What is a Virtual Network?
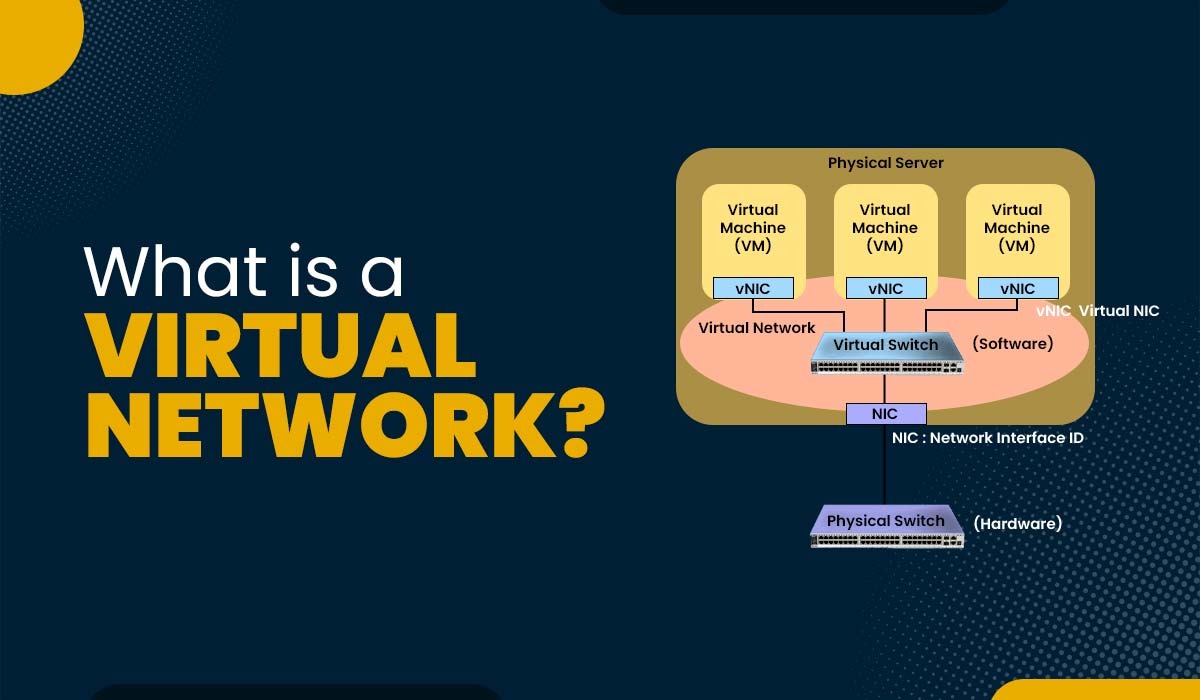
Virtual networks have gained popularity and significance in the field of computing and communication. They offer users the ability to create and manage networks that are independent of the physical infrastructure, such as routers, switches, cables, and servers. It can also isolate and segment traffic from different sources or destinations based on rules and policies. In this blog, we will discuss the virtual network, how it works, its types, and advantages. Before getting into more details, let’s first understand a virtual network. A virtual network is a network that is created and controlled by software rather than relying on physical hardware. It allows various devices like computers, servers, routers, switches, and firewalls to communicate with each other as if they were directly connected by wires or cables. However, in reality, these devices are interconnected through virtual links that utilize the underlying physical network infrastructure. A crucial element within a virtual network is the virtual network interface card (VNIC). VNIC works as a software simulation of a physical network interface card (NIC). It enables devices to connect with the virtual network. VNIC can effortlessly send and receive data packets over the network with the help of its own MAC address. Another significant component of it is the machine (VM). It acts as a software emulation of a physical machine running an operating system along with applications. A VM can be equipped with one or multiple Virtual Network Interface Cards (VNICs), enabling it to establish communication with VMs or devices within the different virtual networks. For a better understanding, let’s compare the physical network and virtual network. Below we have compared both networks in a tabular form based on different factors. Now that we have a basic understanding of these networks, let’s discuss how it works. It operates by utilizing software to generate and oversee network packets, which are the data units that traverse a network. These packets are enclosed with information, like source and destination addresses, and are further directed by either software switches (vSwitch). These switches or routers can be devices or virtual devices running on a host computer. The host computer, being a device, runs one or more VMs (Virtual Machines) and VNICs. It can also have NICs (Network Interface Cards) that connect it to other physical networks. To create and manage the VMs and VNICs, the host computer utilizes a software layer called a hypervisor. Acting as a bridge between networks and physical networks, the hypervisor allows communication between them. Hypervisor is a layer of software that runs on top of the hardware. It oversees the VMs and their VNICs while also having the capability to create and manage switches. These switches serve as software devices connecting VNICs within a network. The hypervisor has the capability to incorporate network functionalities, like firewall, load balancing, NAT, VPN, and more. These functionalities can be implemented as software modules that operate on the switches or routers. Let’s discuss the different types of virtual networks in detail. There are different types of virtual networks depending on different purposes. Below, we have explained three types with examples. These types of networks are mainly used by the devices that belong to them or have access to such types of networks. It creates a secure and isolated virtual environment in order to communicate or send sensitive data between applications. For example, an organization can use such types of networks in order to connect its different branches that are situated at different locations or sometimes to host its internal applications and databases. Now, the internal virtual networks are mainly for the devices that are part of the same server. It is used to divide as well as to organize the traffic and data. For example, an organization can use such type of network in the case when they want to separate their departments or teams. This will give them the opportunity to assign different permissions to different devices or users. An external virtual network is a type of network that is mainly accessible by users outside of a physical network. It is used to connect different networks or services over the internet. For example, an organization can use such types of networks in order to access cloud-based applications or maybe resources. Most of the time, companies use these networks to provide services to their customers or partners. It offers benefits for both users and network administrators, including: The three types of virtual networks are: Private, Internal, and External Virtual Networks. Virtual network devices are mainly the software components that are utilized to emulate the functionality of physical network devices such as routers, switches, etc. One can also configure as well as manage them like real devices. These devices provide more functionalities and scalability than physical devices. There are various uses associated with virtual networks. Some of these are: A virtual network in the cloud is a logical network that connects virtual machines and other resources in a cloud service provider’s data center. In this blog, we have explained the virtual network in detail. We have also compared it with physical network. Apart from that, we have explained the workings of it along with its advantages. If you want to learn more about it, you should move to ENCOR 350-401 Training.Introduction
What is a Virtual Network?
Physical Network vs Virtual Network
Factors Physical Network Virtual Network Hardware Requires physical hardware such as cables, routers, switches, and servers Requires minimal hardware such as a host server and a physical NIC Software Requires less software such as drivers and protocols Requires more software such as vSwitch, network adapter, firewalls, and security Connectivity Connects computers and devices through cabling and other hardware Connects computers and virtual machines through software and wireless technology Management Requires more manual configuration and maintenance of hardware Requires more software-based configuration and management of network services Flexibility Less flexible and scalable as it depends on the availability of hardware resources More flexible and scalable as it can create multiple virtual networks on a single physical network How Virtual Networking Works?
Types of Virtual Networks
Private Virtual Networks
Internal Virtual Networks
External Virtual Networks
Advantages of Virtual Networks
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the three types of virtual networks?
Q2. What are virtual network devices?
Q3. What are the uses of virtual network?
Q4. What is a virtual network in cloud?
Conclusion







