What is TFTP Protocol?
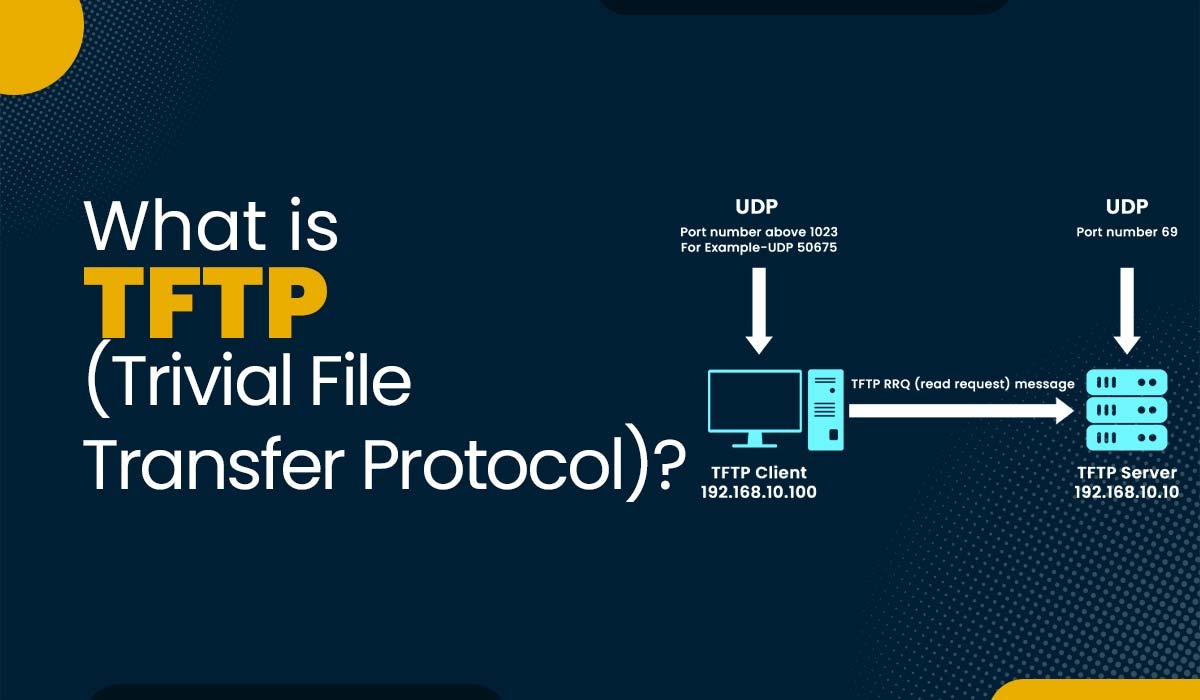
FTP or file transfer protocol is a standard protocol for exchanging files between two devices inside a network. However, FTP also has some drawbacks, such as requiring a lot of resources and having some compatibility issues with different operating systems. That’s why a more straightforward and lighter alternative to FTP is needed. That’s where TFTP protocol or trivial file transfer protocol comes into action. It is lightweight and simple and allows the transfer of files over a network. In this blog, we will be explaining what is TFTP, its purpose, how it works, and its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s first understand what TFTP is. TFTP stands for trivial file transfer protocol that belongs to the application layer of the TCP/IP model. It uses UDP (User Datagram Protocol) as its transport layer protocol. This means it does not guarantee reliable delivery of packets or error detection and correction. TFTP operates on port 69 by default and uses a simple request-response mechanism to transfer files between the client and the server. Now that we have a basic understanding of TFTP, let’s discuss its purpose. The primary purpose of the TFTP protocol is to transfer files over a network simply and efficiently. It is mainly for devices that have limited memory or processing power. Apart from that, TFTP does not require any authentication or encryption. This is the reason it is faster and easier to implement when compared to FTP. TFTP does not authenticate and encrypt, making it less secure and vulnerable to attacks such as spoofing, interception, modification, or deletion of files. Therefore, TFTP can only be used in trusted networks or for non-sensitive data. Let’s move on to the functioning of TFTP. TFTP operates by utilizing a method of communication, i.e., request and response between a client and a server to transfer files. Below, we have explained the step-by-step guide on how TFTP functions. Note: The process is similar to uploading a file from a client to a server, except that the client sends WRQ messages instead of RRQ messages, and the server sends data packets instead of ACK messages. Below are four types of TFTP message formats: It is also called Type 1, and the client uses it to get a duplicate of the file from the server. The read request format is given below. It is also called Type 2 and is used by the client to write a file to the server. The write request format is given below. It is also called Type 3 and consists of a part of the file that is being duplicated. The data block is of fixed size, i.e. 512 octets. The data format is given below. It is also called Type 4, and the data shown at the end of the message consists of an end-of-file (EOF) where the size is less than 512 octets. Both the client and the servicer use acknowledgment to acknowledge the received data. These are the various TFTP Protocol Message Types. The different modes of TFTP are: Here are some applications of TFTP Protocol – The first command used for TFTP service is Copying files from a source location requires the client to have read permissions on that directory and file. To upload files to the destination repository location, the client must have write permission. For example, to retrieve a file named config.file from a remote server named server01, type the command below: The Status and Verbose subcommands are used to confirm TFTP services and to check the documentation or man pages for other options. TFTP is more limited than FTP, and the client does not list, rename, or delete files on the remote system through it, as TFTP is primarily used to transfer files quickly in an automated or scripted manner. Let’s now move on to the advantages and disadvantages associated with TFTP in computer networks. Some of the advantages of using TFTP Protocol are: Besides all the advantages we have discussed, TFTP has some disadvantages. These are: These are the advantages and disadvantages of TFTP – Trivial File Transfer Protocol. TFTP protocol is used for transferring files from one device to another in a network. TFTP uses UDP (User datagram protocol) as UDP is faster and simpler as compared to TCP and also less secure. TFTP is a simple protocol that is mainly used for transferring files which is implemented over UDP/IP protocols at port number 69. The default protocol number for TFTP is 69. TFTP Protocol is a simple and lighter alternative to FTP that allows the transfer of files between two devices in a network. In this blog, we have discussed what is TFTP in computer networks, its purpose, functioning, and advantages and disadvantages. If you have any suggestions or queries, feel free to comment below. Learn CCNA to understand FTP or TFTP Protocols. If you are looking to advance your career, you should go for CCNP ENCOR.Introduction
What is TFTP in Computer Networks?
Purpose of TFTP Protocol
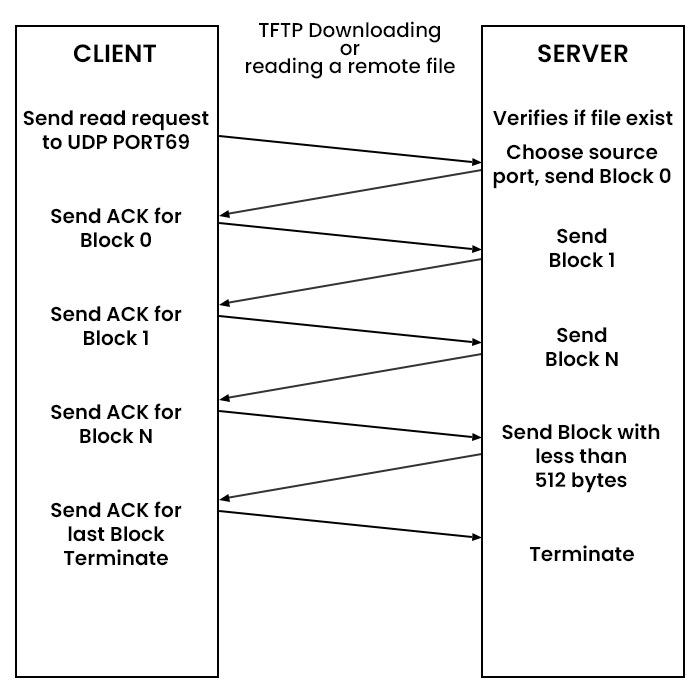
How Does Trivial File Transfer Protocol Work?
TFTP Message Formats
Read request
Read Request (1)
(2 Octets)File Name
(variable)0
(1 Octet)Mode
(Variable)0
(1 Octet)Write request
Write Request (2)
(2 Octets)File Name
(variable)0
(1 Octet)Mode
(variable)0
(1 Octet)Data
Data (3)
(2 Octets)Sequence Number
(2 Octets)Data
(Upto 512 octets)Acknowledgment
Ack (4)
(2 Octets)Sequence Number
(2 Octets)Different Modes of TFTP Protocol
TFTP Protocol Applications
How to use TFTP Protocol?
tftp, and many subcommands are used in this command, which gives additional options. The usage of the utftp command is similar, but it does not overwrite the files while uploading. GET and PUT are important subcommands of tftp and utftp. The put command is used to upload a file to a remote location, and the Get command is used to retrieve a file from a remote location.tftp server01 get config.fileTFTP vs FTP
Advantages of TFTP Protocol in Networking
Disadvantages of TFTP Protocol in Networking
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the TFTP protocol used for?
Q2. Does TFTP use TCP or UDP?
Q3. What port protocol is TFTP?
Q4. What is the protocol number for TFTP?
Conclusion







