VRF Full Form – Virtual Routing and Forwarding
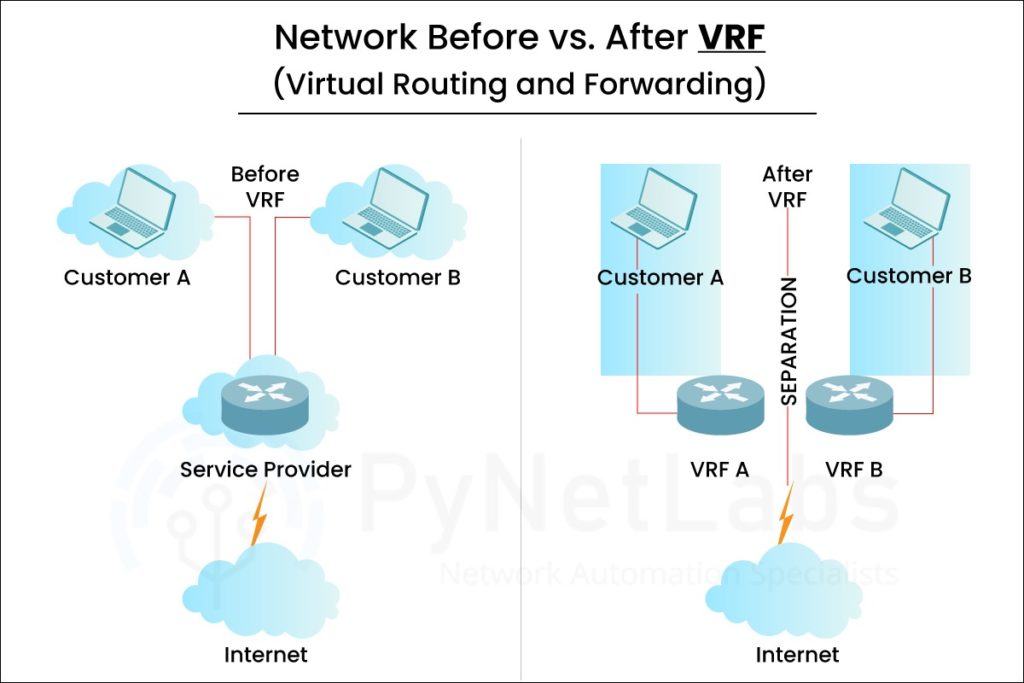
VRF can route traffic from individual customers without affecting or disrupting the traffic of other customers since their routes have been logically isolated from one another. This ensures that consumer networks are kept separate and secure. Service providers may now give their clients more flexible and efficient routing solutions with VRF. In this blog post, we will take a look at what is the full form of VRF in networking, how to configure VRF and its advantages with the most asked questions and answers for a better understanding of VRF concepts. Before getting into the details of VRF, let’s first discuss what VRF really is. The VRF full form in networking is Virtual Routing and Forwarding. It is an IP (Internet Protocol) technology that permits the co-existence of multiple instances of a routing table inside the same router simultaneously. The routing table is globally applicable and suitable for all incoming traffic. As stated VRF full form is Virtual Routing and Forwarding, a technique that allows many virtual Layer 3 routing and forwarding instances to be created on a single physical router. Every VRF instance represents an independent virtual router with its own distinct routing table, forwarding table, and additional data structures. It enables the secure and efficient routing of multiple customer sites over a shared backbone. With VRF, traffic from individual customers may be routed without affecting or disrupting the traffic of other customers since their routes have been logically isolated from one another. This ensures that consumer networks are kept separate and secure. Service providers may now give their clients more flexible and efficient routing solutions with VRF. VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding) works as a logical router, but there is only one routing table in a logical router, while VRF uses multiple routing tables. VRFs are implemented to use the router better and divide the network traffic efficiently. The Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) technology functions as a logical router. The utilization of multiple routing tables is a characteristic feature of a logical router, whereas a VRF instance is distinguished by the use of a single VRF table. Furthermore, the implementation of VRF requires the utilization of a forwarding table that specifies the subsequent hop for every data packet, a list of devices that are potentially responsible for forwarding the packet, and a collection of regulations and routing protocols that dictate the process of forwarding the packet. These tables restrict traffic flow into and out of a VRF, ensuring that only authorized traffic enters and exits the VRF. With Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF), a single router or Layer 3 Switch may host numerous independent routing configurations. The goal is to route and handle customer traffic independently while using common hardware. If VRF is not utilized, traffic may still be separated by customers using sub-interfaces or various physical interfaces and access control lists (ACLs). This is where VRF comes in handy since it can route overlapping IP addresses on a router/L3 device simultaneously. There are two types of VRFs: VRF uses the labelling of traffic at layer 3 to segregate it (Just like VLANs at layer 2). The traffic is segregated from source to destination through MPLS Cloud, which uses MP-BGP. VRF Lite is a subset of VRF but without MPLS and MP-BGP. In Cisco’s terminology, the deployment of VRFs without MPLS is VRF Lite. It is mainly used for enterprises having networks with overlapping IP addresses. Each routed interface belongs to exactly one VRF, making VRF Lite very simple. In light of the success of the VRF, the VRF Lite was accepted with open arms in Data Center and enterprise LAN environments. To understand VRF and VRFs better, we can compare them. The first thing to notice is that VRF is basically a technology, whereas VRF Lite is a way of using this technology. Here are the differences between VRF and VRF Lite: These are the major differences between VRF and VRF Lite. Let’s move to the advantages of VRF. Here are some benefits offered by VRF: It also empowers network administrators to divide their network with required tools, which provides better security and manageability. VRF lets network administrators separate guest traffic from employee traffic, segment large enterprise networks and support multiple customer networks. VRF can also improve the security of networks and could eliminate the need for encryption as well as authentication. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) typically utilize VRF to set up distinct VPNs to serve customers; this is why the technology is called VRF routing or forwarding. VRF-designed networks rely on 802.1q trunks protocol, MPLS tags or GRE tunnels to expand and keep these VRFs together. Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about Virtual Routing and Forwarding: With the multi-VRF capability, service providers can handle several VPNs, even if they have the same IP addresses. To construct virtual packet-forwarding tables and configure routes for multiple VPNs, it will allocate Layer 3 interfaces to each VRF. The following are some of the basic differences between VRF and VLAN: BGP VRF is a feature that allows multiple instances of BGP to run on the same router. Each instance of BGP is associated with a different virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) table, which contains the routing information for a specific VPN or customer network. BGP VRF enables the router to maintain separate routing policies and configurations for each VPN or customer network and to exchange routes with other routers that belong to the same VPN or customer network. VRF is utilized in networks to allow the co-existence of multiple versions of the routing table within the same router simultaneously. It can be utilized to divide the router into multiple routing tables as well as multiple forwarding instances, which allow the segregation of all incoming traffic. VRFs are generally used with MPLS VPNs, and VRFs without MPLS is known as VRF Lite. MPLS permits a service provider to provide multiple VPNs with the same IP Addresses. Example: VRF with MPLS allows two or more customers to share one Customer edge router. Here only one physical link is used between CE and provider edge router. The concept of VRF is the same as of VLANs in Cisco Switches, except that VRFs work on Routers and not switches. VRF uses the same method of virtualization as VLANs in Cisco switches. A single switch works as a multi-switch because of the VLAN, whereas a single router looks like a multi-router because of the VRF. In this blog, we have provided the VRF Full form and explained everything related to it. To conclude, Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) is a technology that allows multiple routing tables to coexist on the same router. VRF enables network segmentation, traffic isolation, and improved security and performance. VRF is widely used in service provider networks, enterprise networks, and cloud environments. VRF is an integral part of Cisco CCNP Enterprise Certification, one of the most in-demand courses in the networking domain. If you wish to learn more about VRF, you can opt for CCNP ENARSI training with PyNet Labs.Introduction
VRF Full Form in Networking
What is VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding)?
How to Configure VRF?
Where is VRF Used?
Types of Virtual Routing and Forwarding
Complete VRF
VRF Lite
VRF vs VRF Lite
VRF VRF Lite It requires MPLS or MP-BGP. It doesn’t support MPLS or BGP functionality. It requires Route Target as a part of its configuration. It doesn’t require Route Target. Various devices that run VRF share details with each other. Devices running VRF Lite doesn’t share with each other. It is highly scalable. It is not scalable at all. It is employed in service provider WAN Environment. It is useful in data centers and enterprise environments. Advantages of VRF
Security in VRF
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – What is Multi VRF?
Q2 – What is the difference between VRF and VLAN?
Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) VRF is often implemented in networks run by service provider networks. Virtual LAN technology is widely used in corporate networks. VRF creates a unique set of routing and forwarding tables for each client location. All client locations on a VLAN share a single broadcast domain. VRF can be used to connect multiple sites or subnets across a WAN. VLAN can be used to connect multiple subnets within a LAN. Q3 – What is BGP VRF?
Q4 – Why do we use VRF in networking?
Q5 – What is VRF In MPLS with example?
Q6 – What is VRF in Cisco Switches?
Conclusion







