BGP vs OSPF – What’s the difference?
Using routing protocols, routers may automatically and dynamically exchange routing data. As each routing protocol has been developed to be ideally suited to a certain network implementation situation, there are several routing protocols to select from, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) are two of the most widely utilized routing protocols in use today. But the question that arises is which one is better. In this blog, we will focus on the fundamental difference, i.e., BGP vs OSPF, and their basic explanation. Let’s begin with the basic difference between OSPF and BGP. The main difference between OSPF and BGP is that OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) used within an autonomous system, primarily focusing on efficient routing within a single network, whereas, BGP is an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) that facilitates routing between different autonomous systems on the internet, prioritizing inter-domain routing and policy-based decision-making. Below we have compared some of the factors of these two protocols. We have explained the fundamental difference between the two; let’s now understand what OSPF and BGP really are. A single Autonomous System (AS) may route packets using the internal gateway protocol (IGP) OSPF. OSPF is a link-state routing protocol, in contrast to other IGPs. In other words, it makes routing choices and calculates route pathways using link-state information. After the beginning of the protocol, each router running OSPF broadcasts link-state advertisements (LSAs) providing details about its connected interfaces and routing metrics across the AS or area. All of the routers in the area get any changes made to any one of the routers. Such an update triggers a repeat of the shortest-path-first algorithm. Each AS is divided into smaller groups termed areas by OSPF. The LSA databases on each router in a given area are identical. The information regarding the other areas has also been summarized. There are several OSPF area types, all of which have been covered in a different blog. Here are some advantages of OSPF – Some disadvantages of OSPF are – BGP or Border Gateway Protocol is a type of external gateway protocol (EGP). BGP is a routing protocol that is mainly used for inter-domain routing. But BGP may also be configured to advertise networks inside an AS and, when doing so, can perform similarly to IGPs. To communicate routing data between routers in the same AS or other ASs, BGP is utilized. A group of routers operating under one administrative authority is known as an AS. The path leading to a destination is an AS path. It also includes a list of the ASs that the route travels through in order to get to a certain router. Additional data is attached to each route in the form of path attributes. In order to modify how the router routes the traffic, routing policies make use of the path attributes. Some advantages of BGP – Here are the same disadvantages of BGP – We now have a basic understanding of OSPF and BGP. Let’s now understand the difference between the two, i.e., BGP vs OSPF, in detail. OSPF and BGP are two routing protocols that are used to exchange information between routers in a network. They differ on the basis of several factors, such as: OSPF: It is mainly used for intra-domain routing, i.e., within the same domain or AS. BGP: It is mainly used for inter-domain routing, i.e., between different domains or ASes. OSPF: Being an inner gateway protocol (IGP), OSPF may only be used in networks that are part of a single autonomous system (AS). BGP: As an external gateway protocol (EGP), BGP communicates with other independent systems or networks that are run by different administrations. OSPF: These are generally easier to implement and configure as compared to BGP. Now, the question that arises is why OSPF are easier to implement. The reason behind this is it uses link-state routing and automatically discovers neighbors as well as adjacencies. BGP: These are complex and require manual configuration of peers as well as policies. The reason behind this is it uses path-vector routing and relies heavily on TCP for reliable communication. OSPF: It converges faster than BGP. The reason behind this is it uses flooding to propagate link-state updates, and whenever there is an update or modification in the network topology, it triggers updates. BGP: As compared to OSPF, BGP converges slower. The reason behind this is it uses incremental updates and applies filters in order to choose the best path for each destination. OSPF: As it keeps a link-state database for each region and uses the Dijkstra algorithm to find the shortest route, OSPF uses more device resources than BGP. BGP: As it maintains a routing table with the optimal route for each destination and employs a straightforward path selection method, BGP requires fewer device resources than OSPF. OSPF: It uses the Dijkstra algorithm, which is a shortest-path-first algorithm. It is mainly used for finding the least-cost path in a network. BGP: In the case of BGP, it uses the Bellman-Ford algorithm, which is mainly a distance-vector algorithm that finds the shortest or lowest-cost path in a network. These are the major difference between OSPF and BGP. BGP and OSPF are both routing protocols. Both these protocols have benefits as well as some drawbacks. But, when we talk about scalability, BGP is generally more scalable than OSPF and is also used for large networks. In terms of the preferred path, OSPF is used to determine the shortest path, while BGP is used to find the best path. There are several differences between OSPF and BGP, but the most important is that OSPF is an intra-domain, whereas BGP is an inter-domain routing protocol. OSPF is faster than BGP in terms of convergence, which means OSPF, as compared to BGP, reacts faster to any network modifications or changes. BGP controls the network layer (Layer 3) by operating on the Open Systems Interconnection transport layer (Layer 4). OSPF and BGP are two routing protocols that differ in many aspects. Understanding the basic difference between the two will assist in choosing the best option for one’s own purposes. In this blog, we have covered the basic differences, i.e., BGP vs OSPF, as well as the basic meaning of both technologies. Join PyNet Labs’ OSPF BGP Training to learn more about these protocols.Introduction
BGP vs OSPF
Factors OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Gateway Protocol OSPF is an internal gateway protocol BGP is an external gateway protocol Type Link State Path Vector Implementation Easy Complex Convergence Fast Slow Design Hierarchical Meshed Need for device resources Memory and CPU intensive Scaling is better but depends on the routing table size Size of the networks Smaller networks that can be managed centrally Larger networks such as the internet Function Prefers the fastest path over the shortest path Prefers best path based on various criteria Algorithm Used Dijkstra algorithm Best path algorithm Protocol IP (Internet Protocol) TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) What is OSPF?
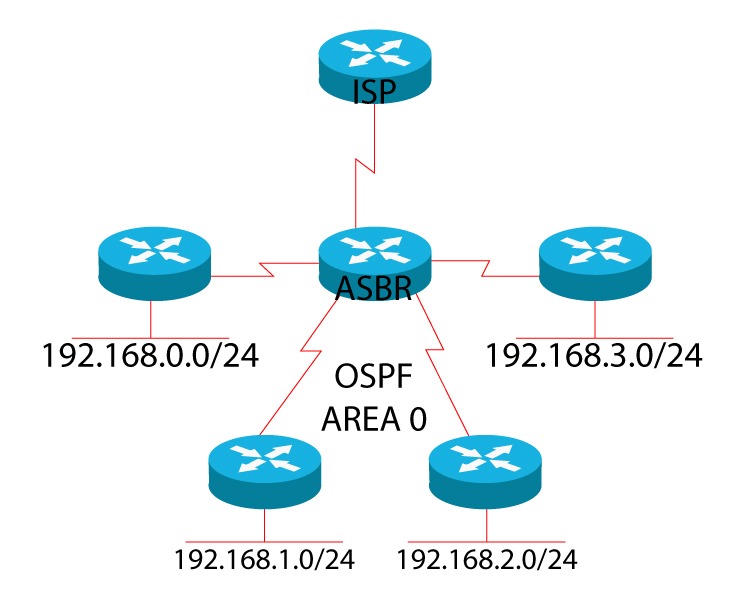
Advantages of OSPF
Disadvantages of OSPF
What is BGP?
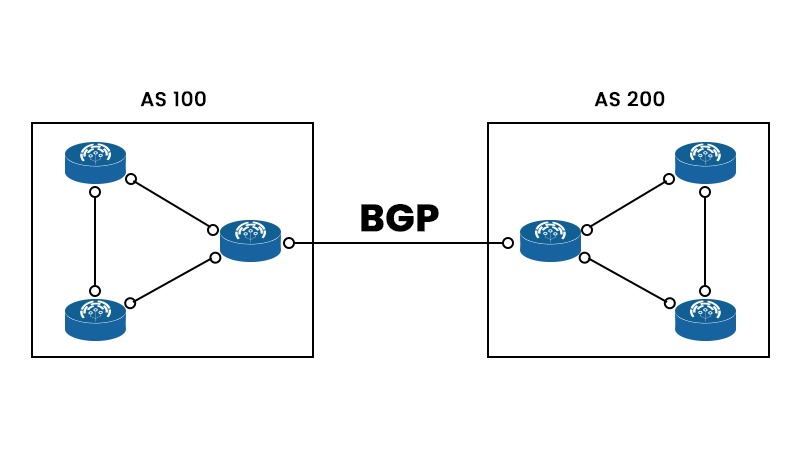
Advantages of BGP
Disadvantages of BGP
Difference between OSPF and BGP
Function
Gateway Protocol
Implementation
Convergence
Need for device resources
Algorithm Used
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – Which is better BGP or OSPF?
Q2 – What is the difference between OSPF and BGP?
Q3 – Why OSPF is faster than BGP?
Q4 – Is BGP a layer 3 protocol?
Conclusion







