VLAN vs Subnet – What’s the difference?
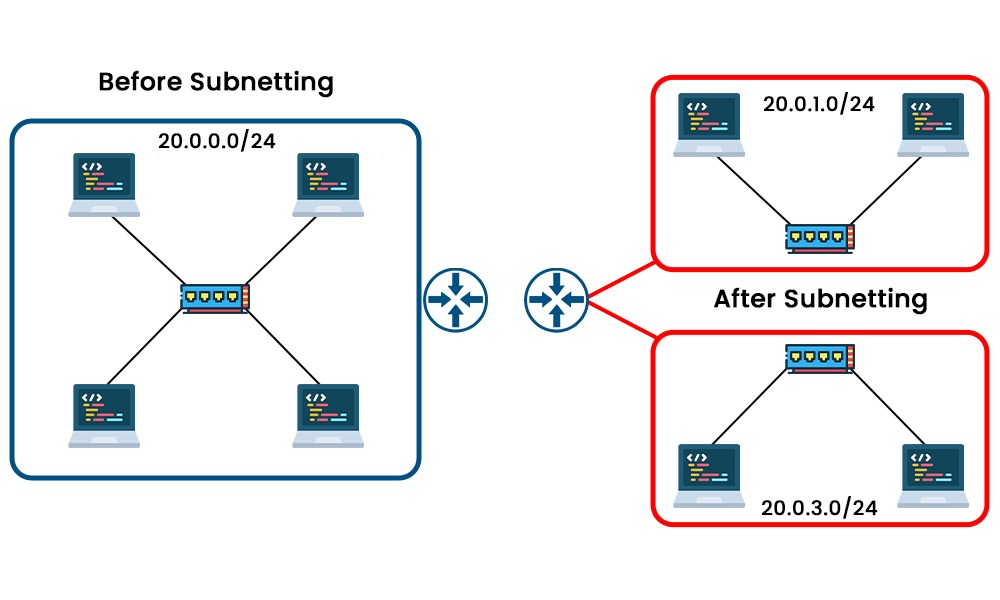
Networking is now crucial to the success of almost every business in the modern digital environment. The importance of understanding how VLAN and Subnet function has grown as networks have expanded in both complexity and size. In this blog, we will explain the basic difference, i.e., VLAN vs Subnet, that will assist in understanding the two concepts more deeply. We will also discuss the basic definition as well as the working of both. Let’s Begin! Below, we have explained the basic difference between the two in a tabular form. We have discussed the basic difference between VLAN and Subnet; let’s now understand these two in detail. A virtual LAN, or VLAN, is a collection of devices that share a virtual LAN connection across several physical locations. With the help of VLAN, one can easily divide a physical network into several virtual networks. Each virtual network has its own set of resources as well as security standards. But the question that arises is why we need VLAN. In a large corporation, there may be several departments or teams with various network requirements. For better understanding, let’s take an example. A company has different departments like marketing, sales, and many others, in a case where the marketing department requires more bandwidth and security as compared to sales teams. In such cases, VLAN can give the marketing department its separate network without physically separating them. The whole process is done by adding a specific header that identifies the VLAN to each Ethernet packet, known as “VLAN tagging.” The switch examines the VLAN tag when a device transmits a frame across a VLAN and only passes the frame to the ports that belong to that VLAN, as you can see in the image below. Here are some of the key advantages of VLANs: Here are some of the key disadvantages of VLANs: Subnet or Subnetwork is a smaller network inside a bigger network. Without the use of routing devices, any IP address within the same Subnet may interact with any other. For easy understanding, think of a subnet as a firm department where employees can interact without leaving their area. In order to reach an outside address of the subnet, a router or modern Gigabit Ethernet switch with router capability must be used to access it. Every subnet is assigned a unique range of IP addresses. As such, no extra routing or access to the main network is required for communication between devices on the same subnet. With the help of a subnet, one can easily increase network performance by lowering the congestion on the primary network. Below, we have shown the subnetting for better understanding. Here are some of the key advantages of Subnet: Here are some of the key disadvantages of Subnet: We have explained VLAN and Subnet in detail. Now let’s dive into a detailed VLAN vs Subnet. Two methods are utilized to build logical networks from physical networks: VLAN and Subnet. But there are some differences between the two; these are: VLAN: With virtual local area networking (VLAN), devices from different locations may be grouped together based on their shared purpose or department of origin. Subnet: Subnets are used to divide a huge network into smaller sections for greater efficiency and availability. VLAN: VLAN utilizes MAC addresses to identify devices and operates at the OSI model’s data connection layer (layer 2). Subnet: Subnet utilizes IP addresses to identify devices and operates at layer 3 of the OSI model, which is the network layer. VLAN: Compared to a Subnet, VLAN offers more security and control since it can separate traffic across different groups of devices and prevent unauthorized access. Subnet: Subnet divides traffic based on network addresses and does not stop broadcast traffic from reaching other subnets; hence, it offers less security and control. VLAN: VLAN is configured at the switch side. It is necessary for VLAN to have a switch that supports VLAN tagging, which adds a VLAN ID to every packet to identify which VLAN it belongs to. Subnet: Subnet needs a router to send and receive packets across several subnets according to their IP addresses. VLAN: VLANs are created and managed by switches; VLAN is primarily a hardware-based technology. Subnet: Subnet depends on routers to construct and maintain subnets; hence, it is mostly software-based. VLAN: Since devices in the same VLAN might be in different physical networks, VLANs create logical networks that can extend over numerous physical networks. Subnet: Devices may only belong to the same subnet if they are on the same network segment; hence, subnets form logical networks that are restricted by physical networks. These is the comparison between VLAN and Subnet. While VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) technology separates various users or groups of users on the same physical network, a subnet is a method of conceptually dividing a network into smaller pieces. A VLAN can have one or more subnets, depending on the network design and configuration. In comparison to subnetting, VLANs provide several benefits, including flexibility, security, and performance. As VLANs may be built and modified without affecting the actual network architecture or cabling, configuring them can save time and money. No, you cannot have a VLAN without a subnet. Each VLAN must have a unique subnet to communicate with other VLANs or networks. VLAN and subnet are fundamental components of network architecture, each displaying unique features and advantages. In this blog, we have covered the basic differences, i.e., VLAN vs Subnet, along with the explanation. If you looking to expand your networking knowledge and understand VLAN and Subnet in detail, you can enrol in the CCNP ENCOR Training.Introduction
VLAN vs Subnet
Factors VLAN Subnet Purpose To create logical segments of devices based on criteria such as function, department, security, etc. To create logical segments of a network based on IP address ranges and reduce broadcast traffic. OSI Layer VLAN operates at the Data link layer i.e., layer 2. The subnet operates at the network layer i.e., layer 3. Configuration Configured at the switch level by assigning ports to different VLANs. Configured at the device level by assigning IP addresses and subnet masks. Security and Control VLANs provide better and more stable network access and can also reduce broadcast traffic and improve network security. Subnets have limited control over network access as compared to VLAN and also improve network performance by reducing network congestion. Hardware/Software Based VLANs are primarily software-based. Subnets are more hardware-based. Logical and Physical Networks VLANs create logical networks that are independent of the physical network topology. Subnets create logical segments of a physical network that reflect the physical network topology. What is VLAN?
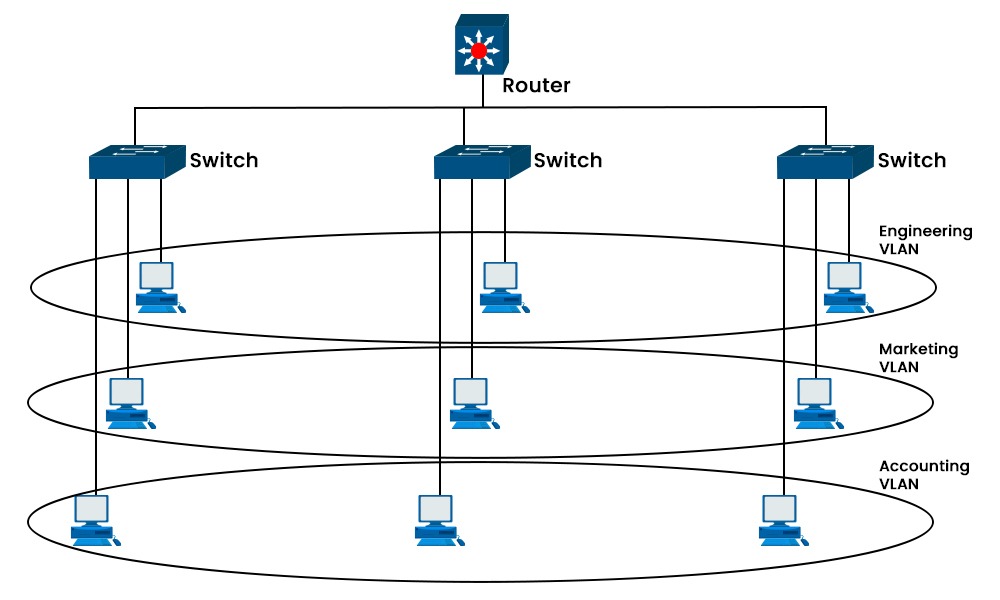
Advantages of VLAN
Disadvantages of VLAN
What is Subnet?
Advantages of Subnet
Disadvantages of Subnet
Difference between VLAN and Subnet
Purpose
OSI Layer
Security and Control
Configuration
Hardware/Software Based
Logical and Physical Networks
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – Is A VLAN the same as a subnet?
Q2 – Does a VLAN have a subnet?
Q3 – Why use VLANs and not subnets?
Q4 – Can you have a VLAN without a subnet?
Conclusion







