What is VTP – VLAN Trunking Protocol?
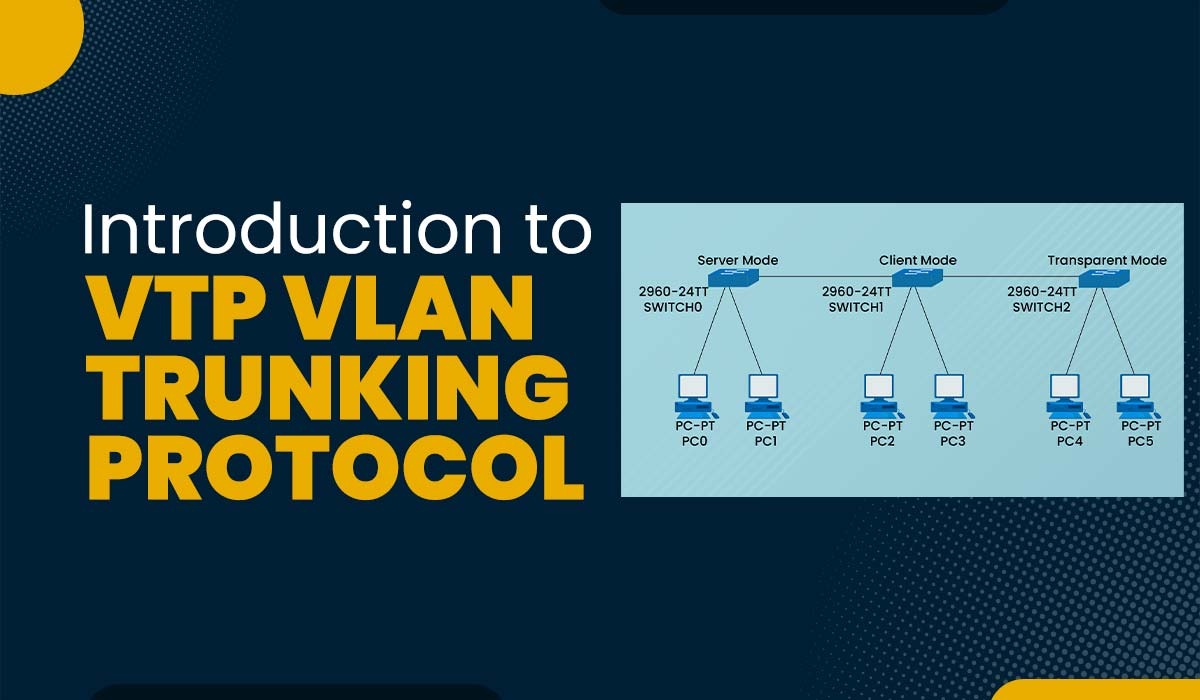
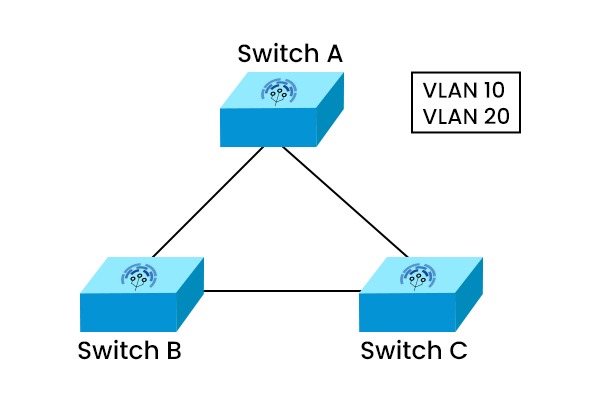
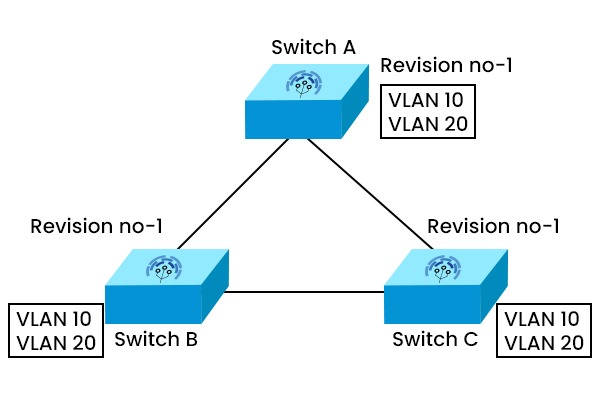
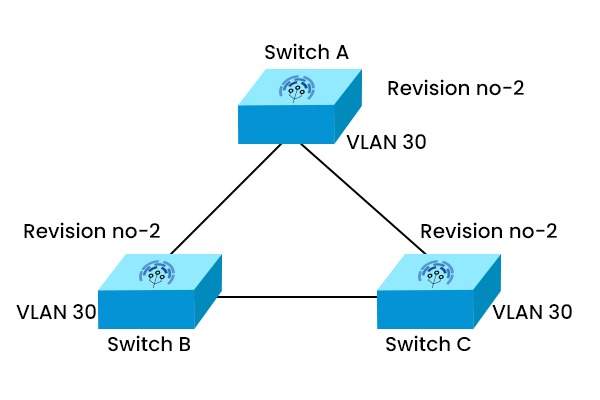
VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol) is a Cisco proprietary protocol used by Cisco switches to synchronize VLAN information across a network. With VTP, network managers can handle VLANs on a single switch and reflect those changes on all other switches in the same VTP domain. It uses trunk links to send and receive VTP messages containing information such as VTP version, domain name, configuration revision number, and VLAN ID and name. The VLAN configurations of all switches belonging to the same VTP domain are made available to one another. VTP can reduce the complexity and errors of VLAN configuration in large networks. Before APIs were available on Cisco platforms, configuring a network switch was a manual process. So, the VLAN trunking protocol was a blessing to network engineers as it reduces the administration in a switched network. Suppose you are working in a large enterprise switched network using hundreds of switches. For each type of traffic, you will need separate VLANs. Now, these VLANs need to be created on all switches, which is a time-consuming task for the network admins. So, to reduce the burden of provisioning VLANs on switches, CISCO came up with this solution: VTP – VLAN Trunking Protocol. VTP (VLAN trunking protocol) is a Layer 2 messaging protocol that maintains VLAN configuration consistency by managing the addition, deletion, and renaming of VLANs within a VTP domain. It is used to store and exchange the VLAN information with multiple switches throughout the network. We can modify the whole network from a single switch (server mode rather than going on every switch to apply or execute the configurations. VLAN Trunking Protocol works by sending VTP messages over trunk links to other switches in the same VTP domain. VTP messages can be of different types, such as summary advertisements, subset advertisements, advertisement requests, and join messages. Each VTP message contains a configuration revision number. When a switch receives a VTP message with a higher revision number than its own, it updates its VLAN database accordingly. Let’s understand with the help of an example. Step 1 Suppose there are three switches, A, B, and C, in the same VTP domain. Switch A is configured as a VTP server and has VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 configured. Switch B and C are configured as VTP clients and have no VLANs configured. Step II When switch A sends a summary advertisement with a revision number of 1, switch B and C receive it and compare it with their own revision number, which is 0. Since 1 is higher than 0, switches B and C update their VLAN database with VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 from switch A. They also increment their revision number to 1. Step III If switch A adds another VLAN, say VLAN 30, it sends another summary advertisement with a revision number of 2. Switch B and C receive it and update their VLAN database again with VLAN 30 from switch A. They also increment their revision number to 2. VLAN Trunking Protocol has two essential technologies: It is used to inspect special information in the VTP domain of an individual frame (MAC address or Layer-3 protocol). The frame tagging method fixes a unique identifier in each frame header as it is redirected to the VTP domain. VLAN Trunking Protocol has three main components: VTP domain, VTP pruning, and VTP advertisements. Let’s understand all three components in detail. The VTP domain limits the extent of configuration changes throughout the network in the event of an error. A switch belongs to a singular VTP domain at any given moment. Establishing or changing VLANs in a VTP server mode is impossible until the VTP domain name has been provided. This particular component comprises one or more interconnected switches. Also known as VTP messages. It comprises VLAN information and is delivered to other switches by VTP servers periodically. It is distributed so that all of a VTP domain’s VLAN configuration is in sync with one another. VTP uses a multicast address for advertising its updates across the trunk links to all the switches in the VTP domain. Multicast Address 01-00-0C-CC-CC-CC VTP pruning reduces unnecessary broadcast traffic on trunk links by pruning VLANs that are not needed on a switch. VTP pruning can improve network performance and bandwidth utilization. VTP Configuration Revision Number Note: – Before adding a switch to the existing VTP Domain, ensure the new switch has VTP revision (0) because as long as the revision number is higher, the switch will accept the update from that switch which is having higher revision number. Here are three kinds of VTP advertisements: 1. Summary Advertisement VTP summary advertisement occurs every 300 seconds if there are some changes in the VLAN database. This advertisement contains details such as VTP version, number of sub-advertisements followed, domain name, revision number, timestamp, etc. There are one or more sub-advertisements that follow the summary advertisement when the VLAN configuration changes. 2. Subset Advertisement After changes to the VLAN configuration, all details for the VTP client to sync the VLAN database to the server are contained in this VTP Subset Advertisement. 3. Advertisement Requests from Clients VTP requests share advertisements by clients to obtain VLAN information. After getting the summary advertisement, the higher CR value in the summary advertisement is checked by VTP clients, so for more profound subset advertisements, it shares a request advertisement with the clients. The three modes of VLAN Trunking Protocol are – There have been 3 VTP versions to date, and these are: Note: VLAN Trunking Protocol has many advantages, some of these are: Join our CCNA training for complete notes of the VLAN Trunking Protocol. For more information, go to the CCNA training page. Meanwhile, you can explore deeper depth to VTP in this video with our trainer Mr Abhijit Bakale. VTP is a CISCO proprietary protocol that is used to ensure consistency across the network. It is also used to synchronize the VLAN information within the VTP domain. It lets network administrators modify, remove and add VLANs which are then transmitted to other switches within the VTP domain. VTP stands for VLAN trunking protocol, whereas STP stands for Spanning Tree Protocol. VTP is the Cisco intellectual protocol used to transmit VLAN on the whole local area network. STP is a layer-2 network protocol, and it is used to prevent looping in a network topology. There are 3 VTP modes: Server, Client, and Transparent. Server mode is the default mode for Cisco switches allowing for creating, adding, and removing VLANs. In the client mode, the clients switch only receives the advertisements from server switches. In contrast, in the transparent mode, the switch doesn’t send or receive the VLAN database from VTP server switches, but it can pass the VLAN traffic to other switches connected to it via trunk links. The three modes of VTP are: In this blog, we have covered everything related to VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP), such as the working of VTP, its components, and the benefits associated with VTP. The VLAN Trunking Protocol is regarded as the core of VLANs in large-scale networks since it totally simplifies and transparently manages every switch on your network.Introduction
What is VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) in Networking?
How VLAN Trunking Protocol works?
Techniques of VLAN Trunking Protocol
Frame Filtering
Frame Tagging
What are the components of VTP in networking?
VTP Domain
VTP Advertisements
VTP advertisements consist of,
Conditions to configure VTP
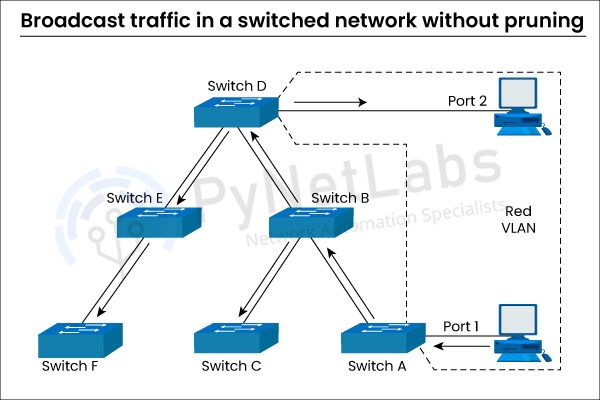
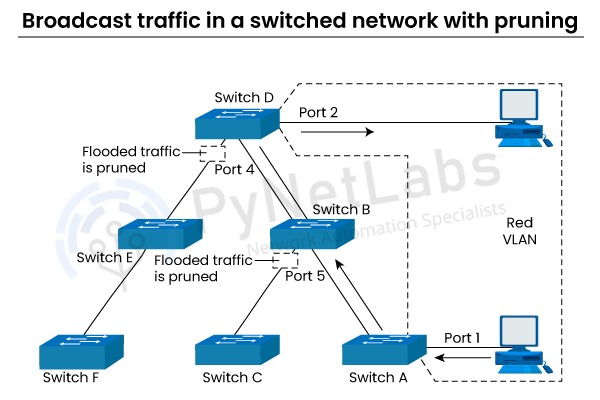
VTP Pruning
Kinds of VTP Advertisements
Modes in VTP
Server Mode
Client Mode
Transparent Mode
VTP Versions
VTP Version 1
VTP Version 2
VTP Version 3
Advantages of VLAN Trunking Protocol
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is VTP used for?
Q2 – What is VTP and STP?
Q3 – What is VTP mode?
Q4 – What are the three modes of VTP?
Conclusion







