What is Switching in Networking?
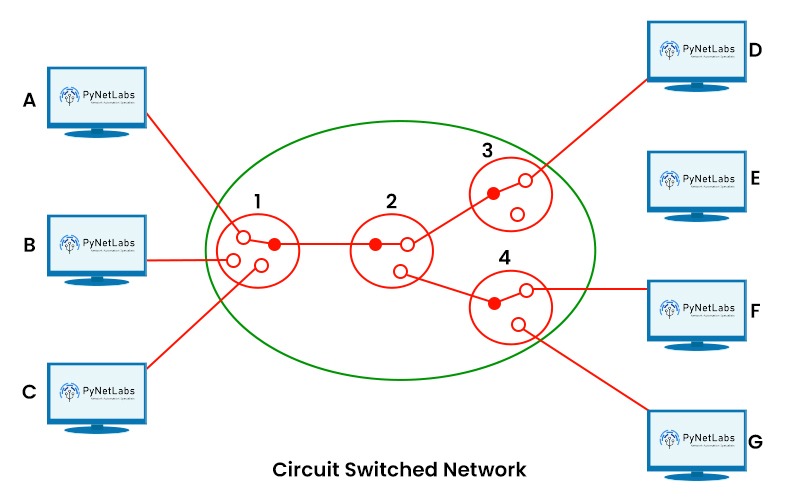
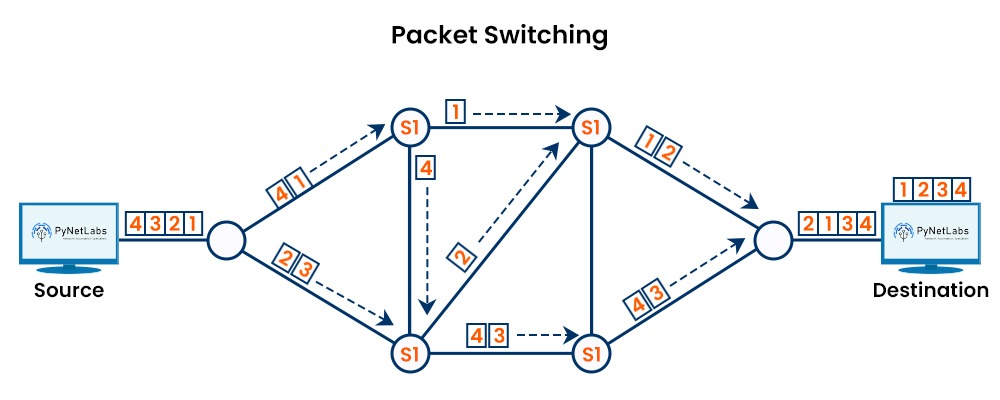
Switching is not a new concept in data communication. Since the early days of telephony, switching has been part of communication where operators manually connected calls via switchboards. As time passes, so do technological advancements, and with the growth of data networks, switching now has become more automated. But what do you mean by switching in networking? Switching is a process of transferring data packets from one device to another in a network using specific devices called switches. In this blog, we will be explaining switching, its types, and the different techniques used in the process of switching. Let’s first understand what switching really is. Data packets are transferred utilizing switches from one network to another or from one device to another during the process of switching. A switch is a piece of hardware that operates at the OSI model’s data link layer, i.e., layer 2. Incoming data packets from a source device or network are largely handled by a switch, which also selects the best port through which the data packets will go to their destination device or network. A switch uses the destination MAC (Media Access Control) address to determine which port a data packet should travel through. Every network interface card (NIC) in a device is given a specific identification number called a MAC address. Switching in networking is mainly divided into two parts. These are: We have a better understanding now of what is switching and its types. But the question that arises now is What is a Switch and how does the switch works. Below, we have explained the switching process in detail. A switch connects devices in a network to each other which allows them to communicate by exchanging data packets. These can be hardware devices that maintain the physical network or software-based virtual devices. The switch executes at the data-link layer, or Layer 2, of the OSI model and looks at the MAC addresses in the LAN via Ethernet to determine where to share each incoming message frame. Switches maintain tables that correspond to each MAC address of the port receiving the MAC address. The switch generally involves the following steps: The switching process includes the following steps: Here are the following reasons that define why switching is needed: Let’s understand the different types of switching techniques in detail. Switching techniques are methods of implementing switching in networking. Mainly, there are three types of switching techniques that are commonly used in data communication. These are: Circuit Switching is a type of connection-oriented switching technique. It means that it establishes a physical or logical path between the source and the destination prior to sending any message. A circuit here is defined as a dedicated channel that transmits data continuously. It can be either permanent or temporary. As you can see in the image below, a circuit switch network with 4 switches connected to each other. Some examples of circuit switching in networking are Analog telephone networks, PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Networks), and many more. Packet switching is a type of connectionless or connection-oriented switching technique that divides the message into units of variable length known as packets, each of which is given a source and destination address. Without buffering or sequencing, the switches independently forward the packets. Depending on the network configuration and the availability of pathways, the packets may travel different paths to reach their destination. The packets are put back together by the destination device to form the original message. Packet switching is suitable for applications that require efficient and flexible communication, such as web browsing or streaming. Packet switching is further classified into two, i.e., Datagram switching and virtual circuit switching. Message switching is a type of connectionless switching technique that stores and transmits data units as a whole message. The message is divided into fixed-length units, also known as blocks. These blocks are assigned with the sequence number as well as the destination address. Until the switch finds the path to the next switch or the destination device, the blocks are stored in buffers. Once the blocks reach the destination, the destination device reassembles the block into the original message. Here, messages can be of any size and format. This type of switching technique is suitable only for applications that do not require real-time communication. Some of the examples are email, file transfer, and many others. We now have a better understanding of the switching and its types. We also have discussed different switching techniques. Let’s discuss the advantages and disadvantages of switching in networking. Some of the advantages of switching in networking are: Here are some disadvantages of Switching – These are the advantages and disadvantages of Switching in Networking. The transmission of data packets or blocks across a network switch is known as switching in information technology and computer networking. Switches transmit data from source ports on computers and other devices to destination ports on routers and other devices. Mainly, there are three methods of switching. These are: Switching is the process of transmitting packets from one host to another inside a Local Area Network (LAN). Routing is a method of doing that between two or more local area networks. Switching in networking is the process of transferring data between devices or networks. There are two types of switching. These are: Switching is a vital process in data communication that enables efficient and secure data transfer between devices or networks using switches. In this blog, we have explained what is switching in networking and its types, how it works, different types of switching techniques, and its advantages and disadvantages. Switching is an important topic for CCNA Exam. So, if you are preparing for CCNA Certification, or taking CCNA Training, you should learn Switching in Depth.Introduction
What is Switching in Networking?
What is a Switch?
How Does Switch Work?
Process of Switching
Why is Switching Required?
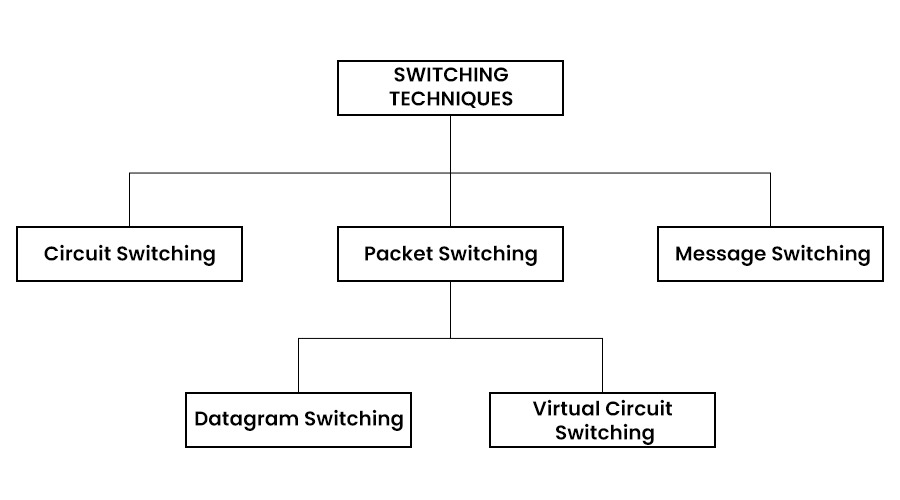
Types of Switching Technique
Circuit Switching
Packet Switching
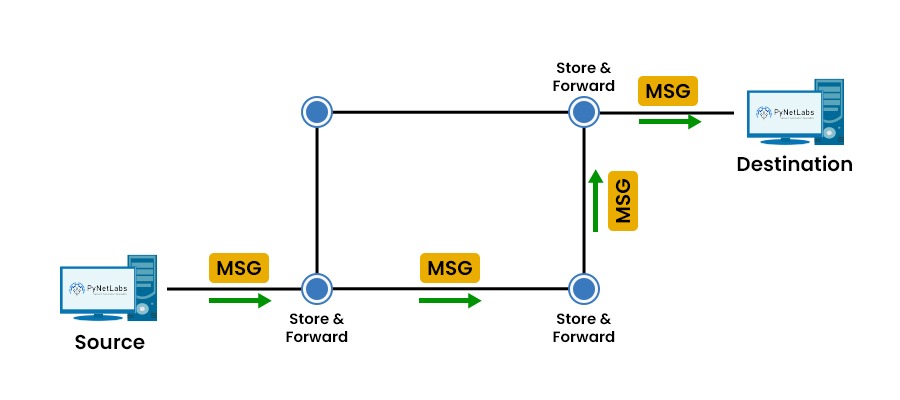
Message Switching
Advantages of Switching
Disadvantages of Switching
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What do you mean by switching network?
Q2 – What are the methods of switching?
Q3 – What is routing and switching?
Q4 – What is switching and types?
Conclusion







