iBGP vs eBGP – What’s the Difference?
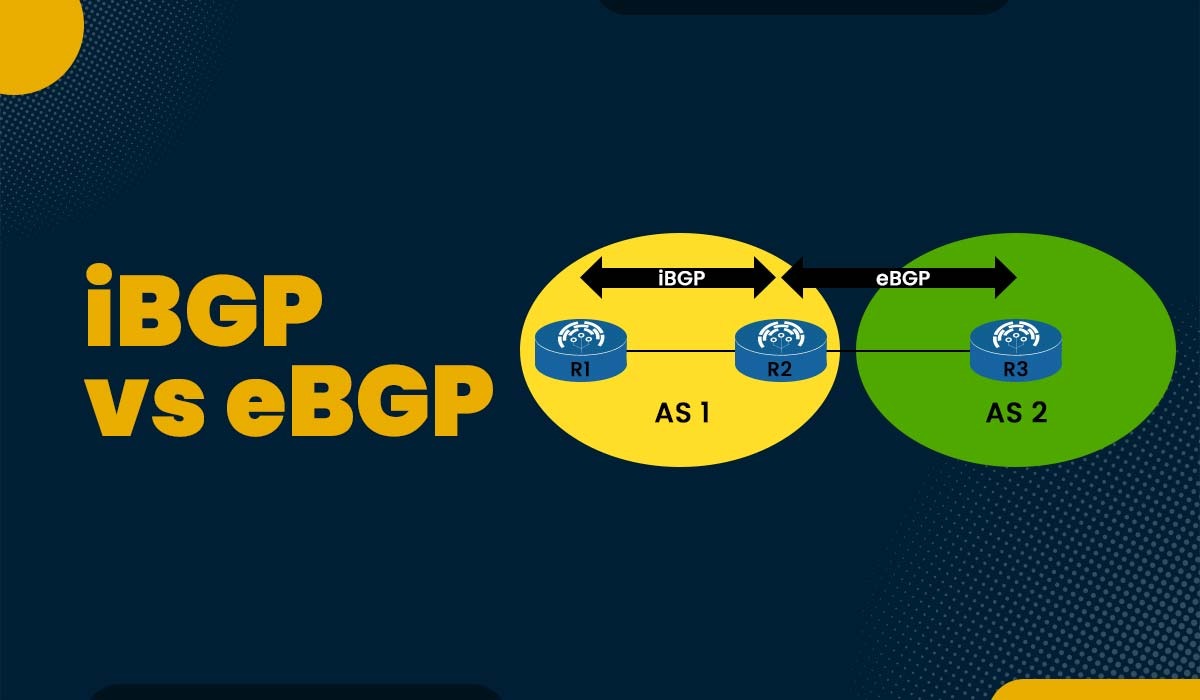
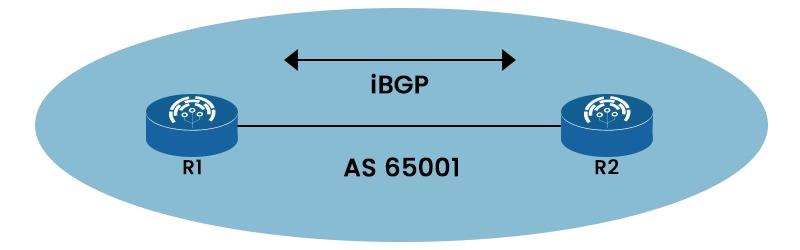
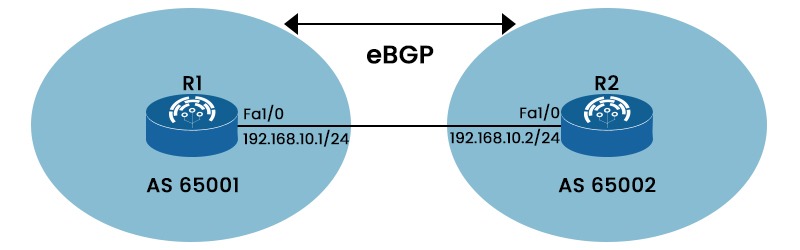
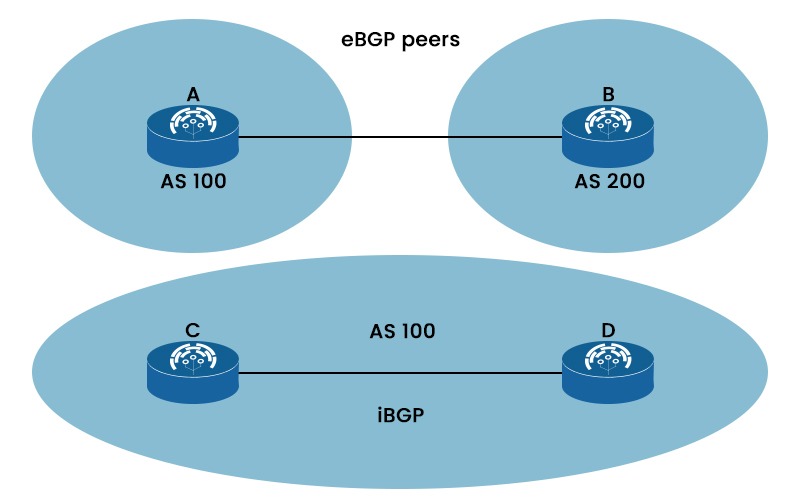
One of the foundations of modern networking is the border gateway protocol or BGP. Without BGP working in the background to allow system communication, the modern internet as it is known today would not be able to operate. The routing protocol known as BGP has two different versions, i.e., eBGP and iBGP. Both provide the best routing pathways for network communications. In this blog, we will look into the detailed iBGP vs eBGP that better explains these two versions. We will also explain both in detail separately. Let’s Begin! iBGP and eBGP are part of the BGP protocol which is covered in OSPF BGP Course. Let’s see the basic difference between the two. Below, we have explained the difference between the two in tabular form based on different factors. Let’s focus on the eBGP and iBGP in detail to understand the comparison of iBGP vs eBGP. Internal Border Gateway Protocol or iBGP is a BGP version used by routers in the same autonomous system (AS). Without using an IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol), iBGP enables routers to share routing data about external networks, such as the Internet. To avoid routing loops, iBGP peers must create a full mesh topology. iBGP bases its routing choices on network regulations and rulesets by using BGP features like local preference. Below, we have shown iBGP with two routers, R1 and R2. An external Border Gateway or eBGP allows communication between several autonomous systems (AS). Network connections via the Internet or between various organizations are made possible by eBGP. eBGP operates in the opposite manner of iBGP, i.e., inside the same AS. eBGP routes don’t need a full mesh topology and have an administrative distance of 20. Now we have a basic understanding of eBGP and iBGP. Let’s understand the difference between iBGP and eBGP in detail. Below, we have compared iBGP vs eBGP in detail based on different factors. While IBGP is used for routing information sharing between routers within the same autonomous system, EBGP is used for routing information exchange between routers in different autonomous systems. As you can see in the picture above, router A in AS 100 and router B in AS 200 are eBGP peers, while router C and router D in AS 100 are iBGP peers. While iBGP peers might be indirectly linked and have the same AS number, eBGP peers are often directly connected and have separate AS numbers. We have shown this in the picture above. iBGP routes obtained from an iBGP peer cannot be advertised to another iBGP peer but may be advertised to an eBGP peer. Conversely, eBGP routes obtained from an eBGP peer can be advertised to both eBGP and iBGP peers. When advertising routes to an eBGP peer, eBGP adds the local AS number to the AS path, but iBGP does not modify the AS path when advertising routes to an iBGP peer. In contrast to iBGP, which sends attributes like local preference to iBGP peers, eBGP does not send such information. The default administrative distance for eBGP is 20, while the default administrative distance for iBGP is 200. This indicates that eBGP routes are automatically favored over iBGP routes. For example, if router A gets two routes from routers B (having AD 100) and C (having AD 200) for the same destination, it will choose the route from router B since it has a lower AD. The default TTL for eBGP peers is 1, while the default TTL for iBGP peers is 255. This implies that iBGP peers might be many hops away; eBGP peers must be directly linked. iBGP needs either a complete mesh topology or one of the route reflectors, while eBGP does not. This is so because iBGP forbids peer-to-peer route redistribution. For example, if an AS has four routers (C, D, E, and F), they must form a complete mesh topology or use other techniques to ensure they all share the same routes. iBGP employs BGP split horizon for loop avoidance, while eBGP uses AS path. This implies that although iBGP accepts routes with the same originator ID or cluster list, eBGP does not allow routes with its own AS number in the AS path. These are the main difference between iBGP and eBGP. eBGP is preferred over iBGP for many reasons, some of these are: TTL stands for time-to-live. The main difference between the eBGP and iBGP TTL is that eBGP packets have a default TTL value of 1 whereas in the case of iBGP, packets have a TTL value of 255. iBGP stands for internal border gateway protocol, and it’s one of the versions of BGP. iBGP is a protocol for exchanging routing information within an autonomous system. It also assists in ensuring consistent and efficient routing among routers within the same network domain. Both eBGP and iBGP are routing protocols crucial to the functioning of modern computer networks. iBGP vs eBGP gives a clear understanding of which one to choose for better productivity. In this blog, we have covered the detailed differences between the two BGP versions and a brief explanation.Introduction
Difference between iBGP and eBGP
Factors iBGP (Internal Border Gateway Protocol) eBGP (External Border Gateway Protocol) Scope Established between routers in the same AS. Established between routers in different autonomous systems. Neighborship Established between routers in the same AS. Established between routers in different autonomous systems. Route advertisement Routes received from an iBGP peer cannot be advertised to another iBGP peer but can be advertised to an eBGP peer. Routes received from an eBGP peer can be advertised to both eBGP and iBGP peers. AS path addition The local AS number is not added to the AS path attribute when advertising a route to an iBGP peer. The local AS number is added to the AS path attribute when advertising a route to an eBGP peer. Attributes Local preference attribute is sent to an iBGP peer. Local preference attribute is not sent to an eBGP peer. AD The default administrative distance is 200. The default administrative distance is 20. TTL Default peers are set with TTL = 255. Default peers are set with TTL = 1. Topology Requires full mesh topology. Does not require full mesh topology. Loop prevention mechanism Uses BGP split horizon for loop prevention. Uses AS path for loop prevention. What is iBGP?
What is eBGP?
iBGP vs eBGP
Scope
Neighborship
Route Advertisement
AS Path Addition
Attributes
Administrative Distance
Time-to-live
Topography
Loop Prevention Mechanism
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – Why is eBGP preferred over iBGP?
Q2 – What is the difference between eBGP and iBGP TTL?
Q3 – What is the full form of iBGP?
Q4 – What is the purpose of iBGP?
Conclusion







