Components of Router
Hey there, if you too, as a kid, used to unscrew all your toys to check what exactly is it made up of? Then this blog is just for you. So today, we will unscrew the most exciting toy for Network Engineers, i.e. a router and look into all the components of this device. Yes, you guessed it right we are going to learn about the Components of a Router. In this blog post, we will explore the main components of a router and how they work together to perform the routing function. We will also discuss the booting process of a router in detail to understand the functioning of routers. Before we get into details, let’s first understand what a router is. A router connects two or more local area networks (LANs) and acts as an intermediary for data exchange between them. To transmit data between two computers on different LANs, routers use the Internet Protocol (IP), which includes the IP addresses of both the sending and receiving devices. Routers are located between these LANs, where the transmitting and receiving devices are linked. Moving on to the components of router. The components of a router are majorly categorised into: 1. External Components 2. Internal Components Let’s discuss both one by one, starting with the external components of router. What does the CPU used for? Well, it is there for computing, but what else? So, everything you are performing is done with the help of the CPU. The algorithms like Dijkstra or DUAL work with the help of the CPU to get things done right. An integral part of each router is its central processing unit. The CPU uses IRQ to talk to the rest of the router’s internal hardware. The CPU of a router handles everything to do with the computerized parts of the router. The central processing unit reads the configuration file and processes the data packets accordingly. The router’s CPU regulates all of the device’s interfaces. It’s something similar to the BIOS chip of our computers. It is used to store the Bootstrap program, required for loading the Operating System of the Router. In Cisco devices, the operating system used is called Cisco IOS (Internetwork Operating System). This operating system is stored inside another component of the router called Flash. It is used for storing the Operating System. When the router is shut down or restarted, the data stored in the flash memory will not be affected. Therefore, the operating system is loaded into RAM from the flash memory whenever the router is switched on. Non-volatile random-access memory (NVRAM) is similar to random-access memory (RAM). This indicates that NVRAM saves data after a router has been powered off. The starting configuration is saved in NVRAM. This is the permanent memory which can be used for storing the configurations. If you want any configurations or changes made on the router permanent, which means that it should not go away even if we reboot the device. Then, we must save the configuration into NVRAM as Startup-config. When a running-config file is used as a source, it copies the routing table and other configuration settings to the startup-config file. The data stored in ROM is fixed and cannot be altered, but NVRAM data may be modified. When turned on, the router only looks in NVRAM for its initial configuration. Like PC RAM, router RAM stores and retrieves data. A router’s random-access memory (RAM) is its fundamental component. Because RAM is volatile, it requires constant power. When switched on or restarted, the router reads the configuration file and the IOS into RAM. It is the main memory used to store the configurations but temporarily. The temporary configurations are called Running-Config, which can be seen using the command “show running-config”. RAM is volatile. If you power off the router, everything you have stored inside the RAM will go away, so make sure you move it to NVRAM by using the command write. Here are some things to understand Router RAM – If someone wants to connect the router to the wire, i.e., a wired connection, multiple interfaces are available to connect to the router. A router can have multiple interfaces or ports, such as Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, or Serial. Each interface or port has a unique name and number that identifies it in the router configuration. Interfaces or ports can also be assigned to different VLANs or sub-interfaces to segment the network traffic. These are the 6 internal components of router. Let’s see external router components. External Components of router include the external ports of the router. These ports are divided into three categories i.e., LAN ports, WAN ports and Admin Ports. This is the port wired to the Wide Area Network or to an external network, which is typically the Internet. This is the port connected to the Local Area Network or, in simpler words, the port which will be connected to your switch. They are used for the administration or configuration of the router with the help of HyperTerminal applications. These ports are available in a variety of categories: These were the external components of a router. After learning about all these components of router, the question comes to mind is, how does this work together to boot up a router? So, let’s understand, how does router works? Whether it’s an email from an employee to a client or a live videoconference, digital data is always transferred in the form of packets via the corporate network and the internet. When sending data via the internet, these packets will include the destination IP address. A router’s job is to determine the best way to deliver IP packets from sending devices to their final destinations. The router keeps track of route-forwarding tables, including the rules that specify the paths for sending data to the local area network. The packet will be sent via the router interface closest to the local area network (LAN) of the device it is destined for. Once a device delivers an IP packet, a router determines the most effective path for it to take over the Internet or an internal network, per quality-of-service agreements. Learn how to configure a router here. Routers can connect LANs and WANs and support various features and functions. Some of the features of routers are: The booting process of router happens in three steps, and it starts with the very first step, performing the POST and loading the bootstrap program. This is the booting process of router explained in three steps. This whole topic is a part of our CCNA training. A router is a networking device that receives and sends data on computer networks. A router consists of the following components: The internal components of routers are: External Components of the router include the external ports of the router. The external components of a router are: The three main functions of a router are: In this blog, we have covered what a router is, how it works, and all the major components of router. A router is a device that connects different networks and routes data packets between them. It has a processor, memory, and interfaces that enable it to perform routing functions. It can also provide security, file-sharing, and content-filtering services for the network and is an essential device for modern network computing, as it allows us to access the Internet and communicate with other devices across different networks. You may also like – Difference between hub, switch and routerIntroduction
What is Router?
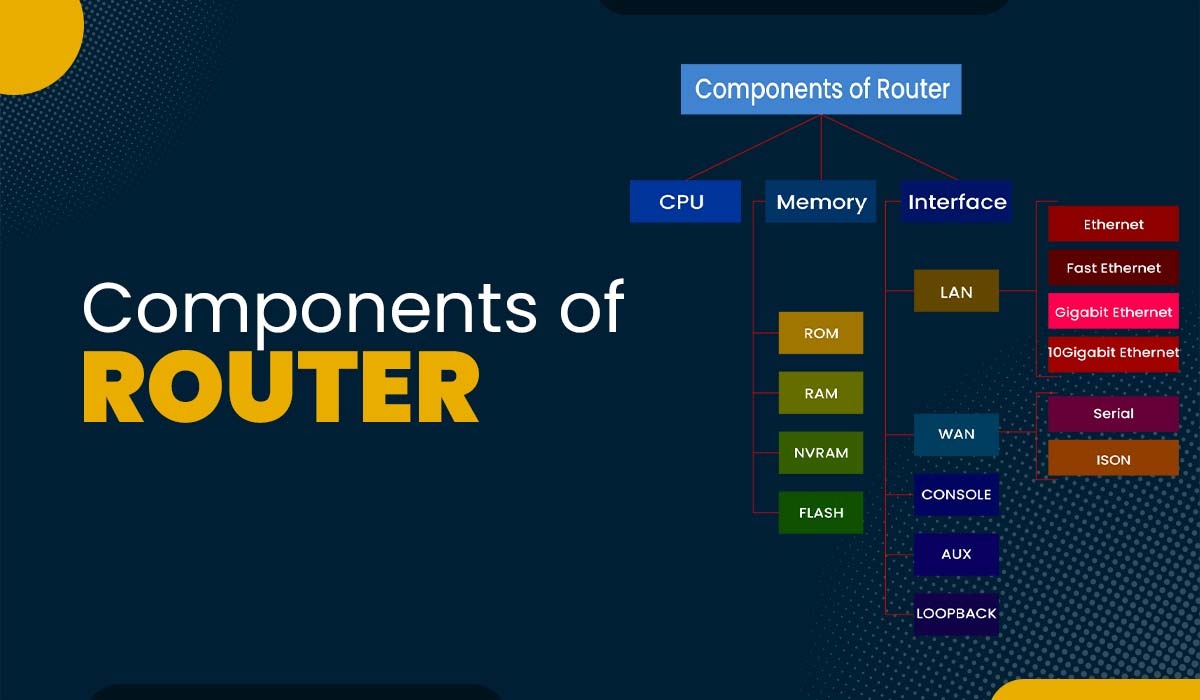
What are the Components of a Router?
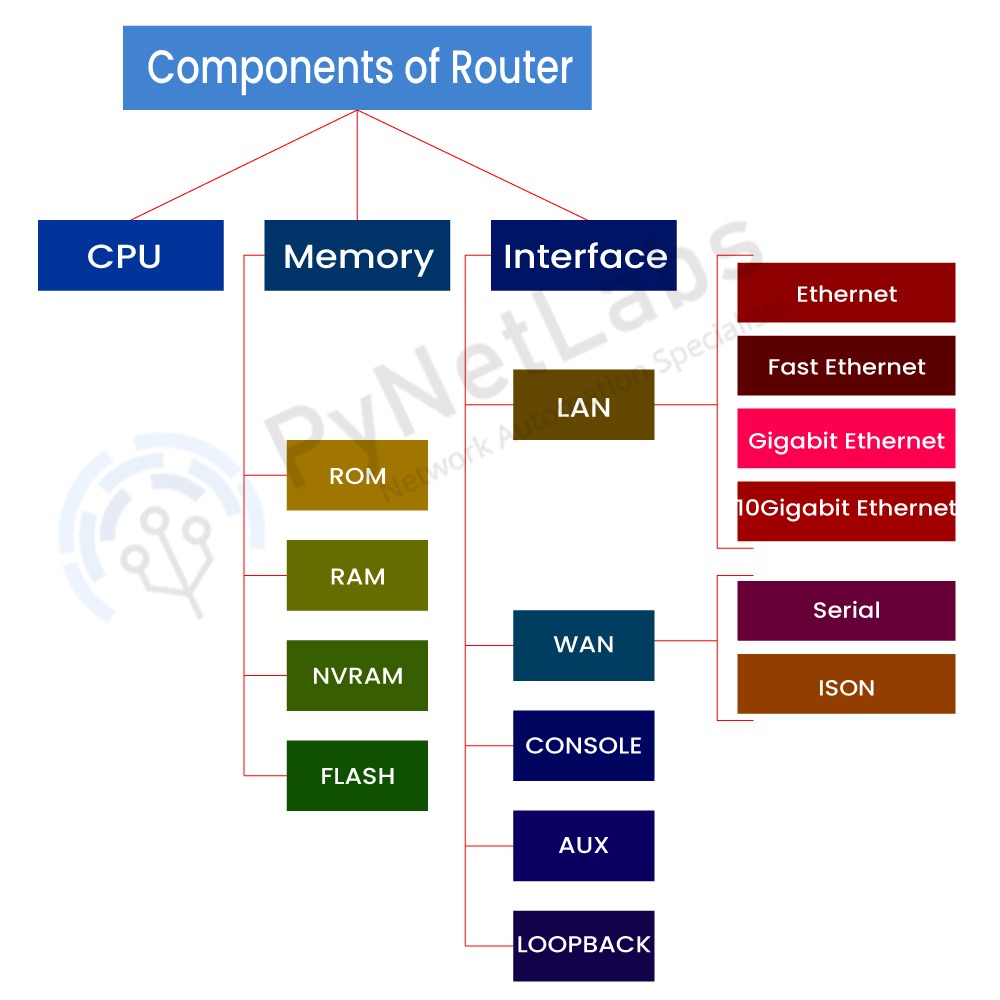
Internal Components of a Router:
1. CPU (Central Processing Unit)
2. ROM (Read Only Memory)
3. Flash
4. Non-Volatile RAM (NVRAM)
5. RAM (Random Access Memory)
6. Interfaces/ports
External Components of Router:
WAN Port
LAN Port
Admin Port
Ethernet
Fast Ethernet
Gig EthernetLAN Port Serial Port WAN Port Console Port
Auxiliary PortAdmin Port How does the router work?
Features of Router
Booting Process of Router
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is a router and its components?
Q2 – What are the internal components of a router?
Q3 – What are the external components of a router?
Q4 – What are the 3 functions of a router?
Conclusion







