What is IGMP Snooping?
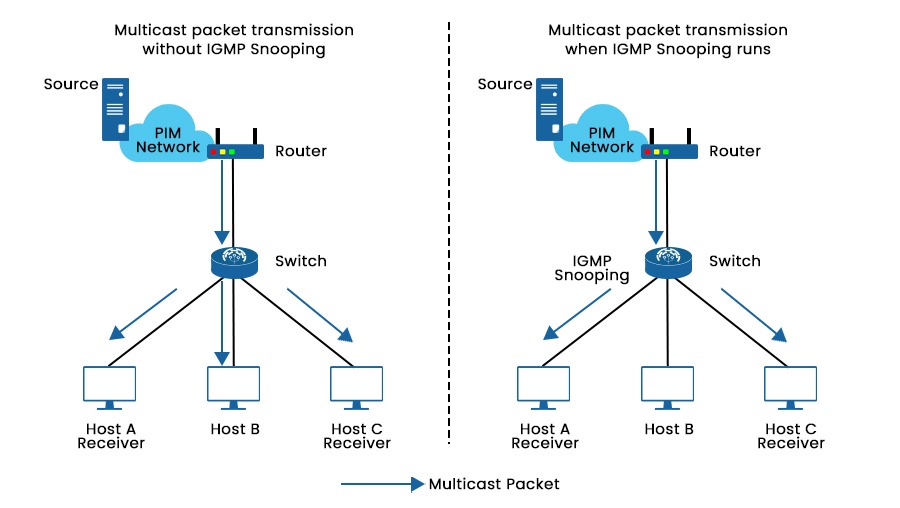
Today’s data transmission demands can’t be met by the inefficient and resource-intensive unicast method used by most networks. Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Snooping was developed as a solution and is now often implemented in network multicast mode. In this blog, we will explain IGMP snooping, its working, functions, and applications. Let’s begin with the basic understanding of IGMP. Network switches use IGMP snooping to limit IPv4 multicast traffic flooding and improve forwarding by transmitting multicast traffic only to interested recipients. Unicast traffic in Cisco switches looks at the Layer 2 MAC address source, which is located in the MAC address table, to identify Layer 2 MAC addresses and their related physical ports. When a received MAC address is not found in the MAC address table, it is considered an unrecognized frame. Consequently, the frame is thereafter sent to all ports within the same VLAN, with the exception of the port from where the frame originated. Recognizing that the destination MAC address in the frame does not belong to them, uninterested receivers simply throw the packet out after realizing this. Note: IGMP snooping is not part of the IGMP protocol, but it is considered an adaptation that switches implement to overcome the limitations of operating at the data link layer. We now have a basic understanding of Internet Group Management Protocol snooping. Let’s understand its working in detail. IGMP messages delivered across the network between multicast-capable devices may be analyzed via IGMP snooping. Hosts use IGMP messages to ask to join or leave a multicast group. This information is used by the switch to identify the network devices that are most interested in receiving multicast traffic. A switch adds a host to the multicast group membership table when it receives an IGMP message from a host asking to join a multicast group. Only those devices that are a member of that multicast group get multicast traffic from the switch after that. The switch removes the device from the multicast group membership table after receiving an IGMP message from a device that no longer wishes to receive multicast traffic. Let’s take an example for better understanding. As we can see in the picture above, Multicast packets are broadcast to Hosts A, B, and C when IGMP snooping is not active on the switch. Whereas when it is active on the switch, the switch can listen for and analyze IGMP messages and create Layer 2 multicast forwarding entries to manage multicast data forwarding. By this, multicast packets are only broadcasted to the interested hosts, in this case, hosts A and C. Here are some of the significant applications of IGMP snooping – One should take into account the following factors when configuring IGMP snooping functions. A multicast router must be installed in the network topology that generates IGMP queries in order to enable Snooping. Without a querier, it is impossible to consistently collect and update group membership tables and IGMP membership reports, which makes Snooping unreliable. In order to produce IGMP report messages from the network switch with multicast memberships, the IGMP Snooping querier, when configured, sends out IGMP inquiries at a scheduled interval. Additionally, IGMP Snooping examines these IGMP reports to determine the proper forwarding. When turned on, the IGMP Snooping switch begins functioning as IGMP Snooping does, and when it receives an IGMP query from a router, it swiftly replies with a report based on its status. When deactivated, hosts’ reports and IGMP requests in the VLAN are flooded. As a result, it reduces the number of reports that an IGMP querier must analyze while also preventing a sudden increase in IGMP report traffic in response to inquiries. Three IGMP protocol versions developed till now are V1, V2, and V3. On a Layer 2 device, you may choose an IGMP snooping version to process IGMP messages in various versions. Generally speaking, IGMPv1 uses the multicast routing protocol to identify the requested router. Group queries, a feature added by IGMPv2, let the querier deliver messages to the hosts in a multicast group. More enhancements for supporting customized source filtering are included in IGMPv3. Let’s understand the benefits and drawbacks of Internet Group Management Protocol snooping. Some benefits of using it on our switches are listed below – By removing unknown MAC addresses, it reduces the possibility of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks from unreliable sources. It is a technique that helps reduce network congestion by minimizing the transmission of packets. This is achieved by selectively forwarding IPv4 multicast datagrams to only those ports on the VLAN that have expressed interest in the multicast stream. By doing so, it prevents all ports from being overwhelmed and ensures that only the relevant ports receive the multicast traffic. Some of the drawbacks of using it are: The switch must process All IGMP messages, adding to the CPU load and delaying the forwarding of multicast packets. Every time the IGMP group membership changes, the switch must update its multicast forwarding table, which may result in temporary interruptions or packet loss for certain streams. IGMP snooping is essential in improving network performance and efficiency, whether it should be enabled or independent (not dependent on the specific environment and needs). In other words, enabling IGMP if multicast traffic comes into the network prevents unnecessary traffic and congestion. But if devices do not support IGMP on the network or the network does not use multicast traffic, there is not as much need to enable IGMP snooping. Additionally, enabling IGMP snooping with older network equipment degrades performance. Ultimately, enabling IGMP snooping depends on carefully considering your network’s needs and capabilities and thoroughly analysing the potential benefits and drawbacks. It depends on your particular network environment and needs whether or not to activate IGMP snooping. It is a crucial function that may boost network performance and efficiency. It is generally advised to enable it if your network has multicast traffic. Internet Group Management mechanism or IGMP is a type of protocol that enables several devices to share a single IP address so they may all access the same data. IGMP is not a security risk by itself, but it can be exploited by attackers to launch denial-of-service (DoS) attacks or to eavesdrop on multicast traffic. IGMP proxy and snooping are two techniques to reduce multicast traffic in a network. IGMP proxy intercepts and processes the IGMP requests from the hosts and forwards them to the upstream router. IGMP snooping listens to the IGMP messages and maintains a table of which ports need which multicast groups. By intelligently routing multicast data, IGMP snooping is an important technique that may significantly increase network effectiveness and performance. It is a useful technique for network administration despite having a few disadvantages.Introduction
What is IGMP snooping?
How Does IGMP Snooping Work?
Applications of IGMP Snooping
IGMP Snooping Configurations Considerations
IGMP Snooping Querier
IGMP Snooping Proxy
IGMP Snooping Version
Benefits of IGMP Snooping
Drawbacks of IGMP Snooping
Should IGMP Snooping be enabled?
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – Should I enable IGMP snooping?
Q2 – What is IGMP good for?
Q3 – Is IGMP a security risk?
Q4 – What is IGMP proxy and snooping?
Conclusion