Difference between SD-WAN and Traditional WAN
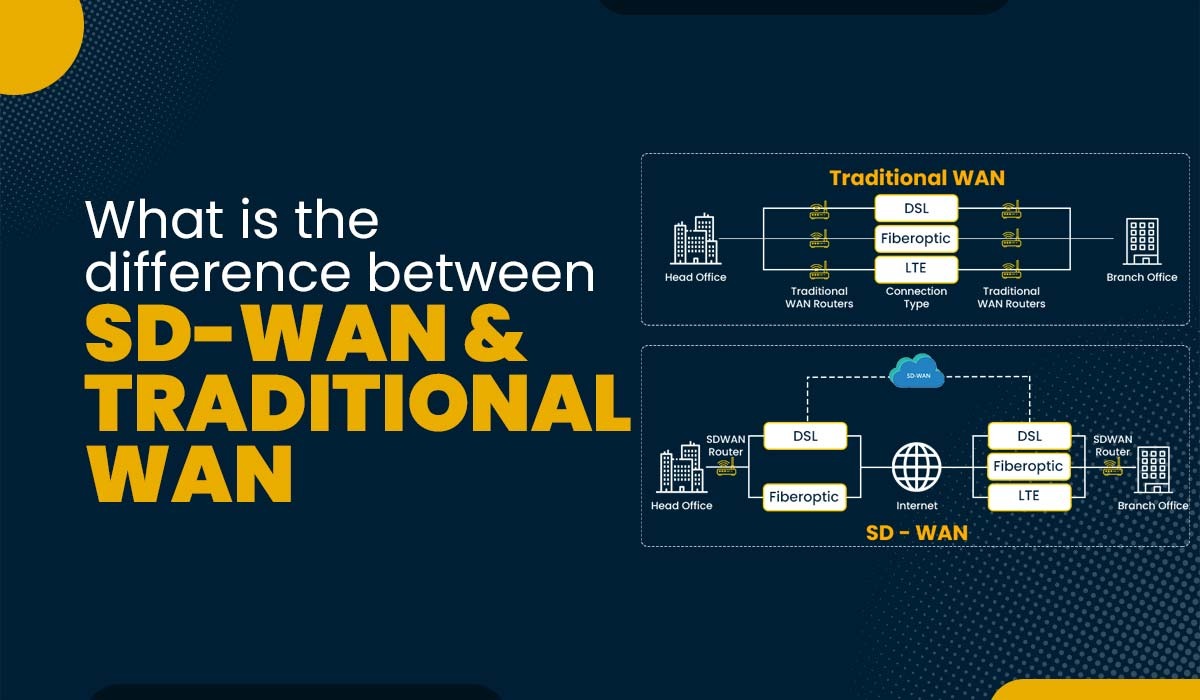
Difference between SD-WAN and Traditional WAN – Technology is meant to evolve, getting better with time. So, is SD-WAN over traditional WAN. SD-WAN is an evolution of the traditional WAN (Wide Area Network) that provides advanced services and decreases costs while at the same time setting the stage for more advanced capabilities in the future. PyNet Labs is world-renowned for its Cisco SD-WAN training, check out our latest batches. Whether your organization is still relying on Traditional WAN, has switched entirely to SD-WAN solutions, or implementing some combination of the two, here’s what you need to know about these two technologies. Before moving to the difference between SD-WAN and Traditional WAN, you need to understand both these technologies. Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) uses SDN technology to connect any user to any application with integrated capabilities for multi-cloud, security, unified communications, and application optimization. Some might say SD-WAN are over-hyped or are becoming an increasingly popular option to businesses worldwide but, its benefits are real. As organizational tools and apps have moved online, network traffic has increased, challenging traditional WANs to their full limits. In such a scenario, SD-WANs provide organizations with an end-to-end view of the entire WAN and the ability to prioritize network traffic over different connections. Moreover, the central network management with SD-WAN offers control and flexibility. Here are some advantages of SD-WAN – Overall, SD-WAN provides organizations with improved network performance, cost savings, centralized management, enhanced security, and the flexibility to meet the demands of a modern and dynamic business environment. Now let’s understand traditional WAN briefly along with its advantages and limitations. Traditional networking or WANs are connections between several local area networks (LAN) with large geographic distances between them, and their configuration is distributed. WAN connects remote offices or campuses to centralized network data centers, sharing data, accessing applications, and performing various business functions. Traditional wide area network (WAN) technology is still a valid and reliable way to deliver and receive network services. But, when companies expand their network infrastructure to new locations and over long distances, the data may travel from multiple carriers. That results in many mis-happening such as network congestion, dropped calls, data packet loss, and possible service outages. Also, as you know, WAN configuration is distributed, every single router and server must be locally updated each time there is a change in provisioning or policy. This is a highly time-consuming and tedious process. Besides, while using data-intensive applications with low latency requirements such as virtual reality (VR), HD video streaming, and video conferencing, WAN starts harming the user experience. You can take these points as the limitations of traditional WAN. Before moving to the difference between SD-WAN and WAN, let’s see some similarities between the two. Here are some similarities between SD-WAN and WAN – Now, let’s move to the difference between SD-WAN and Traditional Wan. The major difference between SD-WAN and WAN are as follow: Traditional WAN running over MPLS allows for prioritization and can give users traffic predictability and reliability but are typically more expensive. Whereas SD-WAN reduces internet costs as users don’t have to pay much to upgrade their bandwidth. SD-WAN runs on 4G LTE and internet broadband, typically less expensive than service delivered via an MPLS network. Also, SD-WAN allows for dozens of application prioritization options resulting in no packet loss. Traditional WANs are secure private and allow for site-to-site secure communication. Similarly, with SD-WAN, users have end-to-end encryption over a VPN connection. On top of it, users can implement and integrate additional security layers like firewalls for unified threat management. Since traditional WAN configuration is distributed, any changes to your WAN has to be done manually. But, with an SDN solution, it’s easier to scale SD-WAN as your organization grows, especially if you partner with a managed service provider. If we compare the two technologies, you will get a better view of the difference between SD-WAN and WAN. These are the main difference between SD-WAN and WAN. SD-WAN is a software-defined approach with centralized control and dynamic traffic routing, using multiple transport options, advanced security, and simplified management. In contrast, traditional WAN relies on hardware-based configurations with static routing, limited transport options, and separate security setups for each location. SD-WAN uses software-defined control and dynamic traffic routing with multiple transport options, offering improved agility and application performance, while traditional routing relies on static configurations and limited transport choices. SD-WAN is more flexible and cost-effective than traditional routing. A traditional WAN is a network infrastructure that connects geographically dispersed locations using hardware-based configurations and static routing protocols like OSPF or BGP. It typically relies on dedicated leased lines or MPLS for secure data transmission. Two benefits of implementing a traditional WAN are predictable performance, especially with MPLS, and compatibility with existing infrastructure, reducing migration complexities. After knowing the difference between SD-WAN and Traditional WAN, you will be able to analyze which technology is a valid and reliable way for your organization to deliver and receive network services. Of course, it’s SD-WAN, but some businesses have a hybrid approach with both (SD-WAN and WAN) in play, and it’s pretty beneficial. In the end, it comes down to what will be more useful for your short-term objectives and long-term needs. So, it depends on the needs and unique situation of each organization. But in both cases, the need for a skilled workforce to manage and maintain network serviceability remains mandatory. Network professionals whose organizations are making the switch to SD-WAN must be prepared for the change to help their organization with whatever comes after. The best way to capitalize on this new market trend is to gain Cisco SD-WAN training and upgrade your skills as per the current networking industry. For this, PyNet Labs’ online Cisco SD-WAN Viptela training facilities are most suitable as you can learn from the comfort of your home. All you need is an Internet connection and a laptop to learn this invaluable skill and lead your networking career in a new direction. Here are the 11 reasons to join SD-WAN training. Connect with us at [email protected] or WhatsApp/ Call us on +919821215002 for more details on our offerings.Introduction
What is SD-WAN?
Advantages of SD-WAN
Disadvantages of SD-WAN
What is WAN?
Advantages of WAN
Disadvantages of WAN
Similarities between SD-WAN and WAN
Difference between SD-WAN and WAN
Reliability, Prioritization, and Cost
Security
Network Scalability and Control
SD-WAN vs WAN
SD-WAN WAN Reduced Network Cost Conventional WANs are usually an expensive mix of private and public data lines. Application prioritization options that let users send important data over the best network link. It offers reliability and predictability with prioritization of critical traffic like voice & video. SD-WAN uses encryption & VPN for secure end-to-end network connections. Traditional WAN’s MPLS connection is very secure. SD-WAN is Easy to update and scale. Changes to traditional WANs need to be done manually. SD-WAN solutions have in-built virus detection, IPsec, firewall management, and encrypted network traffic for data security. While using traditional WANs on MPLS, it offers great QoS. SD-WAN can detect outages in milliseconds. As users and applications have moved beyond the enterprise, traditional WANs Resilience perimeter has dissolved. SD-WAN offers clear network visibility allowing users to check the status of the different devices connected to the network and can operate them from a centralized location. Traditional WANs miss out on the ability to monitor the performance of their network. Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is the difference between SD-WAN and traditional WAN?
Q2 – What is the difference between SD-WAN and traditional routing?
Q3 – What is a traditional WAN?
Q4 – What are two benefits of implementing a traditional WAN instead of an SD-WAN solution?
Conclusion