between EIGRP and BGP, let’s understand them in detail. EIGRP stands for Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol. It is a Cisco proprietary protocol that was developed in order to overcome the limitations of IGRP (Interior Gateway Routing Protocol). EIGRP makes use of the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) to calculate the best route to a destination network based totally on multiple metrics that include bandwidth, delay, load, and reliability. EIGRP additionally helps unequal cost load balancing, which means that it may use more than one path with different costs to reach the identical destination. To function properly, EIGRP maintains three tables in each router. These are: EIGRP makes use of hello packets to establish and maintain neighbor relationships. It also uses update packets in order to advertise new or modified routes, query packets to request information about a destination network, respond packets to answer queries, and acknowledgment packets to confirm the receipt of updates, queries, or replies. EIGRP has an administrative distance of 90, which means that it’s preferred over other routing protocols with higher values. EIGRP may be configured with an autonomous system (AS), which identifies a collection of routers that share the same routing information and policies. RIP stands for Routing Information Protocol. It is one of the oldest and handiest routing protocols, primarily based on the Bellman-Ford algorithm. RIP makes use of hop count as the only metric in order to measure the distance to a destination network. Hop count is the number of routers that a packet has to pass to reach its destination. RIP has a maximum hop count of 15, which means that any network that is more than 15 hops away is considered unreachable. In order to function properly, RIP maintains two tables for every router available in a network segment. These are: RIP has an administrative distance of 120, which means that it’s less preferred than different routing protocols available with lower values. RIP does not support areas or autonomous systems; however, it helps classful and classless addressing modes. Now that we have a basic understanding of what EIGRP and RIP are. Let’s now move on to compare EIGRP vs RIP to understand their differences. Below, we have compared EIGRP vs RIP in a tabular form for better understanding. Now, we have compared EIGRP vs RIP and understood the main difference between the two. EIGRP stands for Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol, and it uses various factors such as bandwidth, load, and delay in order to calculate the optimal path to a destination. OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First, which is a type of link-state routing protocol that uses the SPF algorithm in order to find the shortest path to a destination network. RIP stands for Routing Information Protocol and is a type of distance-vector routing protocol that makes use of hop count as the metric, whereas OSPF is a link-state routing protocol that makes use of bandwidth as the metric. Some of the reasons why EIGRP is used are: BGP stands for Borger Gateway Protocol, which uses path attributes in order to determine the best route to a destination. OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First and is a link-state routing protocol that uses the SPF algorithm in order to determine the optimal path to a destination network. RIP stands for Routing Information Protocol, which uses hop count as the metric in order to select the best path to a destination network. In this blog, we have learned about the difference between EIGRP and RIP. We have seen that EIGRP is a more advanced and efficient routing protocol than RIP, as it uses multiple metrics, supports unequal cost load balancing, maintains multiple tables, and uses a smarter algorithm. However, EIGRP is also more complex and requires more resources than RIP. RIP is a simple and easy-to-configure routing protocol, but it has many limitations and drawbacks, such as using only hop count, having a maximum hop count of 15, maintaining only one table, and using periodic updates.Introduction
What is EIGRP in Networking?
What is RIP in Networking?
Difference between EIGRP and RIP
Factors EIGRP RIP Full form Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol Routing Information Protocol Algorithm Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) Bellman-Ford algorithm Standard Cisco-proprietary routing protocol Industry-standard routing protocol Organization Size EIGRP is best suitable for medium to large organizations’ networks RIP is suited only for small organization’s network Protocol Type Hybrid Protocol (distance vector and link state) Distance vector routing protocol Maximum Hop Count The maximum hop count in EIGRP is 255 The maximum hop count in RIP is 15 Administrative Distance EIGRP AD is 90 RIP AD is 120 Metric Calculation Based on bandwidth and delay Based on the hop count Tables Maintained Neighbor table, topology table, and routing table Routing table and Topology table Autonomous System Support Yes, using the AS number No, RIP does not support AS Symbol in Routing Table EIGRP is denoted by ‘D’ RIP is denoted by ‘R’ Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is difference between EIGRP and OSPF?
Q2. What is the main difference between RIP and OSPF?
Q3. Why is EIGRP used?
Q4. What is the difference between BGP and OSPF and RIP?
Conclusion







