What is VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask)?
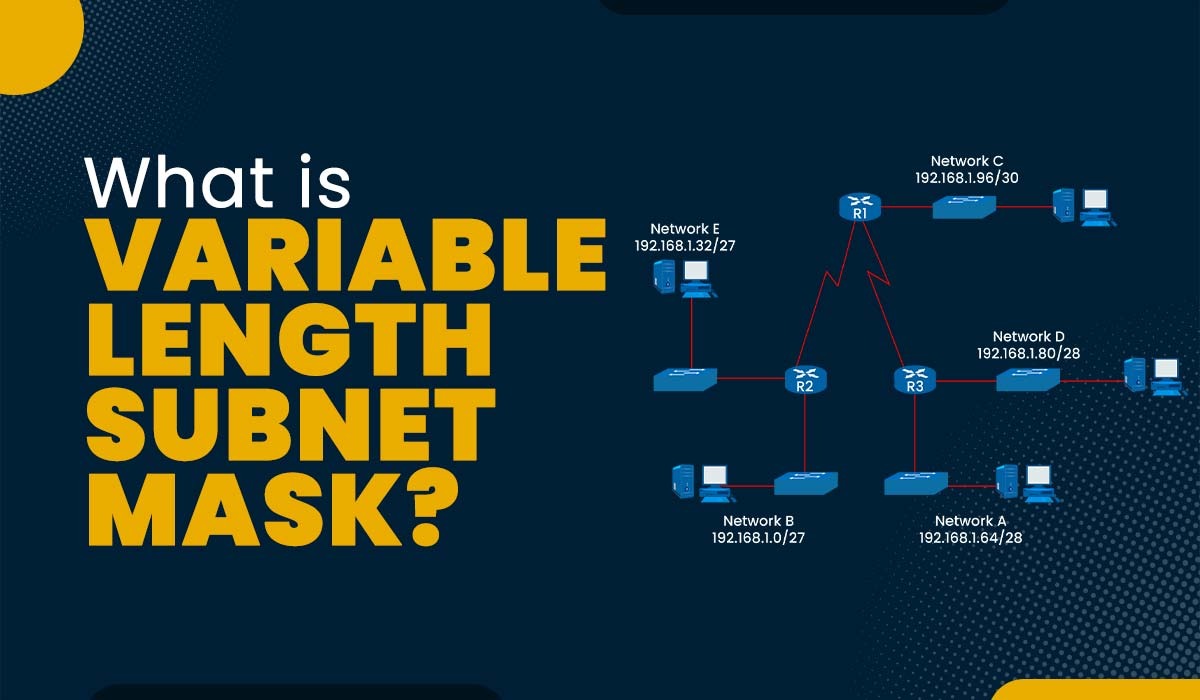
The Internet is a vast network where a number of devices are connected with the help of IP or Internet Protocol. IP addresses are numerical identifiers that are used to uniquely identify each device that is available inside the network. As we all have seen, the internet is growing exponentially day by day, resulting in demand for more IP addresses. This will create a lot of challenges for the networking community. One of the many challenges is the inefficient use of IP addresses for dividing the network into fixed subnets, which can lead to the wastage of IP addresses for different subnets. So, what’s the solution to this problem? To overcome this issue, a technique commonly known as VLSM or Variable Length Subnet Mask was developed. In this blog, we will be discussing what VLSM is, its purpose, and how it works, along with its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s first understand what VLSM really is. VLSM stands for Variable Length Subnet Mask, which is a technique utilized in IP network design to create subnets with different subnet masks. A subnet mask is a 32-bit series of ones and zeros that determines what number of bits of an IP address are used to identify the network prefix and the host identifier. For example, a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 simply means that the primary 24 bits of an IP address deal with the identification of the network prefix, and the last eight bits are used to identify the host identifier. In a traditional subnetting scheme, a fixed subnet mask is applied to all subnets within the network, which can cause inefficient use of IP addresses. For instance, if a network has two subnets, one with 10 hosts and the other with 50 hosts, a traditional subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 would be used for both subnets that we have discussed above; this means that each subnet would have 254 available IP addresses. This could result in wasted IP addresses for the smaller subnet. Variable Length Subnet Mask allows network administrators to create subnets with different subnet masks to efficiently make use of IP addresses. Using the example above, VLSM can be used to assign a subnet mask of 255.255.255.128 to the smaller subnet with 10 hosts, which can offer available IP addresses, and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192 to the bigger subnet with 50 hosts, which might offer 62 available IP addresses. Now that we have a basic understanding of VSLM, let’s move on to the working of VLSM in networking. In order to implement Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM), network administrators must follow these steps: Let’s take an example where a network administrator has a class C network with the IP address 192.168.1.0/24 and needs to create four subnets with varying numbers of hosts; Subnet A requires 100 hosts, Subnet B requires 50 hosts, Subnet C requires 25 hosts, and Subnet D requires 10 hosts. The administrator can utilize VLSM to create these subnets, as explained below. Subnet A The administrator opts for a subnet mask of 255.255.255.128 (/25), which offers 126 IP addresses for hosts. The network address for Subnet A becomes 192.168.1.0/25 and host addresses range from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.126. Subnet B The administrator selects a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192 (/26), providing availability for 62 IP addresses for hosts. Subnet B has a network address of 192.168.1.128/26. The available host addresses for this subnet range from 192.168.1.129 to 192.168.1.190. Subnet C The network administrator chooses a subnet mask of 255.255.255.224 (/27), which allows for 30 IP addresses for hosts on this subnet. The network address assigned to Subnet C is 192.168.1.192/27. The host addresses within this range span from 192.168.1.193 to 192.168.1.222.54. Subnet D The network administrator selects a subnet mask of 255.255.255.240 (/28), which provides 14 available IP addresses for hosts. The network address for Subnet D is 192.168.1.224/28, and the host addresses range from 192.168.1.225 to 192.168.1.238. The network administrator can then configure the routers and hosts with the appropriate IP addresses and subnet masks and use a routing protocol that supports VLSM to exchange routing information. Here are some differences between VLSM and FLSM: Let’s understand the implementation of VLSM in Networking with an example. For example, an office has a huge network that is diversified into many sub-networks such as the HR department, marketing department, and many others. Let’s say we have IPv4 192.168.1.0 that shows up as the office network. The total host addresses on this network can range from 192.168.1.0 (represents the entire network) to 192.168.1.255 (broadcast purposes) which is equivalent to 256 hosts. As we discussed, our office has a human resources department, marketing department, sales department, and IT department. Below are the requirements for the number of hosts for each department. Subnetworks for all departments can be created with VLSM and are shown in the pie chart below. We created sub-networks for different departments indicating that the number of hosts allocated to each department exceeds the number of hosts required. The number of hosts in each department is not the same as in other departments, which is why this is an example of a variable-length subnet mask. Let’s now understand the advantages and disadvantages of Variable Length Subnet Mask. Below, we have explained various advantages of using VLSM. Some of the disadvantages of VLSM are: These are the advantages and disadvantages associated with VLSM in networking. VLSM is a subnet that is a segmented part of a large network that is designed in a way that each subnet mask can have varying sizes. A given IP address 192.168.1.0/24 can be further divided into two subnets with the help of VLSM in the form /25 that can be used for smaller networks and /26 mask that can be used for large networks. VLSM is an important technique because one can easily match the need for the required addresses by segmenting a subnet into smaller subnets as per the size of the network. This will assist in reducing the wastage of IP addresses. VLSM stands for Variable Length Subnet Mask, and FLSM stands for Fixed Length Subnet Mask. VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask) is an IP network design technique that optimizes IP address allocation by using varying subnet masks for subnets based on their host requirements. In this blog, we have covered VLSM in detail, along with its functioning. We also have explained the various advantages and disadvantages of using VLSM.Introduction
What is VLSM in Networking?
How Does Variable Length Subnet Mask Work?
Difference between VLSM and FLSM
Basis Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM) Fixed Length Subnet Mask (FLSM) IP Address Utilization Due to the different sizes of subnets, IP address utilization is maximized. In FLSM, subnet sizes are fixed so IP address utilization is less which can lead to wastage. Flexibility VLSM allows customized subnet sizes as per requirements which provides greater flexibility in network design. FLSM provides less flexibility in network design due to fixed subnet sizes that do not match all requirements. Scalability VLSM creates subnets of different sizes as per requirement due to which it helps in better network scalability. FLSM creates fixed-size subnets that limit scalability, even if they do not keep pace with network growth. Complexity Because of the different subnet sizes and custom configurations, this requires more planning and management. Due to consistent and simple subnet sizes, it is easy to manage. Variable Length Subnet Mask Implementation
Departments Host Required HR Department 87 Marketing Department 47 Sales Department 72 IT Department 50 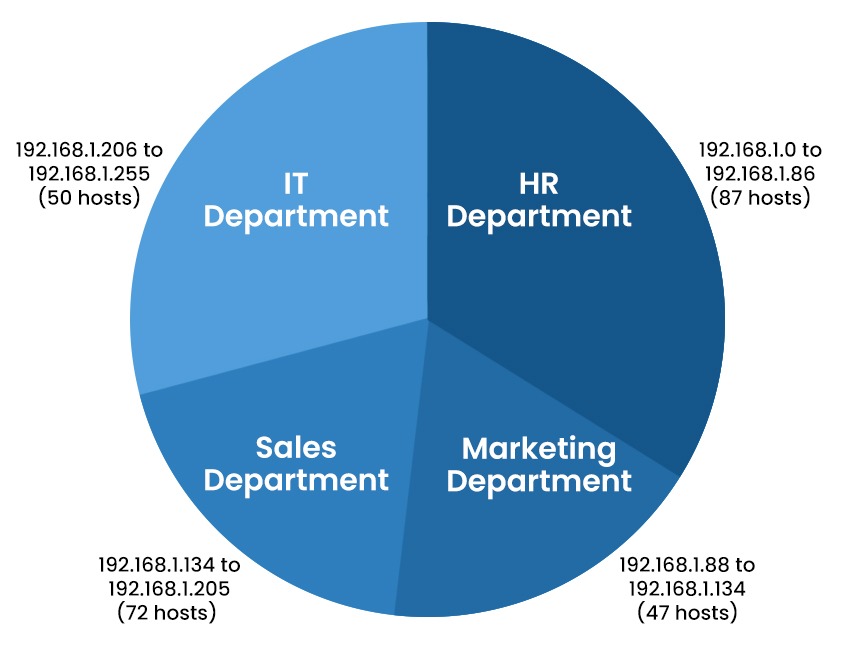
Advantages of VLSM in Networking
Disadvantages of VLSM in Networking
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is a variable length subnetting mask?
Q2. What is an example of VLSM?
Q3. Why is variable length subnet mask important?
Q4. What is the full form of VLSM and Flsm?
Conclusion







