Types of IP Address

The Internet has changed the way we communicate, access information, and share data. With the help of the Internet, one can connect with people as well as devices all over the world, regardless of physical distance or location. But the question that arises now is, how do devices identify each other and communicate? The answer is IP address. IP addresses are numerical labels assigned to each device that wants to connect to the Internet. Some of the examples of such devices are computers, smartphones, routers, etc. In this blog, we will explain what is IP address, different types of IP addresses in networking, and different versions of IP addresses. Let’s first understand what an IP address is. IP stands for Internet Protocol, and it is a set of rules that governs how data is transmitted over the Internet. An IP address is a 32-bit or 128-bit number that uniquely identifies a device on the Internet. An IP address consists of four or eight groups of binary digits separated by dots or colons. For example, 192.168.1.1 or 2001:db8::1 are valid IP addresses. An IP address serves two main functions: An IP address is assigned to a device by a DHCP server, which is a software program that manages the distribution of IP addresses on a network. A DHCP server can assign an IP address dynamically (meaning it can change over time) or statically (meaning it remains fixed). Now we have a basic understanding of IP addresses, let’s discuss different IP address types. There are different types of IP address based on their scope, allocation, and usage. We have classified IP addresses into three categories, i.e., Consumer IP addresses, Website IP addresses, and IP addresses based on Operational characteristics. Let’s Begin! Consumer IP addresses are those users who utilize the Internet. These can be public or private. Private IP addresses can be used within a network, whereas public IP addresses are utilized outside a network. Below, we have explained with the help of an image. A public IP address is an IP address that can be accessed from any device on the Internet. It is also called a primary address or an external address. A public IP address is unique and can be used to locate and identify a device on the Internet. A public IP address is assigned to your router by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Your router then uses a technique called Network Address Translation (NAT) to share this public IP address with all the devices connected to your home network. For example, if you visit What is my IP, you will see your public IP address displayed on the screen. This is the same IP address that other websites or servers see when you access them from your browser. Public IP addresses can be further classified into static and dynamic IP addresses. Let’s understand both these IP addresses in detail. A static IP address is an IP address that does not change over time. It is manually configured by the user or the network administrator and remains fixed until it is changed again. Static IP addresses are usually used for devices that need to be easily identifiable or accessible on a network, such as servers, printers, cameras, or routers. Let’s take an example for better understanding. For example, if you want to set up a web server on your home network, you might assign it a static IP address like 192.168.1.100. This way, you can always access it from any device on your network using this address. A dynamic IP address is an IP address that changes periodically. It is automatically assigned by a DHCP server based on the availability of addresses on the network. Dynamic IP addresses are more common than static ones because they are easier to manage and more efficient in terms of resource utilization. Let’s take an example. For example, if you connect your laptop to a public Wi-Fi network at a coffee shop, you will receive a dynamic IP address from the DHCP server of that network. This IP address will be valid only for the duration of your connection and will be released when you disconnect. A private IP address is an IP address that can only be accessed from devices within your home network. It is also called a secondary address or an internal address. A private IP address is assigned to each device by your router using DHCP. Private IP addresses are not visible to the outside world and cannot be used to communicate with devices on other networks. For example, if you open the command prompt on your Windows PC and type ipconfig, you will see your private IP address displayed under the IPv4 Address. This is the same IP address that you use to access other devices on your home network, such as printers or smart TVs. These are the two Consumer IP Address Types. Let’s now discuss the next one in IP Address types. A website IP address is an IP address that is associated with a website or a domain name. A website IP address can be either dedicated or shared. Let’s understand both of these protocols in detail. A dedicated IP address is an IP address that is exclusively assigned to a single website or domain. It means that no other website or domain can use the same IP address. Dedicated IP addresses are usually more expensive and less common than shared ones. They are mainly used for websites that need higher security, performance, or reliability, such as e-commerce sites, online banking sites, or email servers. For example, if you visit https://www.pynetlabs.com/, you will see that it has a dedicated IP address of 172.67.172.178. This means that only pynetlabs.com can use this IP address, and no other website can share it. A shared IP address is an IP address that is shared by multiple websites or domains. It means that several websites or domains can use the same IP address. Shared IP addresses are usually cheaper and more common than dedicated ones. They are mainly used for websites that do not have high requirements for security, performance, or reliability, such as blogs, forums, or personal sites. These are the two Website IP Address Types. Now, let’s move on to the last one in the list of types of IP Address. There are three types of IP addresses based on their operational characteristics: unicast, multicast, and broadcast. A unicast IP address is an IP address that is used for one-to-one communication between a sender and a receiver. It means that a packet sent from a source device to a destination device with a unicast IP address will be delivered to that specific device only. Unicast IP addresses are the most common type of IP address on the Internet. For example, when you send an email to someone, you use their unicast IP address to deliver the message to their inbox. A multicast IP address is an IP address that is used for one-to-many communication between a sender and multiple receivers. It means that a packet sent from a source device to a destination device with a multicast IP address will be delivered to all the devices that have joined the multicast group associated with that address. Multicast IP addresses are mainly used for streaming media, video conferencing, or online gaming. For example, when you watch a live video on YouTube, you use a multicast IP address to receive the stream from the server along with many other viewers. A broadcast IP address is an IP address that is used for one-to-all communication between a sender and all the receivers on a network. It means that a packet sent from a source device to a destination device with a broadcast IP address will be delivered to every device on the network regardless of their individual addresses. Broadcast IP addresses are mainly used for network discovery, configuration, or maintenance. For example, when you connect your printer to your home network, you use a broadcast IP address to announce its presence and request an IP address from the DHCP server. Learn the difference between Multicast and Broadcast. These are the three types of IP Addresses Based on Operational Characteristics. Let’s now look at the different versions of IP addresses. IP addresses can also be classified based on their versions or formats. There are two versions of IP address: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 stands for Internet Protocol version 4. It is the first and most widely used version of the IP address. It has a 32-bit address space, which means it can support up to 4.3 billion (2^32) unique addresses. However, due to the rapid growth of the Internet and the depletion of available addresses, IPv4 is insufficient to meet the network’s current and future demands. IPv4 addresses are written in decimal notation, which consists of four numbers separated by dots, such as 192.168.1.32. Each number can range from 0 to 255. IPv6 stands for Internet Protocol version 6. It is the latest and most advanced version of an IP address. It has a 128-bit address space, which means it can support up to 340 undecillion (2^128) unique addresses. This is enough to assign an IP address to every atom on Earth and still have plenty left over. IPv6 is designed to overcome the limitations of IPv4 and provide enhanced features such as security, mobility, and scalability. Below, we have shown both the IPv4 and IPv6 IP addresses with the help of an image. Note: one can search for their respective IP address versions in Windows cmd>>ipconfig. The 4 types of IP addresses are: There are two types of IP addresses, namely public and private IP addresses. Private IP addresses are the ones that are used inside a network. Meanwhile, public IP addresses are the ones that are used outside of a network. The four parts of the IP address are: These four sections or hierarchical structures responsible for the proper functioning of computer networks. The two commonly used IP addresses are IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 stands for Internet Protocol version 4, which supports up to 2^32 unique addresses. Whereas IPv6 stands for Internet Protocol version, which supports up to 2^128 unique addresses. IP addresses are crucial for the functioning of the Internet as well as network communication. With the help of IP addresses, devices can share data across the networks. In this blog, we have explained “what is IP address” and types of IP addresses with examples for better understanding. If you have doubts or suggestions, feel free to use the comment section below. We recommend CCNA Course to understand IP Address and its types in detail.Introduction
What is an IP Address?
Types of IP Address
Consumer IP Addresses
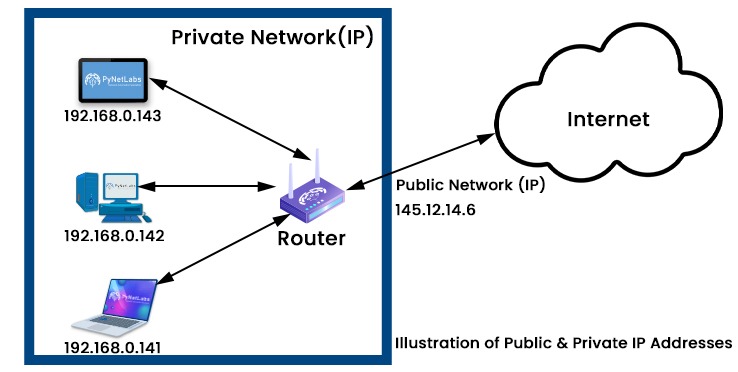
Public IP Address
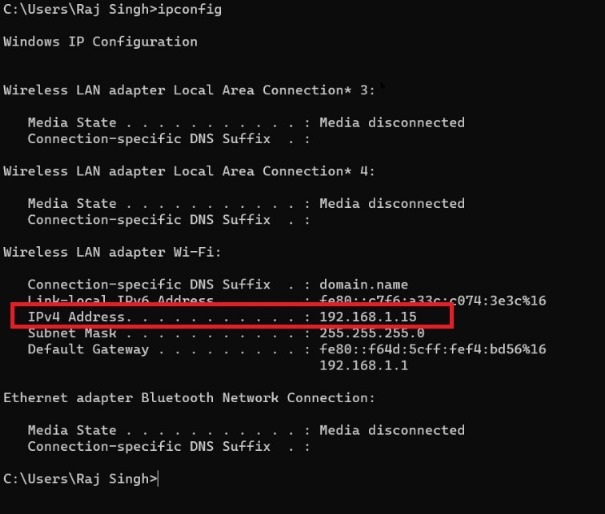
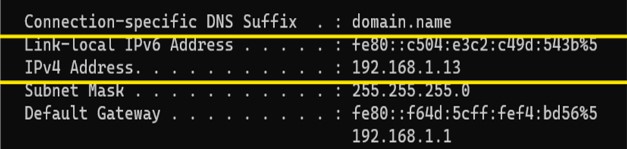
Private IP Address
Website IP Addresses
Dedicated IP Address
Shared IP Address
IP Addresses Based on Operational Characteristics
Unicast IP Address
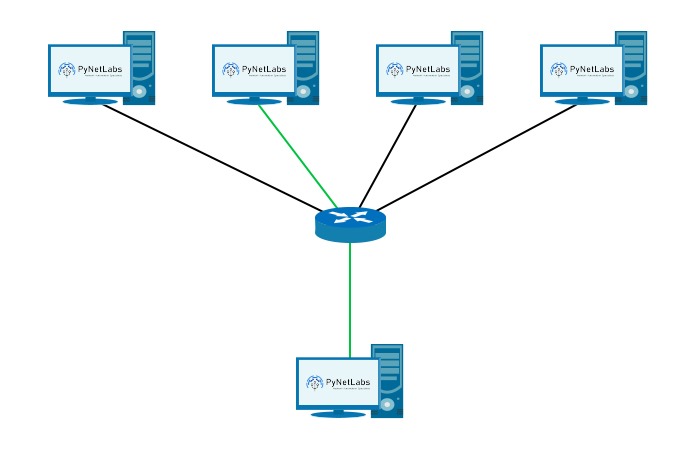
Multicast IP Address
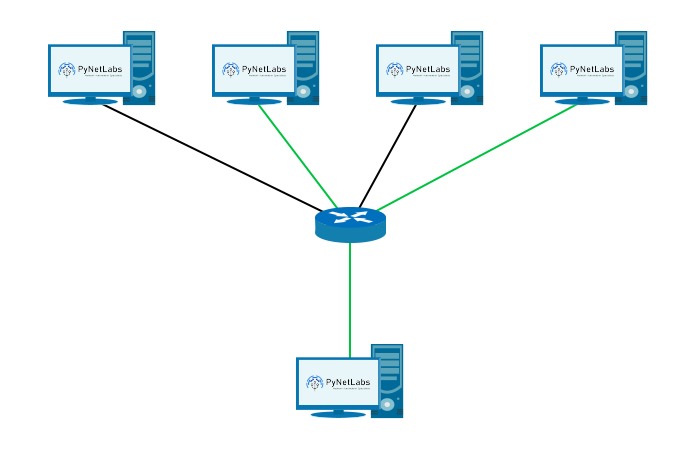
Broadcast IP Address
Versions of IP Address
IPv4
IPv6
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the 4 types of IP addresses?
Q2. Why are there 2 types of IP address?
Q3. What are the 4 parts of the IP address?
Q4. What are 2 commonly used IP addresses?
Conclusion







