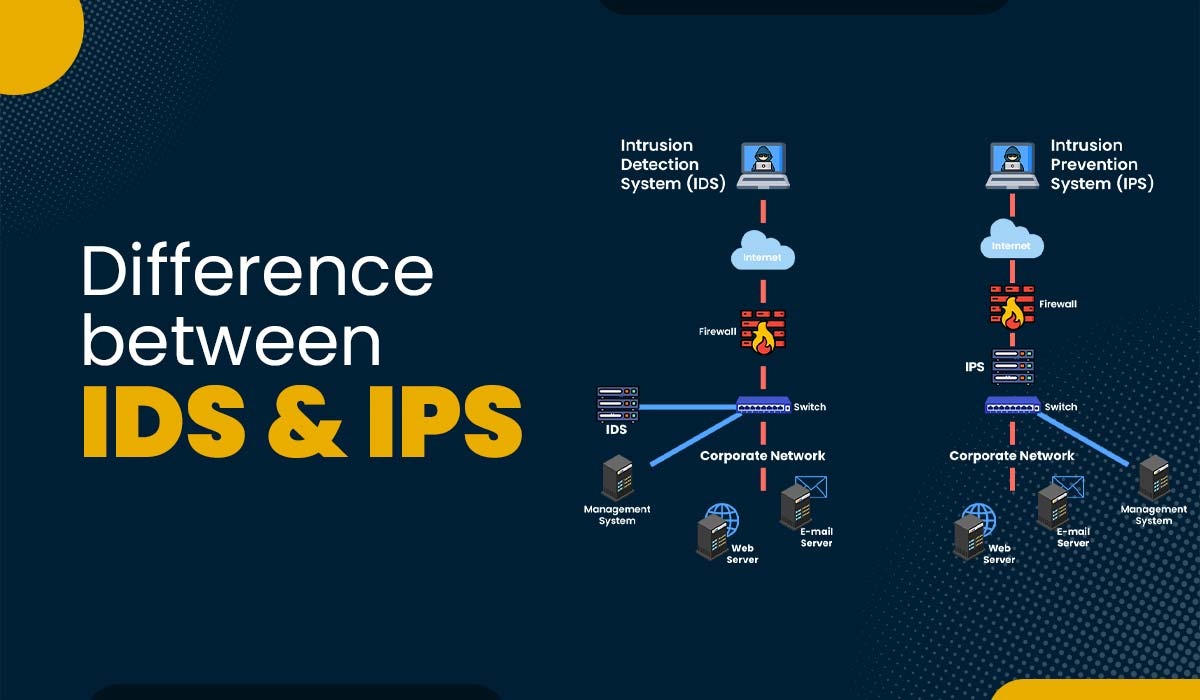
Difference between IDS and IPS
Nowadays, attackers’ knowledge and sophistication level is increasing steadily, making a single defensive method against intruders insufficient in providing substantial security. Instead, organizations should prioritize implementing a comprehensive and multi-layered strategy that combines proactive and defensive measures to safeguard their network and assets from unauthorized individuals. That’s where IDS, IPS, and firewalls come into action. But which security measure to choose? For that, one should know the basic difference between IDS and IPS. In this blog, we will explain IDS and IPS in detail and also the difference between the two. Let’s Begin! Before getting into the IDS vs IPS, let’s first understand what IDS and IPS really are. An intrusion detection system tracks any suspicious behavior that might compromise network security. An IDS will notify the administrator of the issue, but it may not take any further action. Different forms of IDS use various detection strategies. There are two types of IDS, namely HIDS and NIDS. Note: It is important to note that both NIDS and HIDS can work side by side. With HIDS and NIDS working together, sensitive devices or workstations will have further protection from potential threats. While malicious software may be able to bypass a NIDS, their activity will be detected by a HIDS. Intrusion prevention systems are considered as a subset of intrusion detection. Undoubtedly, the foundation of every intrusion prevention strategy lies in the first step of intrusion detection. However, security systems can take further measures and intervene in order to prevent current and potential future attacks. When an IPS identifies the presence of an attack, it has the capability to block incoming data packets, provide instructions to a firewall, and perhaps terminate a connection. There are four types of IPS, namely NIPS, HIPS, WIPS, and NBA. Now we have a basic understanding of IDS and IPS, let’s discuss the basic difference between IDS and IPS. Below, we have explained the basic difference between IDS and IPS in tabular form. Now we have compared IDS vs IPS, but the question that arises now is which one is better? Let’s understand. The best is the one that best serves the company’s purposes. While it’s true that both IDS and IPS solutions have their strengths, IPS is considered a superior all-around cybersecurity option. The automatic characteristics of an IPS are luring many businesses away from IDS systems. Since IDS solutions can only alert users during an attack, many businesses are switching to IPS to prevent further damage. The user is responsible for manually fixing the problem. However, an IPS can detect and stop the assault while it is happening. Whenever a security event occurs, the user-defined automated actions and rules may be triggered immediately. If malicious data is being sent to your network from an outside source, the application may either block that IP address or reset the connection. IPS systems have a significant advantage because of their ability to both detect intrusions and block them. When managing risks, an ISP’s automatic reactions are superior to manually remediating security events after getting an alert. Firewalls assist in blocking as well as filtering network traffic, whereas IDS is only for the detection of intrusions, and IPS assists in blocking as well as alerting of intrusions. IDS and IPS are two types of network security systems that can work together to protect a network from malicious attacks. By combining IDS and IPS, a network can detect and prevent intrusions, enhancing its security posture. The intrusion detection system (IDS) is responsible for monitoring network traffic, analyzing the traffic to identify signatures that match known attacks, and promptly notifying the user in the event of any suspicious activity. Meanwhile, the traffic continues to flow. An intrusion prevention system (IPS) is responsible for the monitoring of network traffic as well as blocking the infected packets or the server from where the packet is transmitting. IDS (Intrusion Detection System) and IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) are needed to monitor and protect network traffic from malicious attacks. When assessing a security solution, it is important to consider that internet security threats are progressively becoming more discreet and harmful. Hence, it is advisable to have multi-layer security against such threats. In this blog, we have explained IDS and IPS in detail, as well as the basic difference between IDS and IPS.Introduction
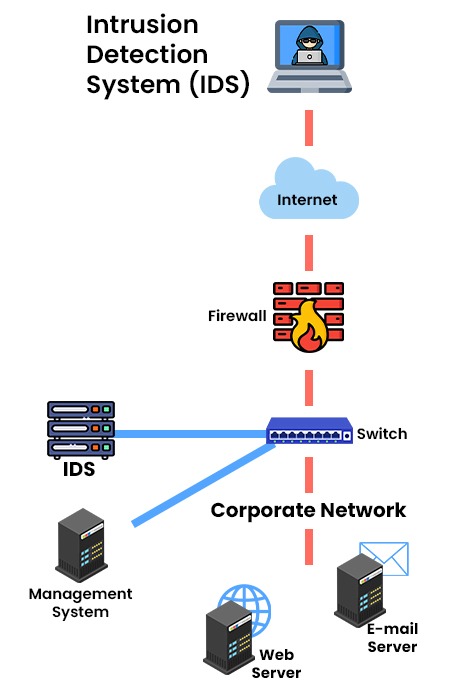
What is an Intrusion Detection System (IDS)?
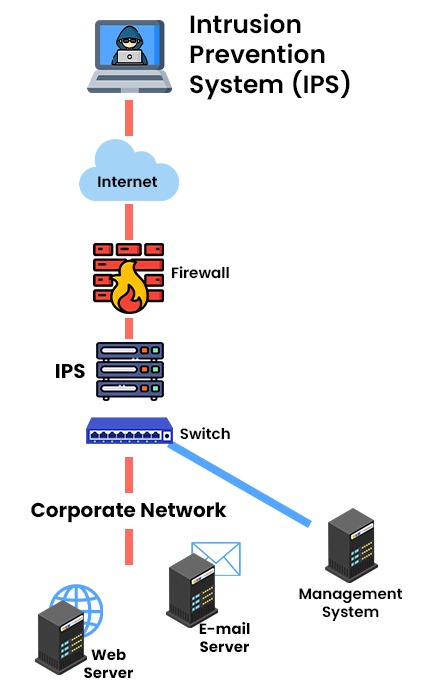
What is an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)?
Difference between IDS and IPS
Factors Intrusion Detection System (IDS) Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) Function IDS only alerts the network administrator when it detects an intrusion. IPS actively blocks or drops the malicious packets before they reach the target. Placement IDS is usually placed outside the network perimeter, such as behind a firewall or a router. IPS is usually placed inside the network perimeter, such as between a firewall and a switch. System Type Passive as it only monitors and then notifies the administrator. Active as it monitor as well automatically defends the network. Anomaly Response Sends a notification to the user or log Drops or modifies malicious packets Performance Low impact on the network speed as it only detects the intrusion. High impact on network speed as it has to analyze and modify or block traffic in real time. Which is better IDS or IPS?
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is the difference between IDS and IPS and firewall?
Q2 – Can IDS and IPS work together?
Q3 – What is IDS and IPS devices?
Q4 – Why are IDS and IPS needed?
Conclusion